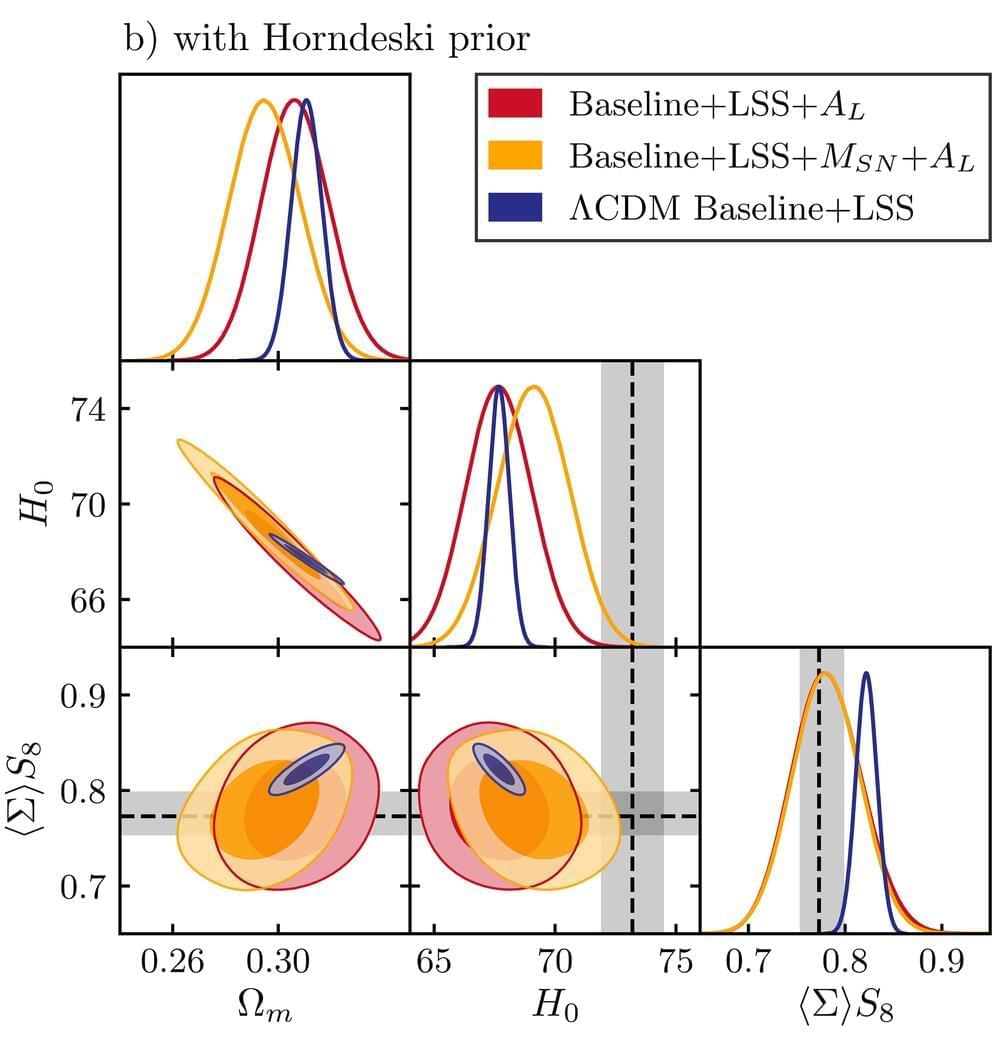
Scientists from around the world have reconstructed the laws of gravity, to help get a more precise picture of the universe and its constitution.
The standard model of cosmology is based on General Relativity, which describes gravity as the curving or warping of space and time. While the Einstein equations have been proven to work very well in our solar system, they had not been observationally confirmed to work over the entire universe.
An international team of cosmologists, including scientists from the University of Portsmouth in England, has now been able to test Einstein’s theory of gravity in the outer-reaches of space.