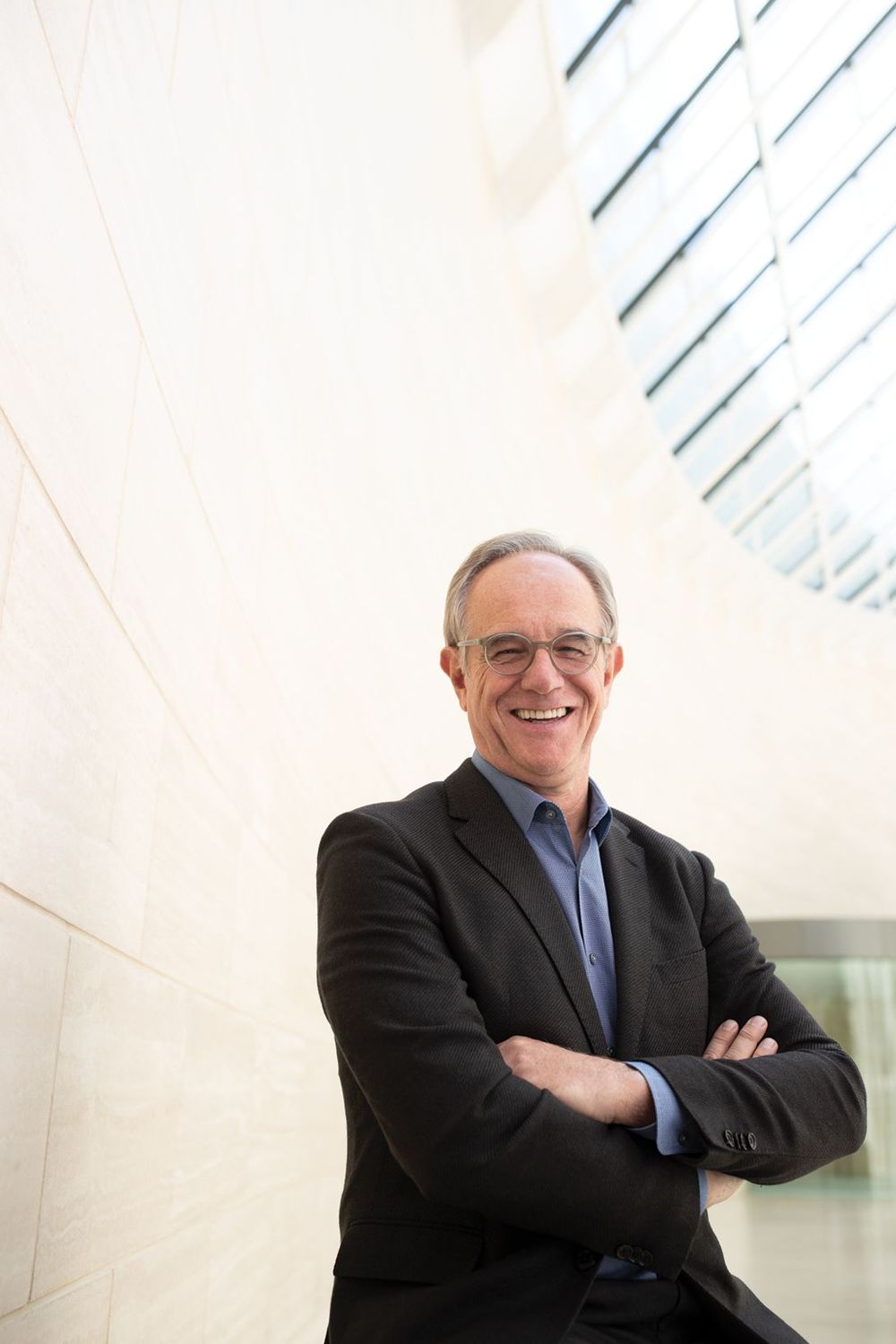
As the number of older Americans begins to rise, director Eric Verdin is leading his organization’s efforts to combat aging.


O.o probs alien o.o circa 2013.
Remember when encyclopaedias were books, and not just websites? You’d have a shelf full of information, packaged into entries, and then into separate volumes. Your genome is organised in a similar way. Your DNA is packaged into large volumes called chromosomes. There are 23 pairs of them, each of which contains a long string of genes. And just as encyclopaedia books are bound in sturdy covers to prevent the pages within from fraying, so too are your chromosomes capped by protective structures called telomeres.
That’s basically how it works in any animal or plant or fungus. The number of chromosomes might vary a lot—fruit flies have 8 while dogs have 78—but the basic organisation is the same.
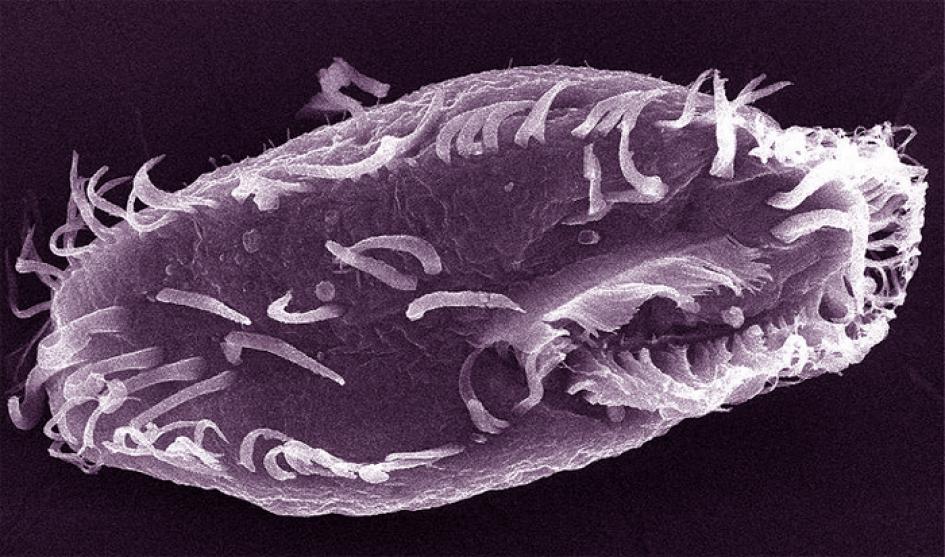
But there’s a pond-dwelling creature called Oxytricha trifallax whose DNA is organised in a very… different… way. A team of US scientists has sequenced its genome for the first time and discovered genetic chaos. It’s like someone has taken the encyclopaedias, ripped out all the individual pages, torn some of them, photocopied everything dozens of times, and stuffed the whole lot in a gigantic messy drawer.

Let’s face it, getting older sucks, and not because of all the extra candles on the birthday cake. Getting cake and presents every year is great, but the loss of health and independence isn’t a particularly good birthday present. (Wow, what’d I get this year? Just what I didn’t want: sarcopenia and hearing loss!)
Given the downsides of aging, it really is surprising how little people talk about it beyond the odd grumble or even as a joke. Normally, it’s to complain about the aches and pains that gradually appear as the years roll by, as we find it harder to walk up the stairs and “bright-eyed and bushy-tailed” turns into “cloudy-eyed and with an aching back”.
That’s not even the serious side of aging, which involves the gradual loss of independence and the age-related diseases that first rob us of our quality of life before they get around to killing us. The serious part is the horror of Alzheimer’s and the loss of self that it brings, the heart disease that cripples us, the frailty that steals our independence, and the lurking threat of cancer that rises dramatically as we age.


Chronic inflammation, which results when old age, stress or environmental toxins keep the body’s immune system in overdrive, can contribute to a variety of devastating diseases, from Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s to diabetes and cancer.
Now, scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, have identified a molecular “switch” that controls the immune machinery responsible for chronic inflammation in the body. The finding, which appears online Feb. 6 in the journal Cell Metabolism, could lead to new ways to halt or even reverse many of these age-related conditions.
“My lab is very interested in understanding the reversibility of aging,” said senior author Danica Chen, associate professor of metabolic biology, nutritional sciences and toxicology at UC Berkeley. “In the past, we showed that aged stem cells can be rejuvenated. Now, we are asking: to what extent can aging be reversed? And we are doing that by looking at physiological conditions, like inflammation and insulin resistance, that have been associated with aging-related degeneration and diseases.”
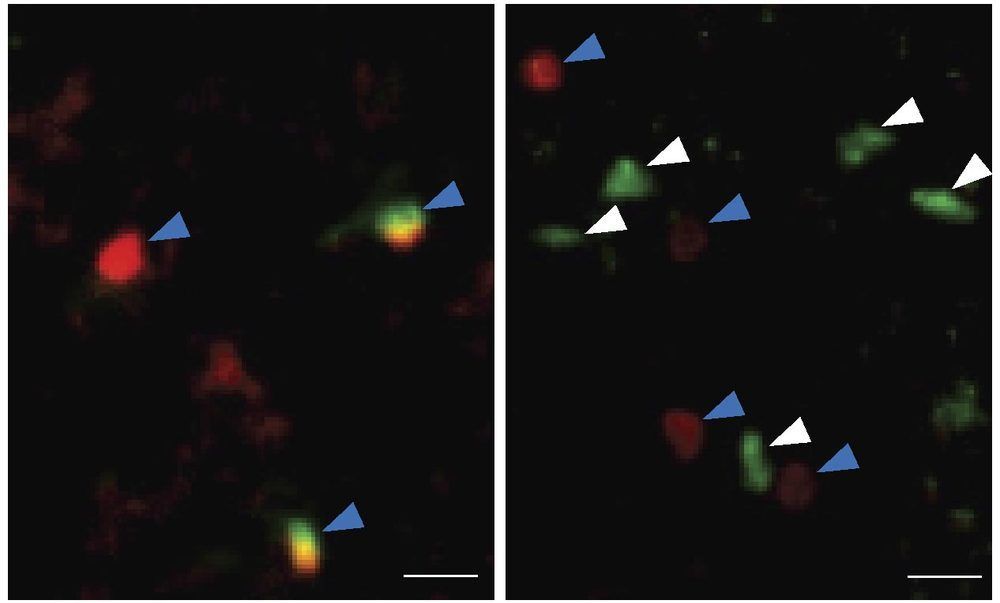
Researchers at Albany Medical College in New York have discovered that a specific type of immune cell accumulates in older brains, and that activating these cells improves the memory of aged mice. The study, which will be published on February 5, 2020, in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), suggests that targeting these cells might reduce age-related cognitive decline and combat aging-associated neurodegenerative disease in humans.
The brain is highly susceptible to aging, with cognitive functions, such as learning and memory, gradually declining as we get older. Much of the body’s immune system also deteriorates with age, resulting in increased susceptibility to infection and higher levels of inflammation. In their new JEM study, however, a team of researchers led by Qi Yang and Kristen L. Zuloaga at Albany Medical College reveal that aging-related changes in a class of immune cell known as group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) could allow doctors to combat the effects of aging on the brain.
ILC2s reside in specific tissues of the body and help to repair them when they are damaged. Recently, for example, ILC2s in the spinal cord were shown to promote healing after spinal cord injury. “However, whether ILC2s also reside in other parts of the central nervous system, and how they respond to aging, was unknown,” Yang says.
Watch the worldwide reveal of brand new game footage from Cyberpunk 2077!
This video contains work-in-progress gameplay — everything you see is potentially subject to change.
Cyberpunk 2077, the open-world, action-adventure story from CD PROJEKT RED, is coming to Xbox One, PS4 and PC April 16th, 2020.
Pre-order now: https://www.cyberpunk.net/pre-order
About Cyberpunk 2077:
In the most dangerous megacity of the future, the real you is not enough. Become V, a cyber-enhanced mercenary outlaw going after a one-of-a-kind implant — the key to immortality. Customize your cyberware and skillset, and explore a vast city of the future obsessed with power, glamour and body modification. The choices you make will determine the story and shape the world around you.
