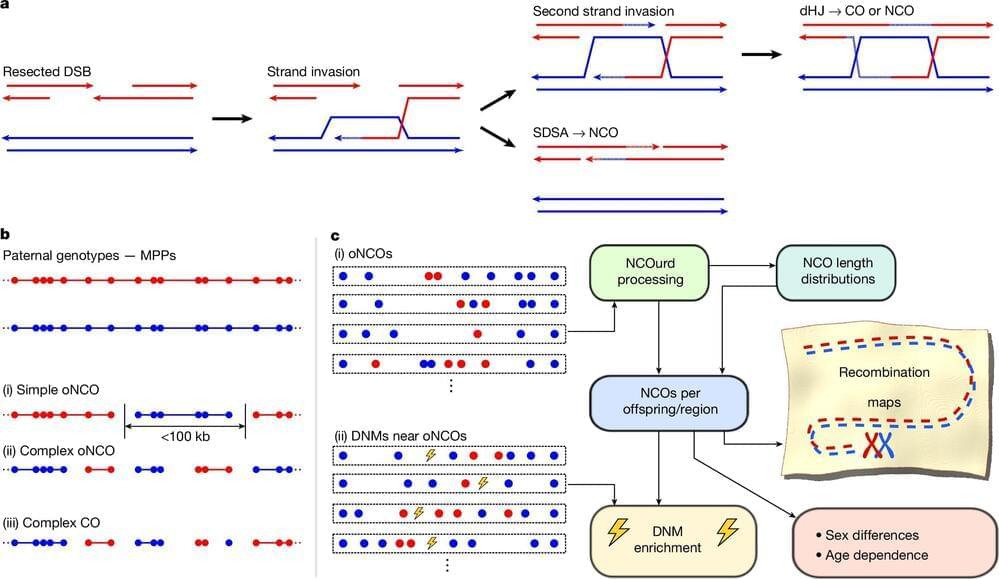
Scientists at deCODE genetics/Amgen have constructed a complete map of how human DNA is mixed as it is passed down during reproduction. The map marks a major step in the understanding of genetic diversity and its impact on health and fertility. It continues 25 years of research at deCODE genetics into how new diversity is generated in the human genome, and its relationship to health and disease.
The new map, appearing today in the online edition of Nature, is the first to incorporate shorter-scale shuffling, (non crossover) of grandparental DNA, which is difficult to detect due to the high DNA sequence similarity. The map also identifies areas of DNA that are devoid of major reshuffling, likely to protect critical genetic functions or prevent chromosomal problems. This insight offers a clearer picture of why some pregnancies fail and how the genome balances diversity with stability.
While this shuffling, known as recombination, is essential for genetic diversity, errors in the process can lead to serious reproductive issues. These failures can result in genetic errors that prevent pregnancies from continuing, helping to explain why infertility affects around one in ten couples worldwide. Understanding this process offers new hope for improving fertility treatments and diagnosing pregnancy complications.