University of Exeter team make senescent cells look younger and begin to divide while exhibiting longer telomeres to reduce cellular aging.




3 minutes for glaucoma eye surgery.
Cataract and glaucoma are eye diseases that progress by aging. Both are severe diseases that can cause blindness, but in Japan, unique treatment methods and causes are being investigated. For cataracts, the world is paying attention to a Japanese doctor who has devised an innovative surgical method which is in just over 3 minutes. And distinctive research is progressing at Japanese universities as to what kind of ingredients can delay the progression of glaucoma. How can we save people from blindness? Explore with us the forefront of Japanese ophthalmic medical care.
Journalist Chip Walter visited our friends at Willoughby-Eastlake Public Library earlier this month to discuss his new book, “Immortality, Inc.” Walter discusses the resources (both the brilliant people and astonishing amount of money) being dedicated to seeing if people do, in fact, have to die.
The UK Cryonics and Cryopreservation Research Network is a group of UK researchers who, together with international advisors, aim to advance research in cryopreservation and its applications.
Although we are a small group, we hope to promote academic and industrial activity on cryopreservation, and discuss its potential applications, including the idea of cryopreserving whole humans, commonly known as cryonics. We acknowledge that cryonics is a controversial topic, but like any unprovable approach we think its scientific discussion is necessary to permit its understanding by the public and by the wider scientific community, and it allows us to address many of the misunderstandings surrounding cryonics. We also think that cryopreservation, cryogenics and cryonics are fields with a huge potential impact on human medicine whose societal implications should be considered and debated.
We hope to attract and excite students and other researchers about cryobiology, contribute to knowledge exchange and help attract interest and funding to the field.
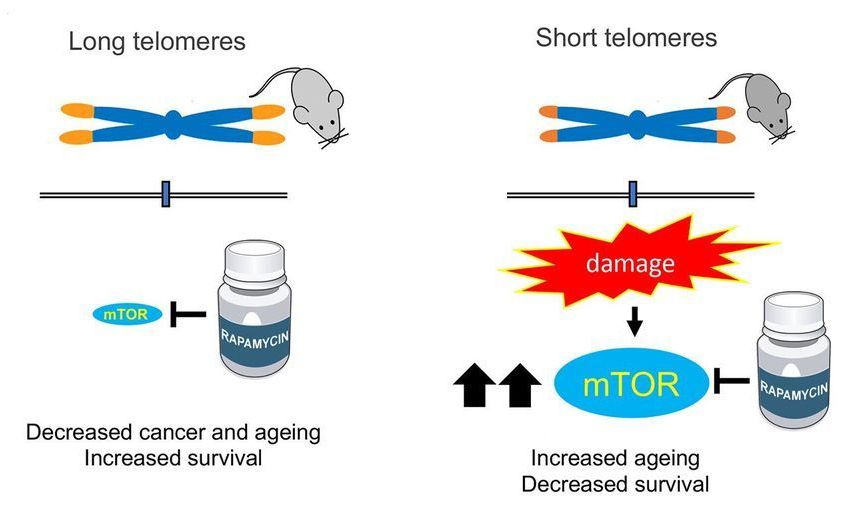
In the past few decades, researchers discovered that the rate at which we age is strongly influenced by biochemical processes that, at least in animal models, can be controlled in the laboratory. Telomere shortening is one of these processes; another is the ability of cells to detect nutrients mediated by the mTOR protein. Researchers have been able to prolong life in many species by modifying either one of them. But what if they manipulate both?
A team from the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) has studied it for the first time, with unexpected results. Blocking nutrient sensing by treatment with rapamycin, an mTOR inhibitor, delays the aging of healthy mice, but curiously, it worsens diseases and premature aging that occur in mice with short telomeres. This finding has important implications for the treatment of diseases associated with short telomeres, but also for age-related diseases that are also associated with short telomeres. The study, done by the Telomeres and Telomerase Group headed by Maria Blasco at the CNIO, is published in Nature Communications with Iole Ferrara-Romeo as the first author.
Telomeres, regions of repetitive nucleotide sequences at the end of chromosomes, preserve the genetic information of the cells. They shorten with age until they can no longer fulfill their function: The cells stop dividing and the tissues age since they are no longer able to regenerate.
Stem cells are possibly Nature’s best-stored secret. These cells, which might be discovered in multicellular organisms, including humans, no longer handiest have the capability to divide (mitosis) but additionally to form various structures such as cartilage, bone and lots of more. The procedure is called as differentiation.
Stem cell knee surgery can be used to successfully treat a wide range of acute and chronic knee situations and injuries. Thanks to advancements in regenerative medicine, we are capable of use stem cell therapy as a possible alternative to many invasive techniques consisting of, total knee joint replacement surgical treatment and arthroscopic knee surgical procedure, to treat knee pain. Additionally, stem cell therapy may additionally be ideally suited for people who do not qualify for surgical processes.

