Integrating large language models (LLMs) into various scientific domains has notably reshaped research methodologies. Among these advancements, an innovative system named Coscientist has emerged, as outlined in the paper “Autonomous chemical research with large language models,” authored by researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Emerald Cloud Lab. This groundbreaking system, powered by multiple LLMs, is a pivotal achievement in the convergence of language models and laboratory automation technologies.
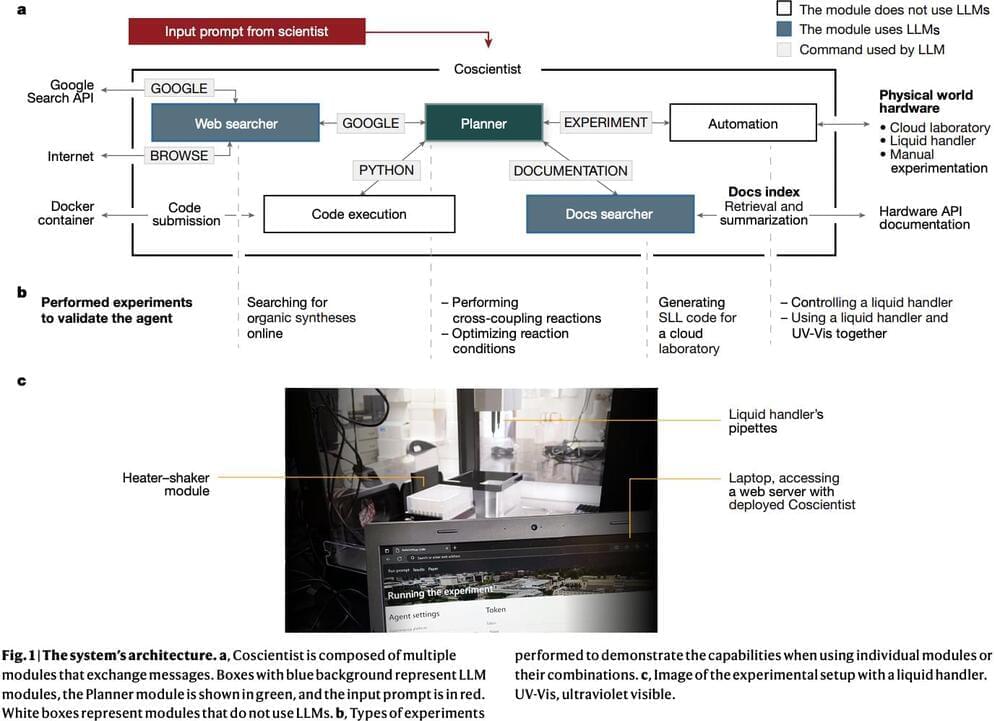
Coscientist comprises several intricately designed modules, with its cornerstone being the ‘Planner.’ This module operates using a GPT-4 chat completion instance, functioning as an interactive assistant capable of understanding user commands such as ‘GOOGLE,’ ‘PYTHON,’ ‘DOCUMENTATION,’ and ‘EXPERIMENT.’ Additionally, the ‘Web Searcher’ module, fueled by GPT-4, significantly enhances synthesis planning. Notably, it has exhibited exceptional performance in trials involving acetaminophen, aspirin, nitroaniline, and phenolphthalein. The ‘Code execution’ module, triggered by the ‘PYTHON’ command, facilitates experiment preparation calculations. Meanwhile, the ‘Automation’ command, guided by the ‘DOCUMENTATION’ module, implements experiment automation via APIs.
The prowess of the GPT-4-powered Web Searcher module in synthesis planning is evident in its success across diverse trials, demonstrating a capacity for efficient exploration and decision-making in chemical synthesis. Furthermore, the documentation search module equips Coscientist with the ability to utilize tailored technical documentation efficiently, enhancing its API utilization accuracy and improving overall experiment automation performance.