New data link low-dose mTOR inhibition to DNA protection in aging immune cells, reframing how rapamycin’s healthspan effects might work.





The study findings also suggest approaches that enhance expression or activity of DMTF1 may have therapeutic potential in reversing or delaying aging-associated decline of neural stem cell function.
While the preliminary findings stemmed mainly from in vitro experiments, the researchers hope to explore if elevating DMTF1 expression can regenerate neural stem cell numbers as well as improve learning and memory under the conditions of telomere shortening and natural aging, without increasing the risk of brain tumors. The long-term objective is to discover small molecules that can enhance DMTF1 expression and activity to improve the function of aged neural stem cells.
“Our findings suggest that DMTF1 can contribute to neural stem cell multiplication in neurological aging,” Dr Liang said. “While our study is in its infancy, the findings provide a framework for understanding how aging-associated molecular changes affect neural stem cell behavior, and may ultimately guide the development of successful therapeutics.”
Kevin Perrott founded OpenCures, has been an adjunct professor at the University of Alberta, co-founded Oisin Biotechnologies, and ran a gym.
Aging impairs the regenerative capacity of skeletal muscle in part through the functional decline of the resident stem cell population called satellite cells. With age, satellite cells exhibit a loss of quiescence, altered proliferation, and impaired differentiation, leading to incomplete myogenesis following injury. Mitochondria are central to stem cell function, providing ATP, regulating redox homeostasis, and integrating several signaling pathways during lineage progression. While mitochondrial remodeling and function is essential for supporting the metabolic demands of myogenesis, the extent to which these processes are altered in aged satellite cells across cell states remains unclear. To address this, we performed a comparative transcriptomic analysis of young and aged satellite cells in quiescent, proliferating, and early differentiating states using three publicly available microarray datasets. Our results reveal that aged satellite cells exhibit a dysregulated senescence profile, characterized by the simultaneous upregulation of both senescence-inducing and-inhibiting genes, suggestive of a metastable senescence state. These features persisted during early differentiation, where aged cells also displayed increased expression of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) components, potentially contributing to a pro-inflammatory niche. Mitochondrial gene expression was relatively stable in quiescent cells but showed marked remodeling upon activation, particularly in aged cells. While young satellite cells upregulated transcriptional programs related to mitochondrial function, aged cells exhibited broader and less coordinated responses enriched for stress, apoptotic, and metabolic pathways. Despite evidence of mitochondrial stress, mitophagy gene activation remained limited in aged cells, raising the possibility of impaired organelle quality control. Together, our findings highlight age-associated disruptions in both senescence and mitochondrial remodeling programs across the satellite cell lifecycle. These transcriptional changes likely underlie impaired regenerative responses in aging muscle and identify potential targets for rejuvenating muscle stem cell function.
Aging is accompanied by a progressive and multifactorial decline in the function of virtually all physiological systems, contributing to increased frailty, disease burden, and reduced regenerative capacity in older individuals (López-Otín et al., 2013; Dodig et al., 2019; Tenchov et al., 2023). While this decline reflects the combined effects of genomic instability, proteostatic stress, metabolic alterations, and chronic low-grade inflammation, a critical component of age-associated tissue deterioration is the loss of stem cell function (López-Otín et al., 2013; Dodig et al., 2019; Tenchov et al., 2023). Adult stem cell populations are essential for tissue maintenance and regeneration throughout life, replenishing differentiated cells during homeostasis and responding to injury with rapid expansion and lineage-specific differentiation (Hawke and Garry, 2001; Dumont et al., 2015b; Dumont et al., 2015a).
Despite the absence of a fully established regulatory framework or unified technological standard for industrial-and clinical-grade organoid biomanufacturing yet, substantial progress has been made toward building the technical and institutional infrastructure required for scalability and reproducibility. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) introduced the Good In Vitro Method Practices (GIVIMP)19, an international quality-assurance framework that defines laboratory quality systems, method qualification, reference controls, equipment calibration, and data integrity—principles that now potentially serve as quantitative benchmarks for process validation in organoid production. Complementing this, the NIH Standardized Organoid Modeling (SOM) Center was recently established to promote the development of organoid platforms that are reproducible, robust, and broadly accessible for translational biomedical and pharmaceutical research.
Expanding these standardization efforts, a recent publication introduced the Essential Guidelines for Manufacturing and Application of Organoids, delineating a systematic workflow encompassing cell sourcing, culture optimization, quality control, and biobanking logistics20. Their framework identifies organ-specific critical quality attributes (CQAs)—including growth-factor composition, morphological fidelity, and quantitative analytical metrics—and recommends standardized cryopreservation conditions (~100–200 organoids per vial) to enhance batch comparability. Likewise, a recent study established quantitative criteria for human intestinal organoid standardization, specifying cell-line provenance, minimum lineage composition thresholds (e.g., ≥30% enterocytes), and molecular marker expression profiles consistent with physiological differentiation21. Taken together, these coordinated initiatives—from international organizations to national agencies and individual laboratories—represent an emerging global framework toward reproducible, quality-controlled, and scalable organoid biomanufacturing, laying the groundwork for eventual regulatory convergence and clinical translation.
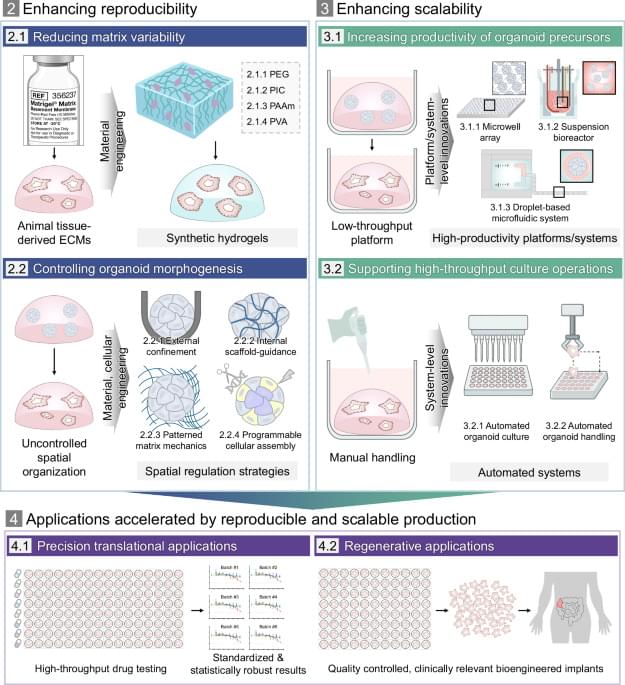
In response to these prevailing limitations and in alignment with global standardization trends, a range of engineering strategies has been developed, shifting the paradigm from organoid culture to organoid manufacturing by enabling reproducible and scalable organoid production. These strategies broadly focus on two goals: improving reproducibility by minimizing uncontrolled variation in the culture environment as well as by regulating intrinsic morphogenetic processes, and enhancing scalability by increasing productivity and throughput. To this end, recent advances can be categorized into three major domains: cellular engineering approaches that regulate morphogenetic processes through programmed cell organization; material-based strategies that establish defined and controllable environmental cues; and platform-or system-level innovations that enable high-throughput and automated workflows. Together, these innovative engineering advances mark aion toward more standardized, efficient production workflows.

New in eNeuro from Dutta Gupta et al: Some older male rats prefer familiarity over new social situations, which can be reversed via transcranial magnetic stimulation without affecting hippocampus-mediated spatial memory.
▶️
Social cognition, central to emotional and cognitive well-being, is particularly vulnerable to aging, where impairments can lead to isolation and functional decline. Despite compelling evidence that altered social behavior is associated with cognitive decline and dementia risk, experimental strategies for testing causative links remain scarce. To address this gap, we aimed to establish a rat model for research on social neurocognitive aging. We conducted a large-scale behavioral study in 169 male young (6 months) and aged (24−25 months) Long-Evans rats. In order to explore potential relationships among aging outcomes, we first documented individual differences in a widely validated water maze test of hippocampal learning and memory. Sociability and social novelty were then evaluated in the same subjects using the three-chamber social interaction test. Aging induced a selective shift in social novelty preference, marked by a striking familiarity bias in a substantial subpopulation of old rats, while sociability remained entirely normal. Changes in social novelty preference were completely independent of individual differences in spatial memory, and unrelated to anxiety or sensorimotor function. Notably, neuromodulation via TMS enhanced social novelty preference selectively in aged rats that exhibited a social introversion phenotype before treatment, consistent with the possibility that this aging condition reflects a distinct and modifiable neural network state. Together, the results establish a valuable preclinical framework for developing a comprehensive neurobiology of social cognition in aging.
Significance statement Social behavior is a critical yet underexplored component of cognitive aging. While both human and animal studies report age-related narrowing of social networks, the behavioral and neurobiological underpinnings remain unclear. Using a well-powered rat model, here we demonstrate preserved sociability in aging alongside marked individual differences in social novelty preference. A subset of aged rats preferred familiar over novel conspecifics, resembling patterns observed in older humans and non-human primates. Social phenotypes were independent of hippocampal-dependent memory, suggesting a dissociation between these aging outcomes. This dissociation was further validated using transcranial magnetic stimulation, supporting the notion of distinct underlying neurobiological mechanisms. Collectively, the findings lay a powerful foundation for advancing the translational neurobiology of social behavior in cognitive aging and reserve.
New preprint reports 17-month lifespan extension in mice with some living nearly 5 years. The intervention targets immune aging through CD4+ T cells and is expected to enter human trials in 2026.
Some links are affiliate links so we will earn a commission when they are used to purchase products.
If you would like to support our channel please consider joining our patreon / modernhealthspan.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Renue By Science (10% off: MHS) https://tinyurl.com/bdew4bfs NMN Powder • Lipo NR
BiOptimizers (15% off: MHBIO) https://bit.ly/47VAa8f — Magnesium Breakthrough.
Seeking Health (10% off: Richard10) https://crrnt.app/SEEK/-dm0MyrQ, Histamine Nutrients https://crrnt.app/SEEK/EpM7paAO
Stemregen (15% off: MODERN) US only https://tinyurl.com/45z968yr.
Wellness Extract (10% off: MODERNWE) http://wellnessextract.com/RICHARDWE Geranylgeraniol • Vit E
AX3 Life (20% off: MODERN20) https://tinyurl.com/2t3w26nw — Astaxanthin.
Oxford Healthspan (15% off: MHS) https://tinyurl.com/hrxfnzpn — Spermidine.
Qitone (10% off: HEALTH10) https://tidd.ly/4jGklry Qitone Esters Powder.
ProHealth (15% off: MODERN) https://prohealth.pxf.io/aObQRR NMNH 500mg.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
A new preprint by Lanna et al. reports one of the largest lifespan extensions ever seen in mice; approximately 17 months, with some mice living close to 5 years. The study focuses on metabolically reprogramming CD4+ T cells from aged mice using a peptide called DOS, which enables these cells to produce \.
The last few weeks in longevity science have been absolutely unreal. In this episode of Longevity Science News, Emmett Short breaks down 5 bombshell breakthroughs that could reshape the future of human health in 2026 — including an FDA-approved trial aiming to reverse cellular aging, cancer vaccines eliminating brain tumors in days, the regeneration of human teeth, one-shot GLP-1 Ozempic-style gene therapies, and a shocking new discovery linking gut bacteria to multiple sclerosis.
These aren’t sci-fi predictions — these are real developments happening right now in clinical trials, biotech labs, and cutting-edge medical research. If you care about anti-aging, regenerative medicine, epigenetic reprogramming, cancer immunotherapy, GLP-1 weight loss drugs, or the future of human lifespan, this is the episode you don’t want to miss.
Hume Band 20% off with Code LSN20
https://humehealth.com/pages/hume-ban… Huma Band Review: • Best Fitness Tracker For Longevity: Hume B… JOIN LSN Patreon for exclusive access to news, tips and a community of like minded longevity enthusiasts: https://www.patreon.com/user?u=29506604 ✅ Chapters 00:00 – The Longevity Science Explosion 00:48 Hume Band 20% Off 01:02 – Exclusive Interviews 01:43 Bombshell #1: FDA Approves Age Reversal Trial (Yamanaka Factors) 04:40 – Bombshell #2: Cancer’s Worst Month Ever (Vaccines + Immunotherapy) 09:19 – Bombshell #3: The Regeneration Revolution (Cartilage, Teeth, Liver) 11:30 – Bombshell #4: The One-Shot Ozempic Gene Therapy 12:25 – Bombshell #5: Gut Bacteria Linked to Multiple Sclerosis 13:55 – Final Recap + What Breakthrough Comes Next? Links in Script David Sinclair FDA Trial Tweet
https://twitter.com/davidasinclair/status/2
… FDA Greenlights Age Reset Trial (Endpoints) https://endpoints.news/exclusive-fda–… Life Biosciences Epigenetic Reprogramming Video • Reprogramming Human Life — Michael Ringel… mRNA Brain Cancer Vaccine Tweet
just setting up my twttr
— jack (@jack) March 21, 2006
… ANKTIVA Glioblastoma Case Tweet
https://twitter.com/LoriMills4CA42/status/2
… Dr. Patrick Soon-Shiong ANKTIVA Clip Tweet
stalking my coworkers
— crystal (@crystal) March 24, 2006
… Dr. Soon-Shiong Cancer Clip (YouTube) • Patrick Soon-Shiong’s cancer drug Anktiva… MIT/Stanford AbLecs Cancer Breakthrough Tweet
https://twitter.com/ShiningScience/status/2
… Universal mRNA Cancer Vaccine Tweet
https://twitter.com/ShiningScience/status/2
… AI Urine Test for Cancer Detection Tweet
https://twitter.com/Dr_Singularity/status/2
… Akkermansia Gut Bacteria + Immunotherapy Tweet
https://twitter.com/drwilliamli/status/2006
… Cartilage Regeneration Tweet (Liz Parrish)
I feel bad for Pluto. No one likes being demoted.
— David Warner (@hiddeninput) August 24, 2006
… Stanford Cartilage Regeneration Article https://news.stanford.edu/stories/202… Tooth Regrowth Drug Trial Tweet
https://twitter.com/kimmonismus/status/2006
… NewLimit Liver Rejuvenation Tweet
https://twitter.com/byersblake/status/20086
… One-Shot GLP-1 Gene Therapy Thread (Cremieux) https://twitter.com/cremieuxrecueil/status/.… MS Gut Bacteria Breakthrough Video Tweet
trying to get odeo thoughts down
— Ev (@ev) March 23, 2006
… ⚠️ Disclaimer: This video is for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult a qualified clinician before making health or treatment decisions. 🔗 EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEWS & BONUS CONTENT Get extended conversations, deep dives, and behind-the-scenes research ans a YouTube Member Patreon: 👉 / u29506604 YT Membership: 👉
/ @longevitysciencenews PRODUCTION CREDITS ⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺⎺ Executive Producer – Keith Comito @Retromancers Host, Producer, Writer – Emmett Short @emmettshort
Full huma band review: • best fitness tracker for longevity: hume B…
JOIN LSN Patreon for exclusive access to news, tips and a community of like minded longevity enthusiasts: https://www.patreon.com/user?u=29506604
✅ Chapters.