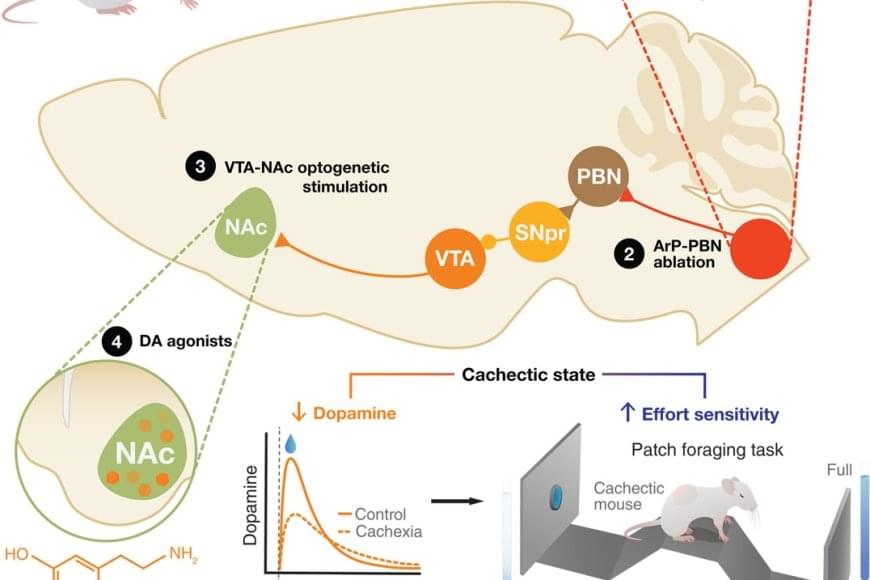
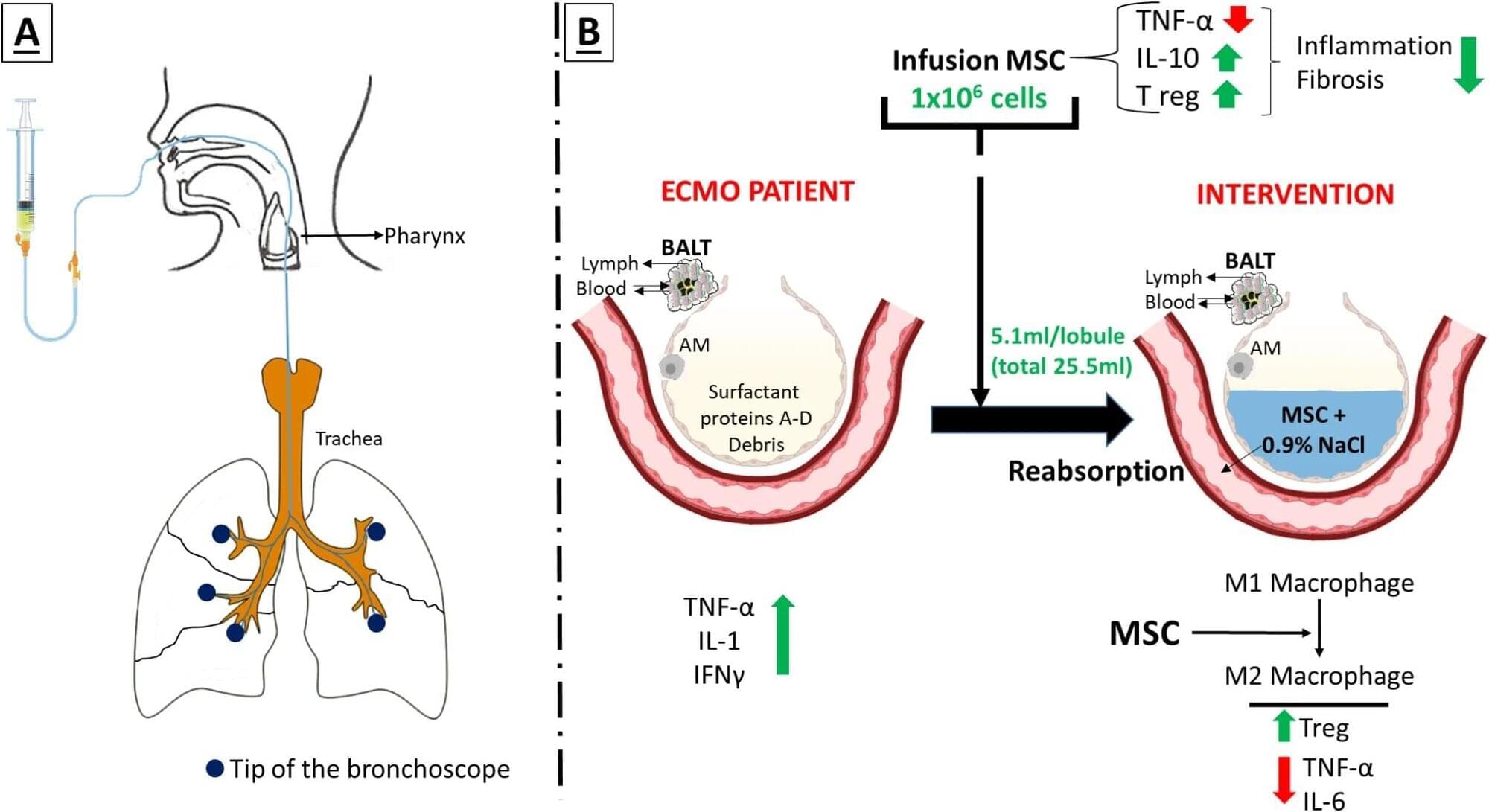
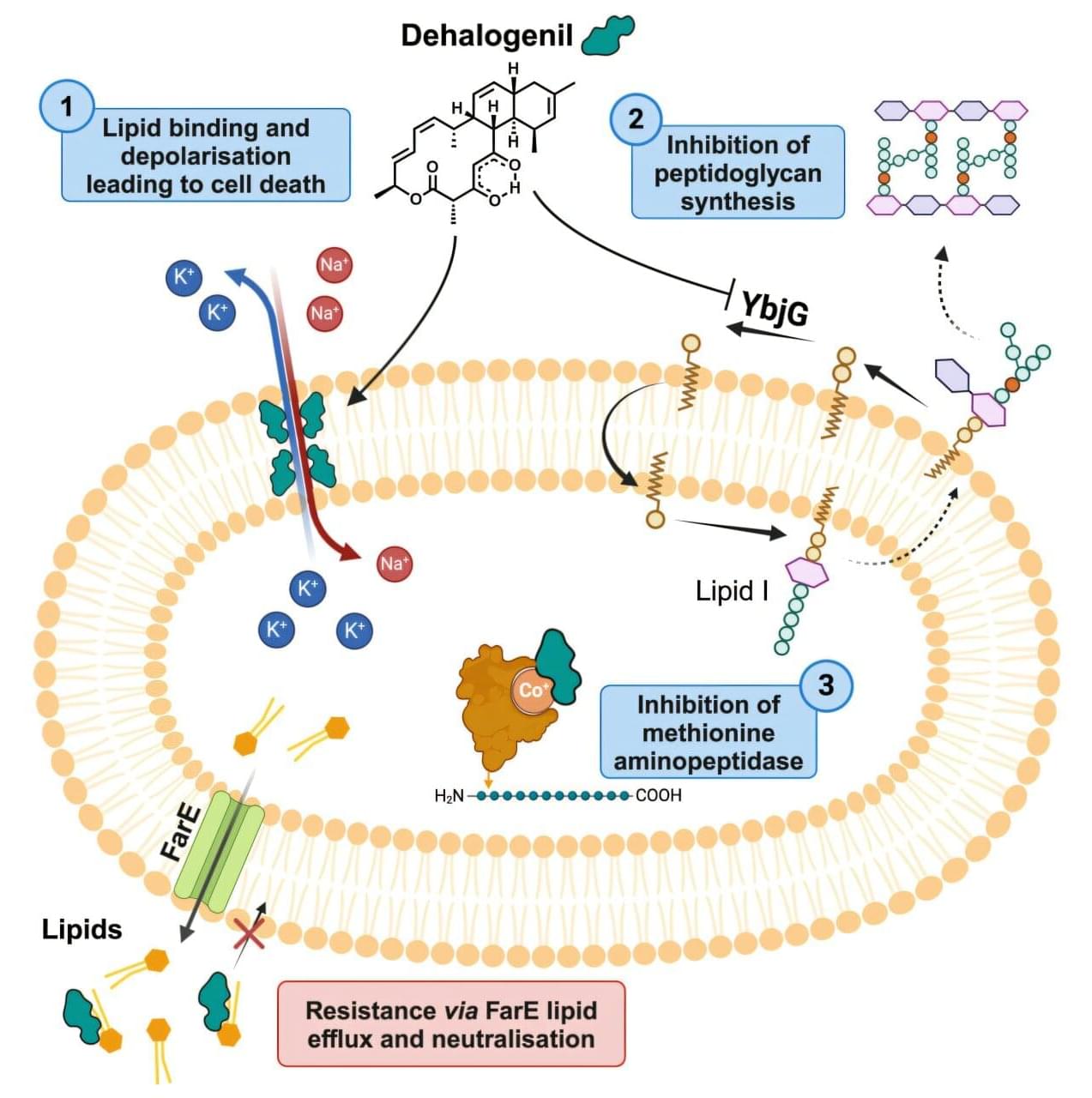
The fatigue and lack of motivation that many cancer patients experience near the end of life have been seen as the unavoidable consequences of their declining physical health and extreme weight loss. But new research challenges that long-held assumption, showing instead that these behavioral changes stem from specific inflammation-sensing neurons in the brain.
In a study published in Science, the researchers report that they identified a direct connection between cancer-related inflammation and the loss of motivation characteristic of advanced cancer. Studying mice with cancer-linked cachexia, a condition typical of the disease that leads to muscle wasting and weight loss, they discovered a previously unrecognized pathway in the brain. This pathway senses inflammation and actively suppresses dopamine — a key driver of motivation — resulting in apathy and loss of drive.
Blocking the pathway restored motivation, even though the cancer and weight loss continued. This indicates that apathy can be treated separately from the disease itself.