- In the future, going to the doctor’s office might start to feel different, with you or your insurer paying a monthly fee for routine access to your doctor without paying a copay.
- It’s the model for Iora Health, a startup that works with “sponsors” — mainly employers or private health plans for the elderly (known as Medicare Advantage) — that cover the monthly fee. Iora also built out care teams of nurses and other health professionals that can help the doctors within the practice.
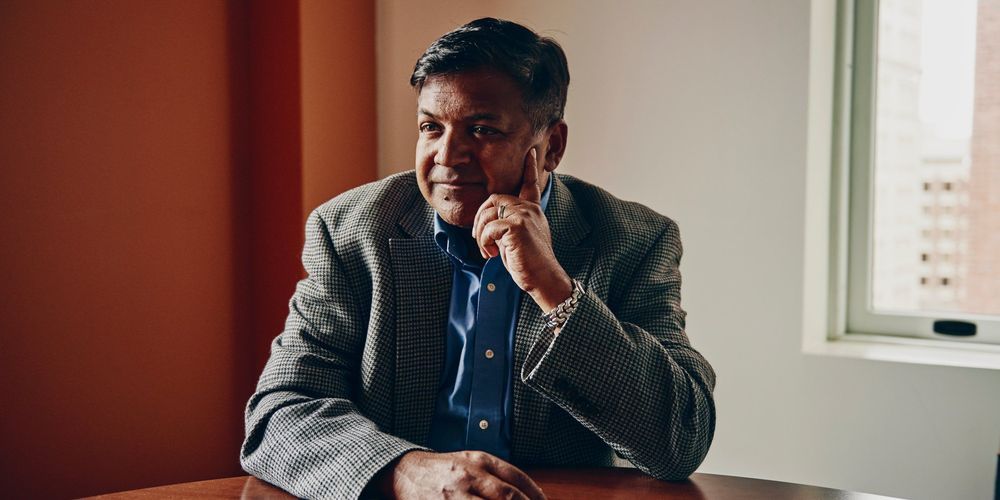
- We spoke with Iora’s CEO Rushika Fernandopulle about how he built a company that’s raised more than $250 million with plans to grow to 50 practices around the US by the end of 2019.
- Fernandopulle is one of Business Insider’s 10 people transforming healthcare.
- Visit BusinessInsider.com for more stories.
Fifteen years ago, Rushika Fernandopulle had a radical idea.
A primary care doctor by training, he had been treating patients in the standard, insurance-backed way. But he started to realize that wasn’t working, and insurance wasn’t covering what he wanted to do for patients.