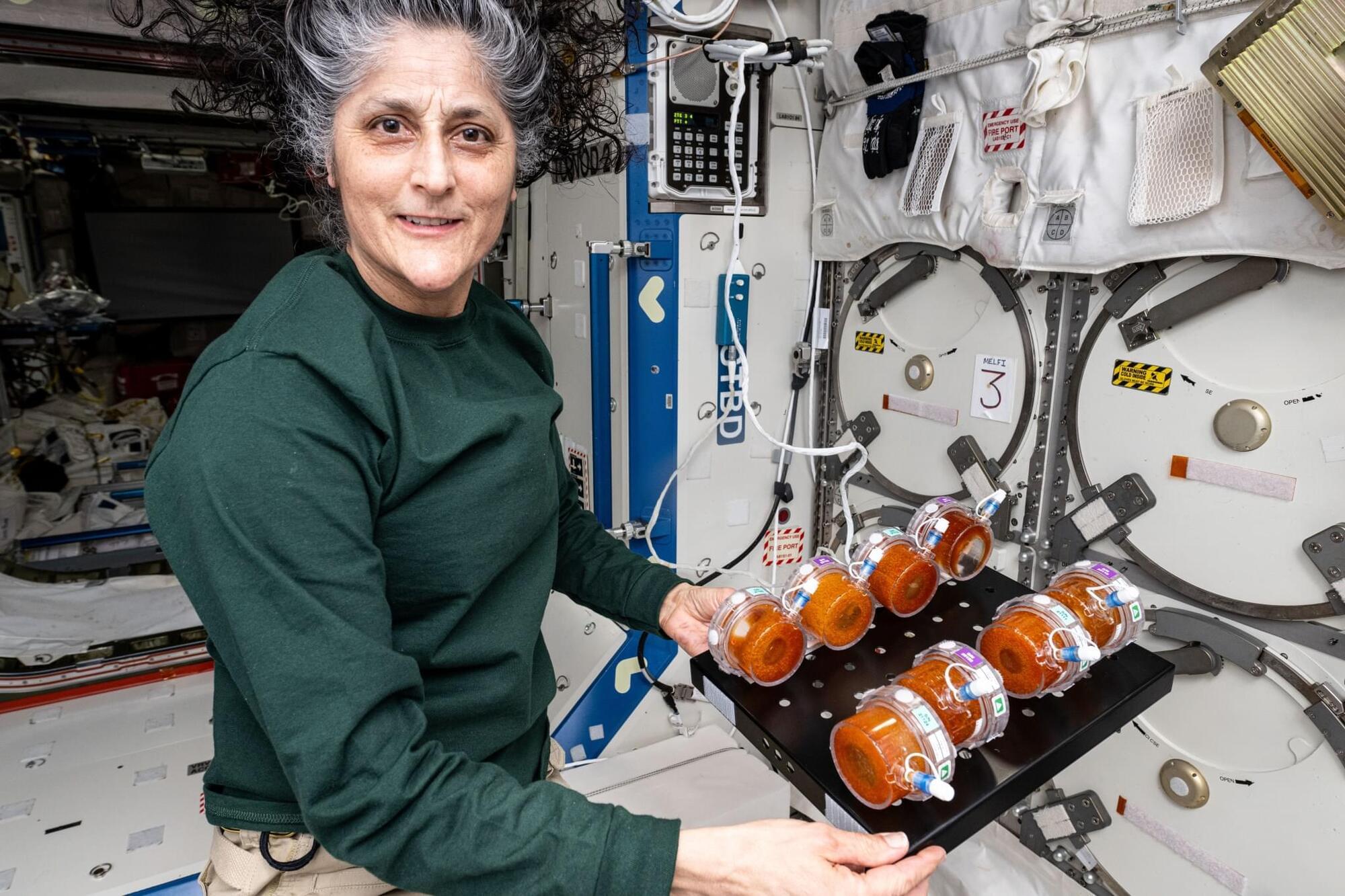
NASA’s BioNutrients series of experiments is testing ways to use microorganisms to make nutrients that will be needed for human health during future long-duration deep space exploration missions.
Some vital nutrients lack the shelf-life needed to span multi-year human missions, such as a mission to Mars, and may need to be produced in space to support astronaut health. To meet this need, the BioNutrients project uses a biomanufacturing approach similar to making familiar fermented foods, such as yogurt. But these foods will also include specific types and amounts of nutrients that crews will be able to consume in the future.
The first experiment in the series, BioNutrients-1, set out to assess the five-year stability and performance of a hand-held system—called a production pack—that uses an engineered microorganism, yeast, to manufacture fresh vitamins on-demand and in space.