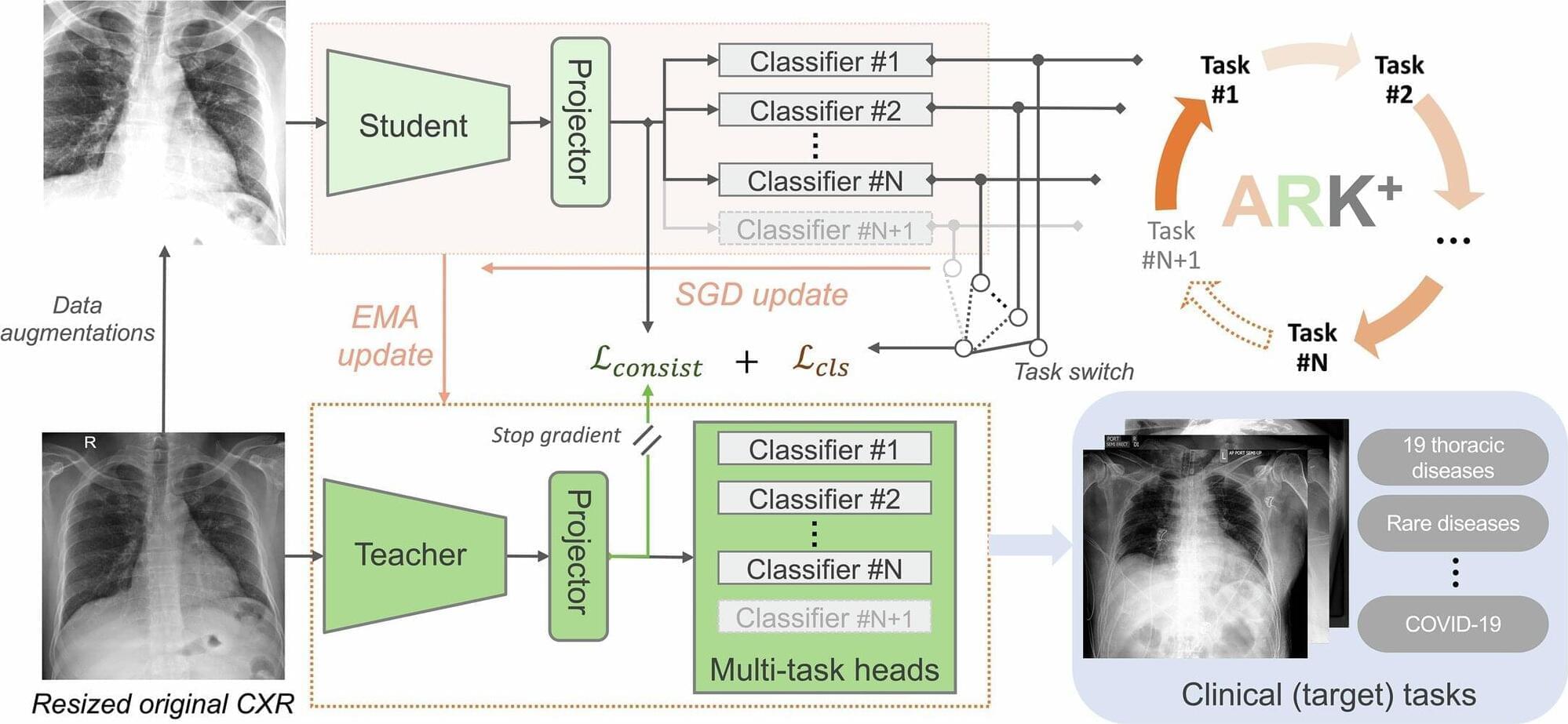
Deep within the arid and rugged terrains of Rajasthan roams a remarkable creature—the camel, often referred to as the “ship of the desert.” Known for their endurance, unique gait, and ability to survive extreme conditions, camels have long fascinated both scientists and locals alike.
Over time, they’ve been subjects of various studies that revealed surprising abilities, from surviving on sparse resources to even consuming snakes as part of traditional practices. Scientists are now exploring camel tears for rare enzymes and medicinal compounds that could revolutionise treatments for infections, inflammation, and eye diseases. But now, a new claim places camel tears in the spotlight for their potential medical value.
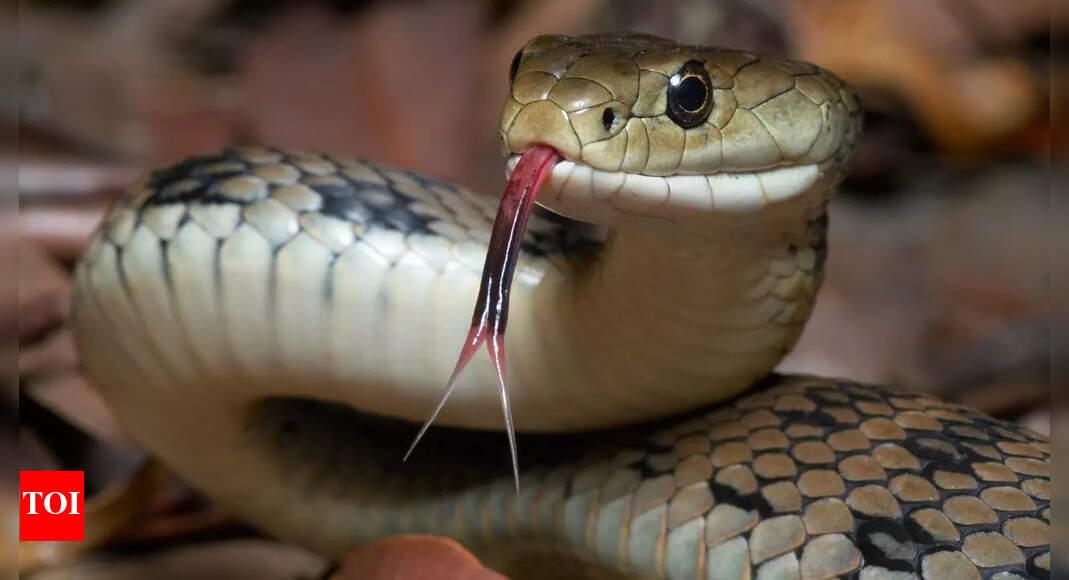
According to a study reportedly conducted by the Central Veterinary Research Laboratory in Dubai, camel tears may have the extraordinary ability to neutralise venom from up to 26 snake species. If validated, this could mark a significant turning point in snakebite treatment, especially in countries like India, where venomous snakebites are a major public health challenge. Though the findings have yet to be peer-reviewed or widely published, the potential has generated global attention for its revolutionary implications in antivenom research.
Camel tears may neutralise venom from 26 snake species. A Dubai lab study suggests this. It could help snakebite treatment, especially in India. Camel tears have bioactive compounds. These may neutralise snake venom toxins. This could lead to affordable snakebite drugs. Camel tears also fight desert infections. They contain proteins and lysozyme. This discovery may help toxicology and medicine.