A hierarchical #Atlas of the human #cerebellum for functional precision #mapping
Contribute to DiedrichsenLab/cerebellar_atlases development by creating an account on GitHub.
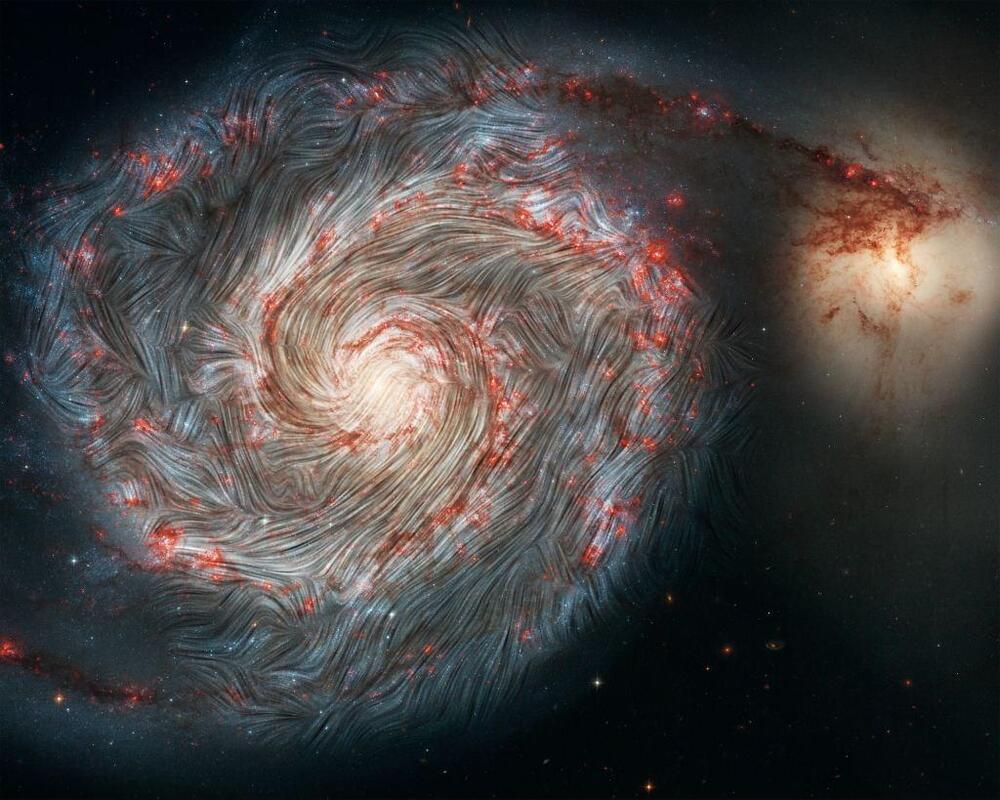

Researchers have developed the first 3D maps of magnetic field structures within a spiral arm of the Milky Way. While we’ve seen smaller-scale magnetic fields before, this is much larger, showing the overall magnetic pattern in our galaxy. These fields are incredibly weak, about 100,000 times weaker than the Earth’s magnetic field, but they impact the galaxy, strongly influencing star-forming regions.
In Neuromorphic Computing Part 2, we dive deeper into mapping neuromorphic concepts into chips built from silicon. With the state of modern neuroscience and chip design, the tools the industry is working with we’re working with are simply too different from biology. Mike Davies, Senior Principal Engineer and Director of Intel’s Neuromorphic Computing Lab, explains the process and challenge of creating a chip that can replicate some of the form and functions in biological neural networks.
Mike’s leadership in this specialized field allows him to share the latest insights from the promising future in neuromorphic computing here at Intel. Let’s explore nature’s circuit design of over a billion years of evolution and today’s CMOS semiconductor manufacturing technology supporting incredible computing efficiency, speed and intelligence.
Architecture All Access Season 2 is a master class technology series, featuring Senior Intel Technical Leaders taking an educational approach in explaining the historical impact and future innovations in their technical domains. Here at Intel, our mission is to create world-changing technology that improves the life of every person on earth. If you would like to learn more about AI, Wi-Fi, Ethernet and Neuromorphic Computing, subscribe and hit the bell to get instant notifications of new episodes.
Jump to Chapters:
0:00 Welcome to Neuromorphic Computing.
0:30 How to architect a chip that behaves like a brain.
1:29 Advantages of CMOS semiconductor manufacturing technology.
2:18 Objectives in our design toolbox.
2:36 Sparse distributed asynchronous communication.
4:51 Reaching the level of efficiency and density of the brain.
6:34 Loihi 2 a fully digital chip implemented in a standard CMOS process.
6:57 Asynchronous vs Synchronous.
7:54 Function of the core’s memory.
8:13 Spikes and Table Lookups.
9:24 Loihi learning process.
9:45 Learning rules, input and the network.
10:12 The challenge of architecture and programming today.
10:45 Recent publications to read.
Architecture all access season 2 playlist — • architecture all access season 2
Intel Wireless Technology — https://intel.com/wireless.
Cognitive neuroscientist Clayton Curtis describes an elegant experiment that leads us to ask: Does the brain honor the distinction implied in most textbooks between spatial attention, motor control, and spatial working memory?
For more info/content, please visit: https://postlab.psych.wisc.edu/cog-ne…
Relevant paper:
Jerde, T. A., Merriam, E. P., Riggall, A. C., Hedges, J. H., \& Curtis, C. E. (2012). Prioritized maps of space in human frontoparietal cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(48), 17382–17390.


Over ten years ago, the Dark Energy Survey (DES) began mapping the Universe to find evidence that could help us understand the nature of the mysterious phenomenon known as dark energy.
I’m one of more than 100 contributing scientists that have helped produce the final DES measurement, which has just been released at the 243rd American Astronomical Society meeting in New Orleans.
Dark energy is estimated to make up nearly 70 percent of the observable Universe, yet we still don’t understand what it is. While its nature remains mysterious, the impact of dark energy is felt on grand scales. Its primary effect is to drive the accelerating expansion of the Universe.
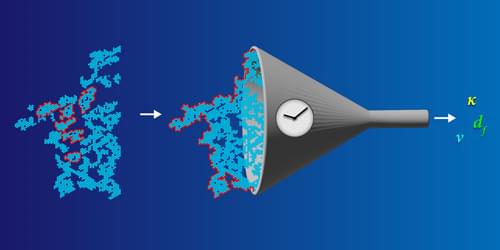
New theoretical work explores the onset of rigidity in granular materials and other disordered systems by mapping out the edges of rigid regions.
Phase transitions are a common part of our daily lives. Many of them are intuitive: water transforms into steam or ice, birds spontaneously form a flock, and random piles of marbles suddenly jam together into a solid. Possibly the most basic phase transition, however, is a more abstract version called connectivity percolation (CP). In systems displaying CP, individual units such as persons or polymers are mapped by their contacts—or connectors—to a graph consisting of nodes and edges. As the number of connectors increases, the system switches from being disconnected (filled with small, separate clusters) to being connected (spanned by one large cluster). This connectivity phase transition is commonly seen in polymer solutions and pandemic spreading, but researchers have also used the percolation perspective to describe the onset of mechanical rigidity in disordered systems, otherwise known as rigidity percolation (RP).
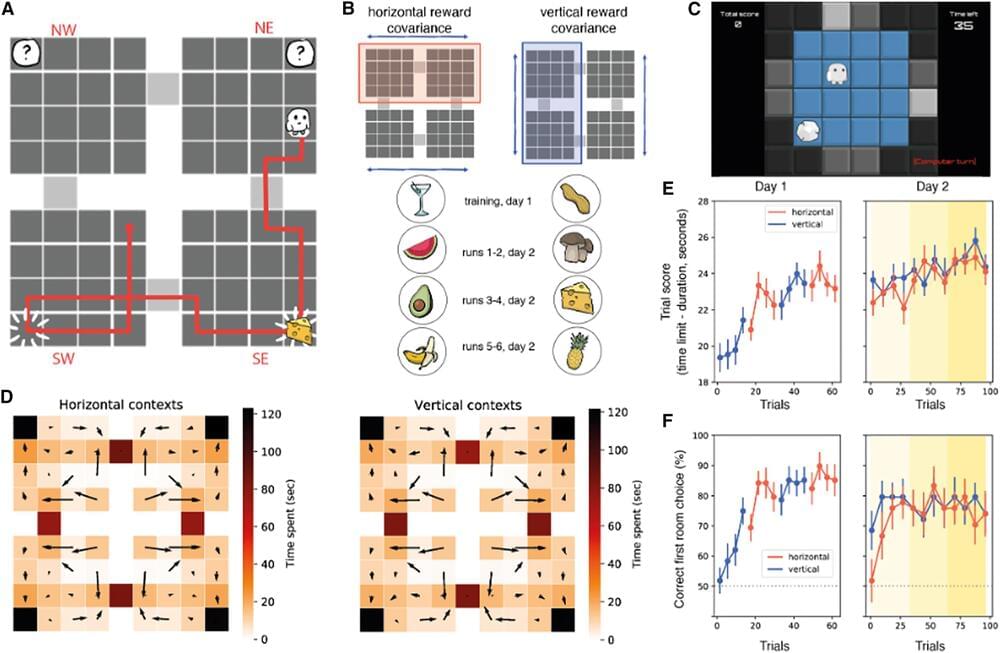
Human decision-making has been the focus of a wide range of research studies. Collectively, these research efforts could help to understand better how people make different types of everyday choices while also shedding light on the neural processes underpinning these choices.
Findings suggest that while making instantaneous decisions, or in other words, choices that need to be made quickly based on the information available at a given moment, humans greatly rely on contextual information. This contextual information can also guide so-called sequential decisions, which entails making a choice after observing the sequential unfolding of a process.
Researchers at the University of Oxford, the National Research Council in Rome, University College London (UCL), and the Max Planck Institute for Human Development recently carried out a study exploring the impact of context on goal-directed decision-making. Their findings, published in Neuron, suggest that goal-seeking ‘compresses’ spatial maps in the hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortices in the brain.
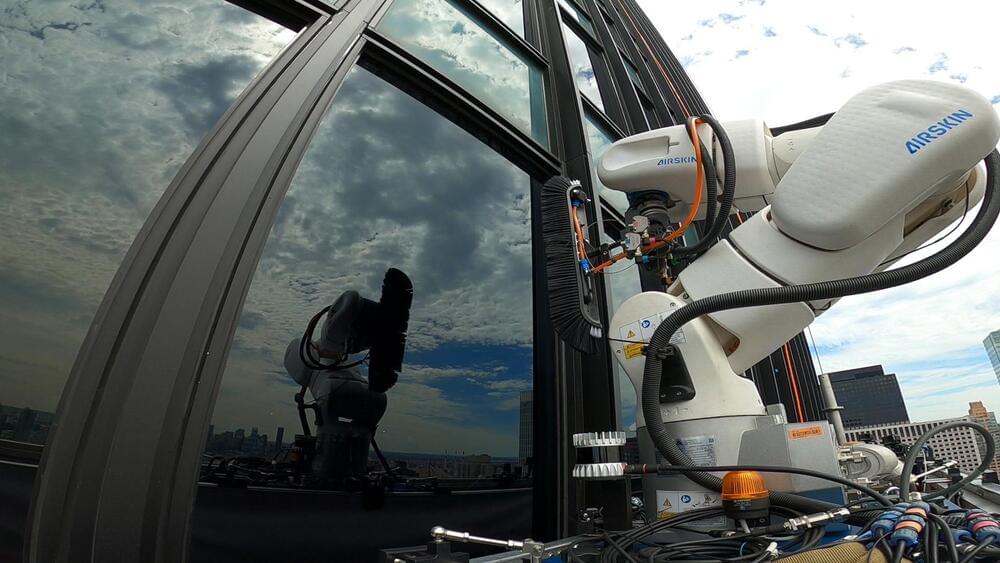

Skyline Robotics is disrupting the century-old practice of window washing with new technology that the startup hopes will redefine a risky industry.
Its window-washing robot, Ozmo, is now operational in Tel Aviv and New York, and has worked on major Manhattan buildings such as 10 Hudson Yards, 383 Madison, 825 3rd Avenue and 7 World Trade Center in partnership with the city’s largest commercial window cleaner Platinum and real estate giant The Durst Organization.
The machine is suspended from the side of a high-rise. A robotic arm with a brush attached to the end cleans the window following instructions from a LiDAR camera, which uses laser technology to map 3D environments. The camera maps the building’s exterior and identifies the parameters of the windows.