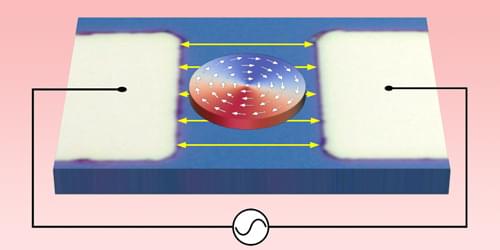
Imposing time-dependent strain on a magnetic disk induces vortex dynamics and offers a path toward energy-efficient spintronic devices.
Nanoscopic magnetic vortices made from electron spins could be used in spintronic computers (see Research News: 3D Magnetism Maps Reveal Exotic Topologies). To this end, researchers need an energy-efficient way to excite these vortices into a so-called gyrotropic mode—an orbital motion of the vortex core around the central point. The direction of this orbital motion would determine which of two binary states the vortex represents. Vadym Iurchuk at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, Germany, and his colleagues have now demonstrated such a method by imposing a time-varying strain on a magnetic material [1].
The excitation of gyration dynamics by an oscillating strain was suggested by a separate team in 2015 [2]. The idea involves depositing a magnetic film, in which magnetic vortices form spontaneously, on a piezoelectric substrate. Applying an alternating voltage to the substrate transfers a time-varying mechanical strain to the film, dynamically perturbing its magnetic texture. This perturbation displaces a vortex core from its equilibrium position, thereby exciting the gyrotropic mode.