While autonomous robots have started to move out of the lab and into the real world, they remain fragile. Slight changes in the environment or lighting conditions can easily throw off the AI that controls them, and these models have to be extensively trained on specific hardware configurations before they can carry out useful tasks.
This lies in stark contrast to the latest LLMs, which have proven adept at generalizing their skills to a broad range of tasks, often in unfamiliar contexts. That’s prompted growing interest in seeing whether the underlying technology—an architecture known as a transformer—could lead to breakthroughs in robotics.
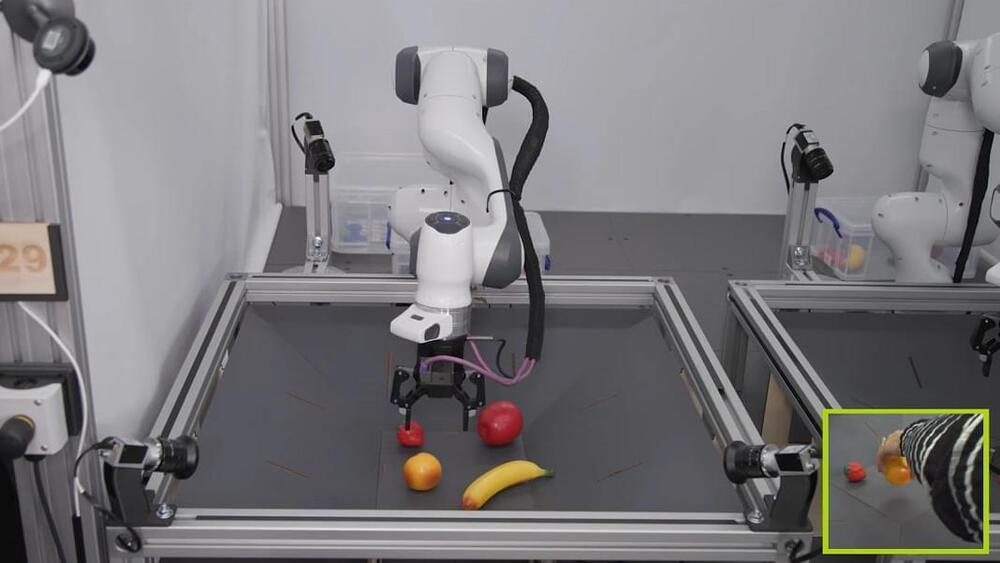
In new results, researchers at DeepMind showed that a transformer-based AI called RoboCat can not only learn a wide range of skills, it can also readily switch between different robotic bodies and pick up new skills much faster than normal. Perhaps most significantly, it’s able to accelerate its learning by generating its own training data.