Human longevity records may be broken in the next few decades, a new modeling study suggests.

Jennifer Garrison is an assistant professor at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging and also holds appointments in the Department of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology at University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) and the Davis School of Gerontology at the University of Southern California.
Over 321 books from 170 plus interviews over 5 years.
Over 321 books from 170 interviews over 5 years for autodidacts
Jennifer Garrison Links.
https://www.buckinstitute.org/lab/garrison-lab/
https://www.linkedin.com/in/drjennifergarrison.
https://twitter.com/jenngarrison?lang=en.
PODCAST INFO:
The Learning With Lowell show is a series for the everyday mammal. In this show we’ll learn about leadership, science, and people building their change into the world. The goal is to dig deeply into people who most of us wouldn’t normally ever get to hear. The Host of the show – Lowell Thompson-is a lifelong autodidact, serial problem solver, and founder of startups.
LINKS
Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/66eFLHQclKe5p3bMXsCTRH
RSS: https://www.learningwithlowell.com/feed/podcast/
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCzri06unR-lMXbl6sqWP_-Q
Youtube clips: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC-B5x371AzTGgK-_q3U_KfA
Website: https://www.learningwithlowell.com/
Shownotes/ Timestamps.
00:00 Introducing Jennifer Garrison.
01:20 Broken Science funding.
10:00 Progress and accountability.
12:10 Why don’t we have the Garrison system.
20:48 Cost to run a lab & cost of university and support systems.
25:18 Neuro peptides and aging.
30:40 Complexity of neuropeptides.
33:12 How do neuropeptides know where to go.
37:20 Human vs animal neuropeptide differences and divergences.
44:42 Reproductive system.
46:20 Regenerating reproductive systems and aging.
48:55 Women reproductive health support.
51:35 Women and diverse population in clinical trials.
53:54 The first domino.
58:15 Why you should care about women’s health even if not a women.
01:00:23 Turning Menopause on and off.
01:04:45 Causes of aging.
01:06:00 2023 projects and thoughts.
01:08:40 What help she needs to accelerate the future at buck.
01:13:30 OBGYN issues and problems women have.
01:20:10 Resources for women and doctors.
01:26:58 Books.
01:29:50 LzzyHalesLegs listener q for identifying opportunities to work on.
Social links.


One can only hope.
A former Google engineer has just predicted that humans will achieve immortality in eight years, something more than likely considering that 86% of his 147 predictions have been correct.
Ray Kurzweil visited the YouTube channel Adagio, in a discussion on the expansion of genetics, nanotechnology and robotics, which he believes will lead to age-reversing ‘nanobots’.
These tiny robots will repair damaged cells and tissues that deteriorate as the body ages, making people immune to certain diseases such as cancer.

Pensions behave as government mandated ponzi schemes. New contributors are needed to pay for past contributors. But what if there are less and less new contributors and contributions? And what if past generations live longer and longer lives?
Limited time: get 5 free stocks when you sign up to moomoo and deposit $100 and 15 free stocks when you deposit $1,000. Use link https://j.moomoo.com/00iPZo.
France is facing massive protests in response to its recently announced pension reform. While France is the only country facing massive protests for now, almost all developed countries will likely be forced to conduct similar pension reforms in the future as they face rapidly aging populations.
0:00 — 1:50 Intro.
1:51 — 5:03 French pension system.
5:04 — 7:15 The Ponzi scheme.
7:16 — 9:42 Pension crisis.
9:43 — 11:20 Demographic time bomb.
11:21 A warning to us all.
Email us: [email protected].
University of Pittsburgh.
A metamaterial is any material engineered to have a property that is elusive to naturally occurring materials. The research introduces the use of metamaterials in the creation of concrete, providing the option to alter its brittleness, flexibility, and shapeability to allow builders to use less of the material without sacrificing strength or longevity.
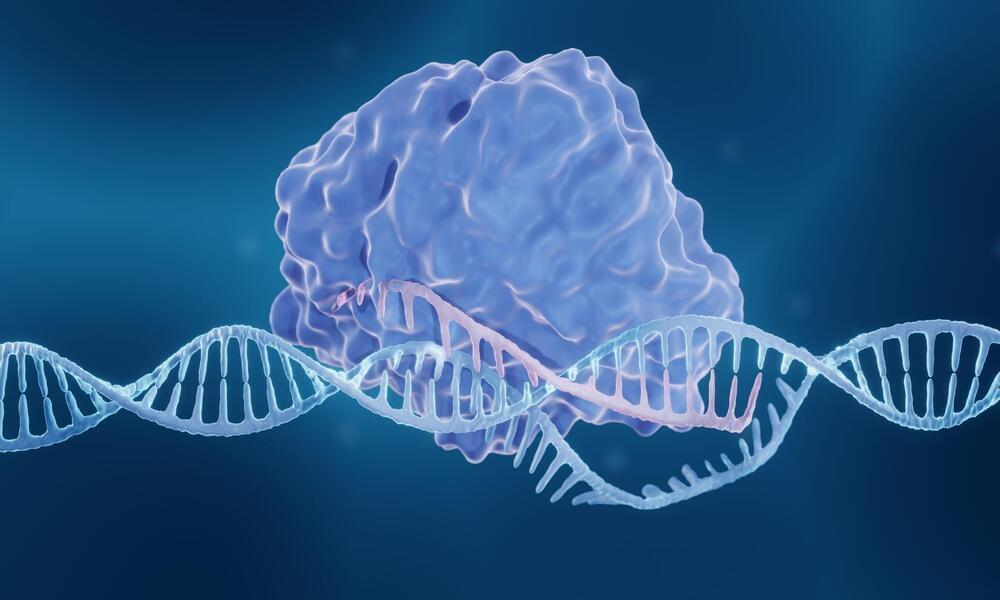
The researchers add that these data demonstrate that CRISPRa is generally applicable across chromatin states and cell types, and highlights the factors that impact the degree of gene activation and how easy it is to reproduce the effects. Understanding these factors is important in the design and analysis of CRISPRa screens, which are used to look for genes involved in genetic diseases, the team points out.
Further study is required to continue to add to these rules and to see whether different CRISPRa or CRISPR interference techniques behave in a similar way.
“Our research has established a system for reporting the effectiveness of CRISPR activation in stem cells, allowing us to gain a better understanding of how CRISPRa works in multiple cell states,” says Qianxin Wu, PhD, first author from Wellcome Sanger. “We also showed that CRISPR gene activation is powerful enough to induce stem cells to differentiate into other cell states. This suggests that CRISPRa screens can be used to search for genes involved in cellular processes or to generate more accurate models of cell types in the body, aiding research into genetic diseases and regenerative medicine.”
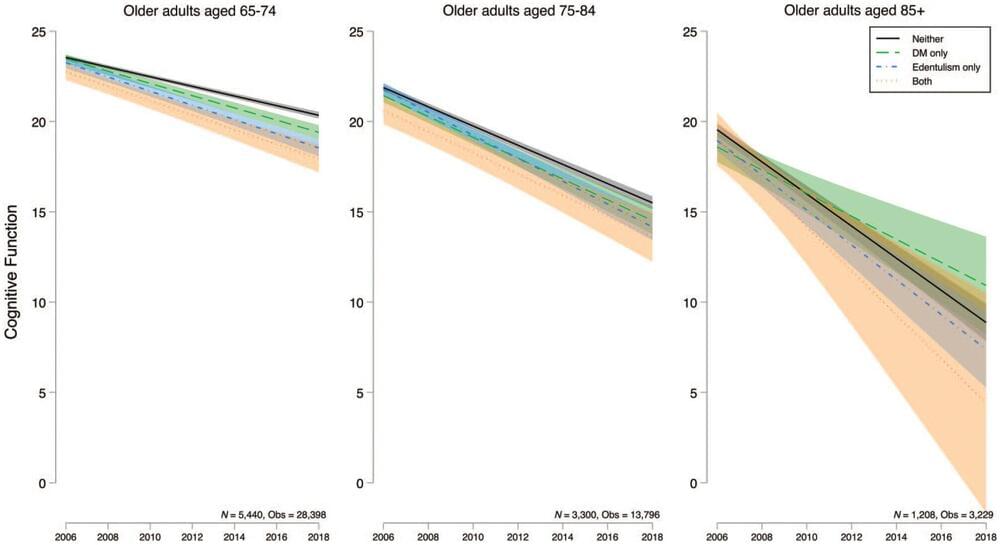
Having both diabetes and tooth loss contributes to worse cognitive function and faster cognitive decline in older adults, according to a new study published in a special issue of the Journal of Dental Research focused on aging and oral health.
“Our findings underscore the importance of dental care and diabetes management for older adults in reducing the devastating personal and societal costs of Alzheimer’s disease and other related dementias,” said Bei Wu, vice dean for research at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and co-director of the NYU Aging Incubator, as well as the study’s lead author.
Diabetes is a known risk factor for cognitive decline and dementia. Several of the hallmarks of diabetes —high blood sugar, insulin resistance, inflammation, and related heart disease—are thought to contribute to changes in the brain.
Michael Levin is a biologist at Tufts University working on novel ways to understand and control complex pattern formation in biological systems.
Michael Levin links.
Michael’s Twitter: https://twitter.com/drmichaellevin.
Michael’s Website: https://drmichaellevin.org.
PODCAST INFO:
The Learning With Lowell show is a series for the everyday mammal. In this show we’ll learn about leadership, science, and people building their change into the world. The goal is to dig deeply into people who most of us wouldn’t normally ever get to hear. The Host of the show – Lowell Thompson-is a lifelong autodidact, serial problem solver, and founder of startups.
LINKS
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCzri06unR-lMXbl6sqWP_-Q
Youtube clips: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC-B5x371AzTGgK-_q3U_KfA
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/lowell-thompson-2227b074
Twitter: https://twitter.com/LWThompson5
Website: https://www.learningwithlowell.com/
Shownotes/ Timestamps.
00:00 Introducing Michael Levin.
00:30 Epigenetic Head Exploding adaptation Planaria.
05:45 Generalize vs intelligent search epigenetic adaptation.
08:55 Designing studies to test these hypothesis.
12:35 Implications of hypothesis proven out.
19:40 Mitochondria domestication hypothesis.
25:50 Where are memories stored if not the brain.
34:45 Regeneration of memories evidence.
38:00 Voltage on both sides of amputated limb, and what catalyzes regeneration.
42:55 Induce physiology of extinct species from live species.
47:55 Biomanufacturing.
55:30 Anatomical compiler development.
57:45 Horse vs zebra domestication.
59:20 Bioelectricity resurrection.
01:02:05 Regeneration vs Brain computer interface for restoring function.
01:06:50 What is needed to achieve his vision for regeneration, bioelectricity, etc.
01:08:42 Structure needed to support development.
01:11:03 Groups coming together.
01:12:25 Longevity & health span — high level vs low level approach.
01:14:45 Cancer — why mortal cell become an immortal cell.
01:19:20 Advice for 25–35 year olds.
01:22:46 Age he discovered life goal.
01:23:55 How old he feels mentally.
01:24:55 Books.
01:25:55 Working to learn currently.
#Bioelectricity #MichaelLevin #Regeneration