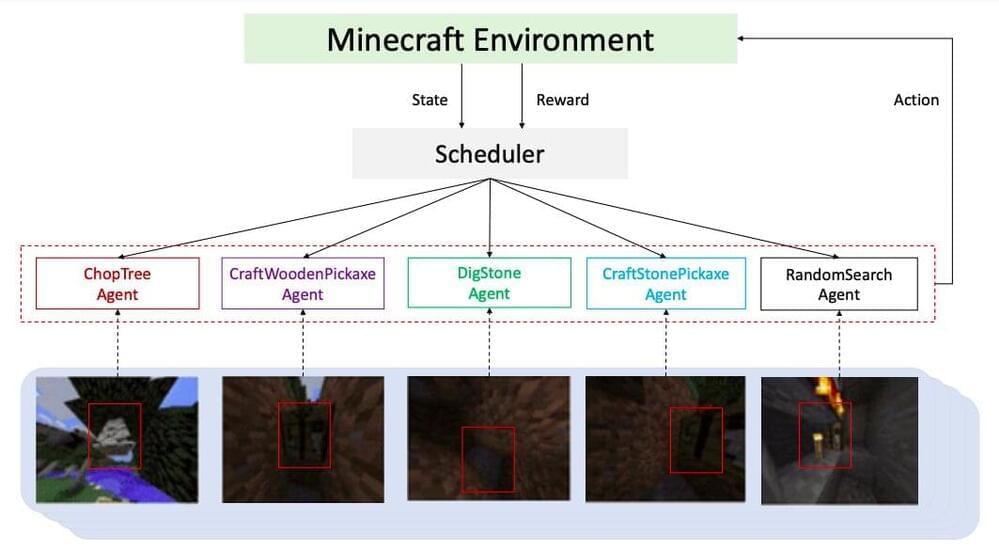
Recent theoretical breakthroughs have settled two long-standing questions about the viability of simulating quantum systems on future quantum computers, overcoming challenges from complexity analyses to enable more advanced algorithms. Featured in two publications, the work by a quantum team at Los Alamos National Laboratory shows that physical properties of quantum systems allow for faster simulation techniques.
“Algorithms based on this work will be needed for the first full-scale demonstration of quantum simulations on quantum computers,” said Rolando Somma, a quantum theorist at Los Alamos and coauthor on the two papers.