The team’s article in Nature Photonics says the demonstration ‘constitutes a milestone towards a global quantum internet,’ as it is one of the longest distances over which quantum teleportation has been achieved using a fibre-optic network in this way.
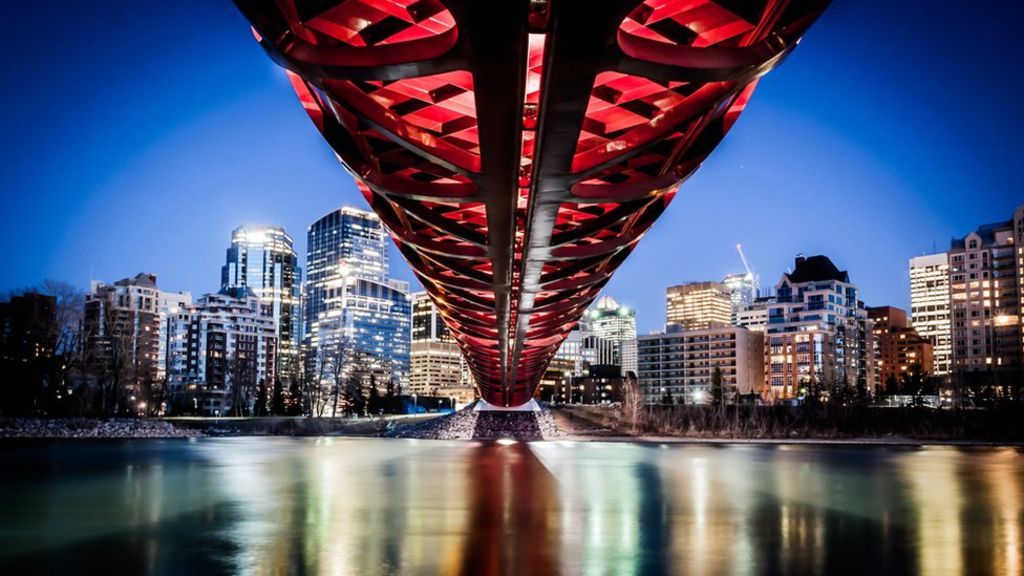
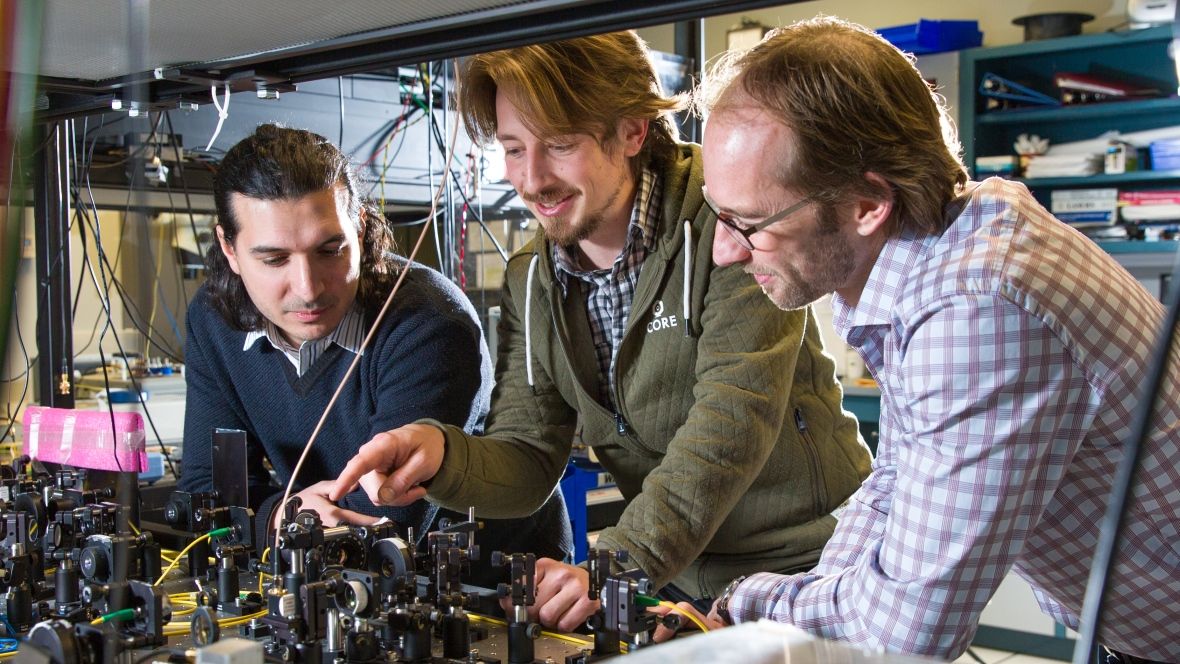
In a “major step” toward practical quantum networking, researchers at the University of Calgary have successfully demonstrated the teleportation of a light particle’s properties between their lab and the city’s downtown area, six kilometres away.
“What is remarkable about this is that this information transfer happens in what we call a disembodied manner,” said physics professor Wolfgang Tittel, whose team’s work was published this week in the journal Nature Photonics.
“Our transfer happens without any need for an object to move between these two particles.”