In a new study, an aging clock has revealed neuron-specific aging, as well as potentially neuroprotective compounds.


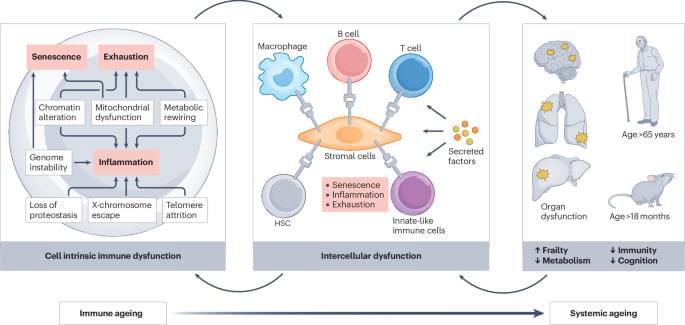
Ageing of the immune system is now realized to drive systemic ageing, and there is interest in targeting immune ageing in order to promote healthy ageing. Here, the authors detail how ageing affects different immune cell populations and discuss strategies to rejuvenate the immune system in order to extend healthspan.

Getting older might seem like a slow, gradual process – but research suggests that this is not always the case.
In fact, if you wake up one morning, look in the mirror, and wonder if your aging somehow accelerated, you might not be imagining things.
According to a 2024 study into the molecular changes associated with aging, humans experience two abrupt lurches forward, one at the average age of 44 and the other at around age 60.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
Blood testing with LifeExtension.com: https://www.anrdoezrs.net/click-101614996-15750394
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1

Factors that promote inflammation in C9ORF72 mutation carriers with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or frontotemporal dementia (FTD) have remained elusive. McCourt et al. identified pro-inflammatory forms of glycogen in gut contents of people with ALS/FTD and demonstrate that targeting glycogen in a C9orf72 mouse model extends lifespan and reduces neuroinflammation.

Humans develop sharp vision during early fetal development thanks to an interplay between a vitamin A derivative and thyroid hormones in the retina, Johns Hopkins University scientists have found. The findings could upend decades of conventional understanding of how the eye grows light-sensing cells and could inform new research into treatments for macular degeneration, glaucoma, and other age-related vision disorders. Details of the study, which used lab-grown retinal tissue, are published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“This is a key step toward understanding the inner workings of the center of the retina, a critical part of the eye and the first to fail in people with macular degeneration,” said Robert J. Johnston Jr., an associate professor of biology at Johns Hopkins who led the research. “By better understanding this region and developing organoids that mimic its function, we hope to one day grow and transplant these tissues to restore vision.”
What if worn-out parts of your body didn’t need to be replaced just regenerated?
Stanford researchers recently published work showing cartilage lost to aging or arthritis can be regrown, using either an oral drug or a local injection.
If this translates to humans, it could make knee and hip replacements unnecessary.
Millions of people undergo major joint replacement surgery every year.
Regenerating cartilage instead of replacing joints would mean less pain, lower cost, and far better outcomes.
That future may be closer than we think.

Extending the life of the bypass, the operation that saves the heart when the coronary arteries close, by intervening in the biological behaviour of the implanted vessels. This is the idea behind the first gene therapy administered during a heart bypass. The first patient in the world to receive it was a 73-year-old man in Scotland’s Golden Jubilee University National Hospital.
Bypass allows blood flow to the heart to be restored by bypassing blocked arteries, using vessels taken from other parts of the body to act as a graft, i.e. a ‘bridge’ to the blocked arteries. In most cases, veins taken from the leg (usually the great saphenous vein) are used because they are readily available and simple to implant. In the case of the 73-year-old British man, gene therapy was added to the bypass, which consists of carrying the TIMP-3 gene into the vein before implanting it as a graft. The new gene therapy aims to make the vessel more stable and resistant right from the start by affecting its biological behaviour before it is implanted in the heart. The researchers are thus attempting to overcome one of the main limitations of the bypass procedure: once connected to the heart, the veins have to withstand much higher pressure than they are designed for, which in time leads them to shrink and reduce blood flow, until they lose their function.
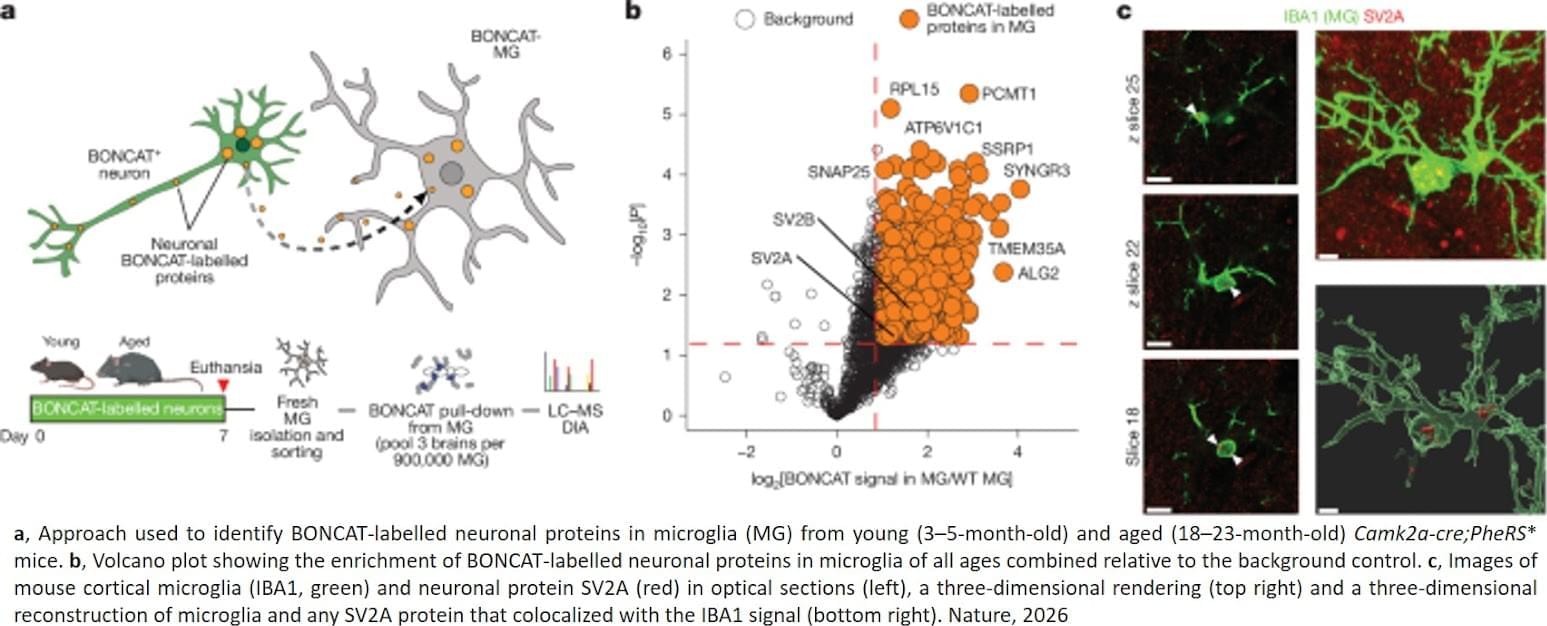
It is increasingly clear, though, that the loss of synapses—the flexible and adaptive relay stations central to our brains’ ability to think, learn, and remember—is central to the rise of cognitive decline and dementia in old age.
Now, researchers have discovered clues that may tie synapse loss to another hallmark of brain aging: the declining ability of brain cells to break down and recycle damaged proteins.
Published in Nature, the study shows that synaptic proteins are particularly susceptible to this age-related garbage-disposal problem: In old age, synaptic proteins break down much more slowly, they become more likely to pile up into the tangled clumps of protein characteristic of neurodegenerative disease, and they are more likely to make their way into microglia, immune cells that prune away damaged synapses.
Those findings are the latest in a series of discoveries that suggest new links between the brain’s waste management systems, microglia, and neurodegeneration—and they could yield new insights into human brain aging and neurodegeneration, said the study’s lead author. ScienceMission sciencenewshighlights.