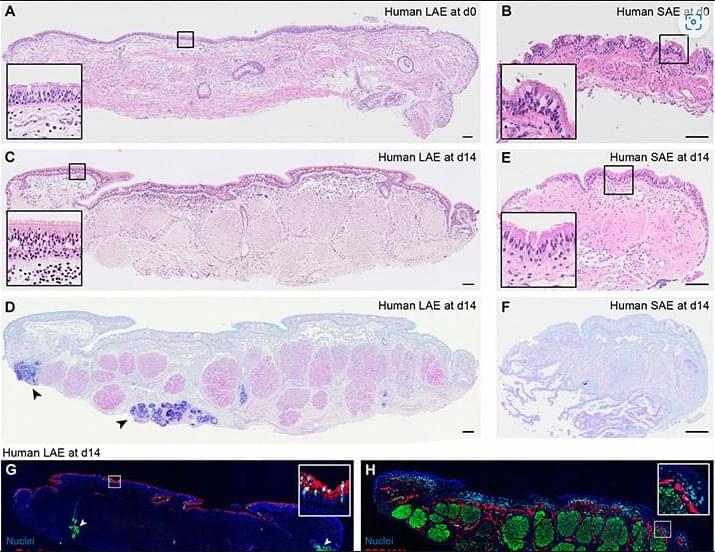
Leading health experts have warned that the US is staring down the barrel of another pandemic as bird flu spirals out of control on US farms.
So far, the H5N1 outbreak has affected nearly 1,000 dairy cow herds and resulted in more than 70 human cases, including the first confirmed death.
The US poultry industry is at significant risk, say experts from the Global Virus Network (GVN), particularly in areas with high-density farming and where personal protective practices may be lacking.