A team of cognitive neuroscientists and acoustic engineers at Adam Mickiewicz University, in Poland, has found no evidence that wind turbine noise causes mental impairment. In their study, published in the journal Humanities and Social Sciences Communication, the group conducted experiments exposing human volunteers to various noises and measured a range of impacts.
Over the past several years, several groups and individuals around the world, most particularly in the U.S., have conceived of the idea of something called “wind turbine syndrome”—a theory that suggests noise from windmills can cause mental illness, or other health problems such as cancer. To date, such claims have not been backed up by research or any other type of proof. In this new effort, the research team in Poland sought to find out if there is any merit to the theory.
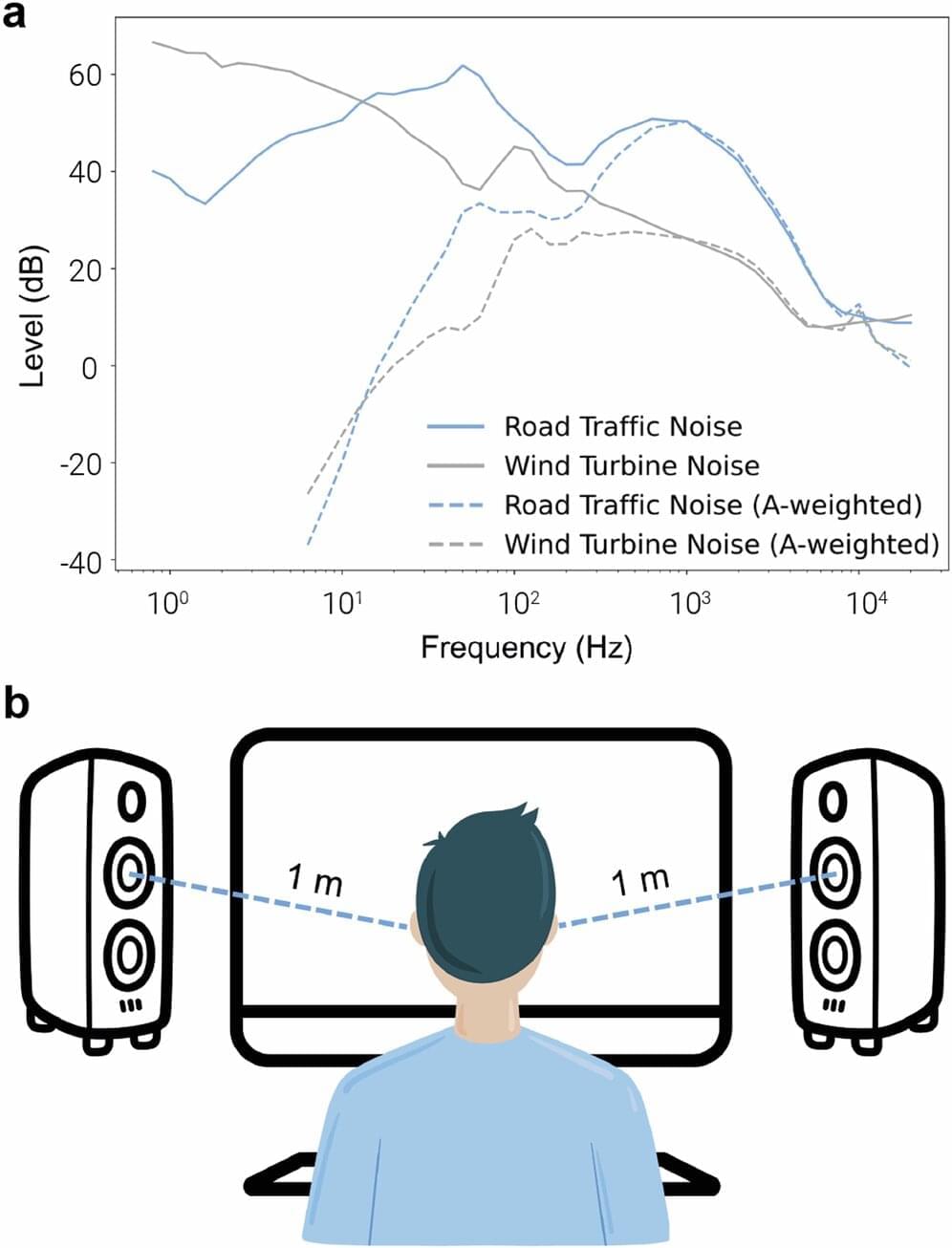
The researchers recruited 45 students at a local university who listened to various noises while wearing devices that measured their brainwaves. The researchers intentionally chose young volunteers because prior research has shown they are more sensitive to noise than older people.