A CIMC salon at the internet archive in san francisco.
Category: internet – Page 2

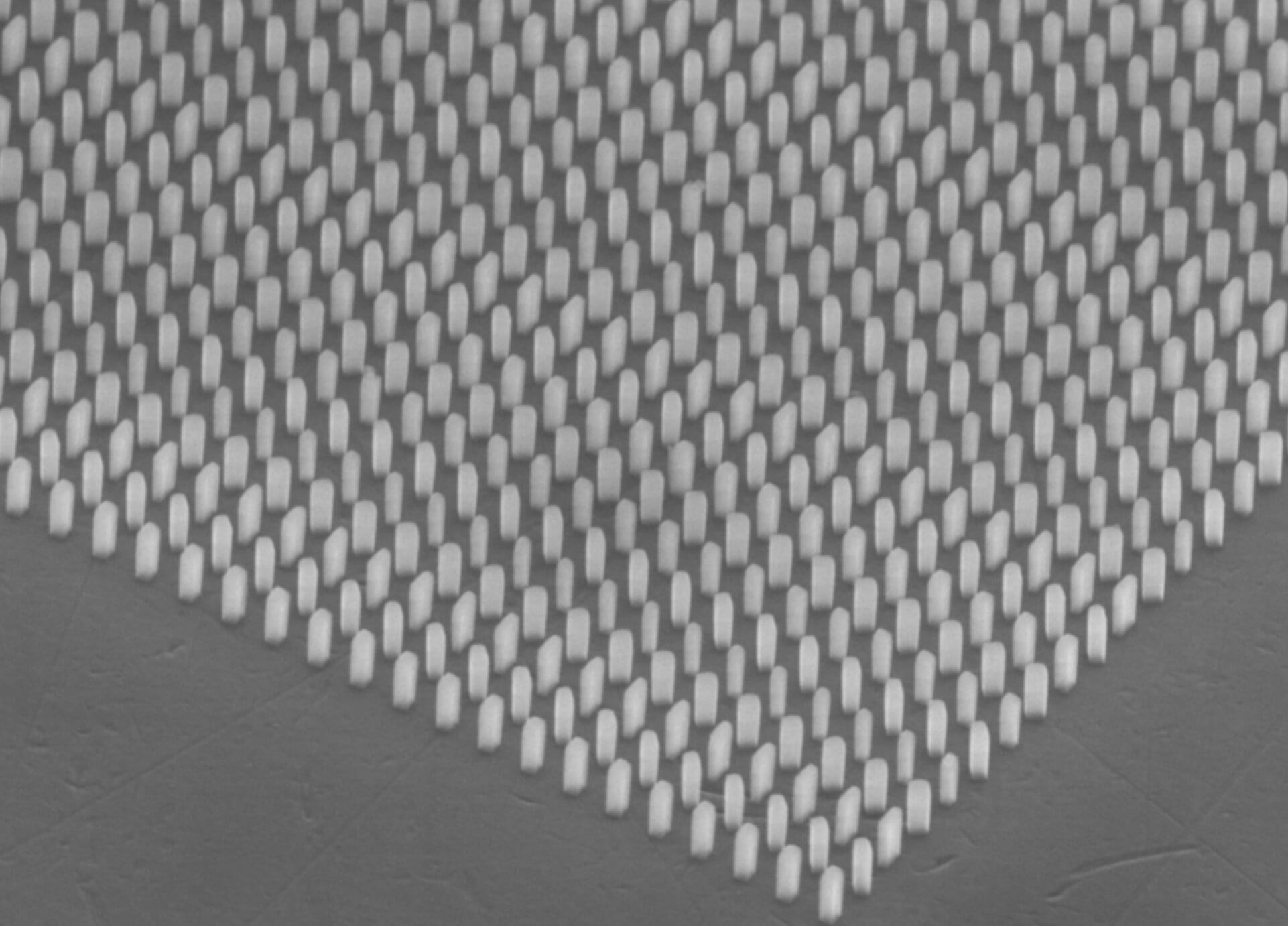
Ultra-thin metasurface can generate and direct quantum entanglement
Quantum technologies, devices and systems that process, store, detect, or transfer information leveraging quantum mechanical effects, have the potential to outperform classical technologies in a variety of tasks. An ongoing quest within quantum engineering is the realization of a so-called quantum internet: a network conceptually analogous to today’s internet, in which distant nodes are linked through shared quantum resources, most notably quantum entanglement.
Researchers at Nanjing University and University of Science and Technology of China have developed a new ultra-thin metasurface that could contribute to this goal, as it can control the behavior of light, while also generating and directing entanglement across many channels.
This metasurface, presented in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, has so far proved to be promising for the development of scalable and integrated quantum technologies.

When Cloud Outages Ripple Across the Internet
Cloud outages expose identity systems as critical failure points, turning infrastructure disruptions into major business continuity risks.
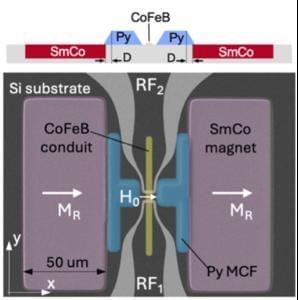
Telecommunications beyond 6G: the first standalone spin-wave chip with a built-in magnetic field
Milan, 13th January 2025 — The Politecnico di Milano has created the first integrated and fully tunable device based on spin waves, opening up new possibilities for the telecommunications of the future, far beyond current 5G and 6G standards. The study, published in the journal Advanced Materials, was conducted by a research group led by Riccardo Bertacco of the Department of Physics of the Politecnico di Milano, in collaboration with Philipp Pirro of Rheinland-Pfälzische Technische Universität and Silvia Tacchi of Istituto Officina dei Materiali — CNR-IOM.
Magnonics is an emerging technology that uses spin waves – collective excitations of electronic spins in magnetic materials – as an alternative to electrical signals. The spread of this technology has been restricted until now by the need for an external magnetic field, which has prevented it being incorporated into chips.
The new device developed at the Politecnico overcomes this hurdle: it is miniaturised (100 × 150 square micrometres, so much smaller than current radiofrequency signal processing devices based on acoustic waves); it is fully integrated on silicon – and therefore compatible with existing electronic platforms, and it functions without external magnets, thanks to an innovative combination of permanent SmCo micromagnets and magnetic flux concentrators.

Emerging Technology Convergence Will Shape Our Future
The future won’t be built on one breakthrough. It will be shaped by how well we mesh AI, quantum, 5G, IoT, and human intelligence into secure, resilient systems. Technology advantage now comes from orchestration, not adoption.
My latest Forbes article explores why this convergence will define the next decade.
#AI #QuantumComputing #EmergingTechnology #Cybersecurity #Leadership #FutureOfTech.
Link to article.
The next decade of innovation will not be defined by a single breakthrough technology. Instead, it will be shaped by the convergence of multiple emerging technologies.

A Breakthrough That Cuts Blockchain Delays Nearly in Half
The idea of a fully connected digital world is quickly becoming real through the Internet of Things (IoT). This expanding network includes physical devices such as small sensors, autonomous vehicles, and industrial machines that collect and exchange data online.
Protecting this data from tampering is essential, which has led engineers to explore blockchain as a security solution. Although blockchain is widely known for its role in cryptocurrencies, its core function is as a decentralized digital ledger. Instead of data being controlled by a single organization, information is shared and maintained across many computers.

Chip-sized optical amplifier can intensify light 100-fold with minimal energy
Light does a lot of work in the modern world, enabling all types of information technology, from TVs to satellites to fiber-optic cables that carry the internet across oceans. Stanford physicists recently found a way to make that light work even harder with an optical amplifier that requires low amounts of energy without any loss of bandwidth, all on a device the size of a fingertip.
Similar to sound amplifiers, optical amplifiers take a light signal and intensify it. Current small-sized optical amplifiers need a lot of power to function. The new optical amplifier, detailed in the journal Nature, solves this problem by using a method that essentially recycles the energy used to power it.
“We’ve demonstrated, for the first time, a truly versatile, low-power optical amplifier, one that can operate across the optical spectrum and is efficient enough that it can be integrated on a chip,” said Amir Safavi-Naeini, the study’s senior author and associate professor of physics in Stanford’s School of Humanities and Sciences. “That means we can now build much more complex optical systems than were possible before.”
Are Space Elevators Still a Thing for the Future?
🔒 Remove your personal information from the web at https://JoinDeleteMe.com/DROID and use code DROID for 20% off 🙌 DeleteMe international Plans: https://international.joindeleteme.com.
It’s been an idea that has been around since 1895 but only since the 1960s that it was taken seriously. But the biggest issue is how to make a cable over 36,000km that is light enough and strong enough. We now have the ability to make the materials but can we make them long enough to make it a reality, find out in today’s video.
Written, researched and presented by Paul Shillito.
To give one-off tips and donations please use the following :
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/curiousdroid.
Patreon : https://www.patreon.com/curiousdroid — For longer term channel support.
Paypal.me : https://paypal.me/curiousdroid — For 1 off direct tips and thank you payments.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/curiousdroid.