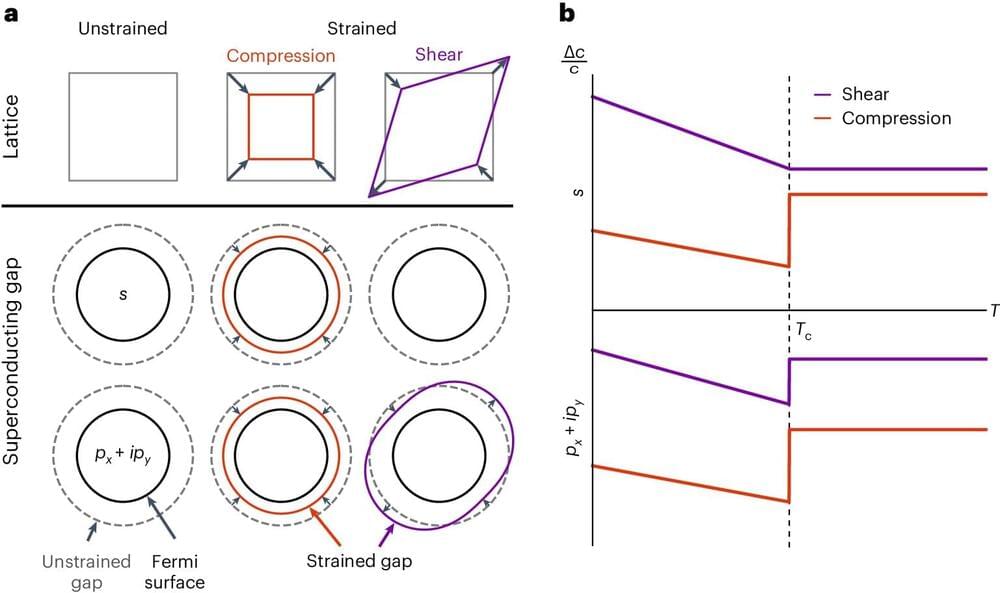
With pulses of sound through tiny speakers, Cornell physics researchers have clarified the basic nature of a new superconductor.

Astronomy Magazine — Project Lyra is the cover feature!
A big thank you to Maciej Rebisz for the images and the entire Project Lyra team for the research work!
Project Lyra develops concepts for reaching interstellar objects such as 1I / ‘Oumuamua and 2I / Borisov with a spacecraft, based on near-term technologies. But what is an interstellar object?
On October 19th 2017, the University of Hawaii’s Pan-STARRS 1 telescope on Haleakala discovered a fast-moving object near the Earth, initially named A/2017 U1. It is now designated as 1I/’Oumuamua. This object was found to be not bound to the solar system. It has a velocity at infinity of ~26 km/s and an incoming radiant (direction of motion) near the solar apex in the constellation Lyra. Due to the non-observation of a tail in the proximity of the Sun, the object does not seem to be a comet but an asteroid. More recent observations from the Palomar Observatory indicate that the object is reddish, similar to Kuiper belt objects. This is a sign of space weathering.
When will such an object visit us again? End of 2019, a second interstellar object, 2I/Borisov was discovered, which is a comet. As 1I/‘Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov are the nearest macroscopic samples of interstellar material, the scientific returns from sampling the object are hard to overstate. Detailed study of interstellar materials at interstellar distances are likely decades away, even if Breakthrough Initiatives’ Project Starshot, for example, is vigorously pursued. Hence, an interesting question is if there is a way to exploit this unique opportunity by sending a spacecraft to 1I/’Oumuamua to make observations at close range.
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers have unveiled a novel 2D material improving optical modulation for advanced systems and communications.
Responding to the increasing demand for efficient, tunable optical materials capable of precise light modulation to create greater bandwidth in communication networks and advanced optical systems, a team of researchers at NYU Abu Dhabi’s Photonics Research Lab (PRL) has developed a novel, two-dimensional (2D) material capable of manipulating light with exceptional precision and minimal loss.
Tunable optical materials (TOMs) are revolutionizing modern optoelectronics, electronic devices that detect, generate, and control light. In integrated photonics circuits, precise control over the optical properties of materials is crucial for unlocking groundbreaking and diverse applications in light manipulation. Two-dimensional materials like Transition Metal Dichalcogenides (TMDs) and graphene exhibit remarkable optical responses to external stimuli. However, achieving distinctive modulation across a short-wave infrared (SWIR) region while maintaining precise phase control at low signal loss within a compact footprint has been a persistent challenge.
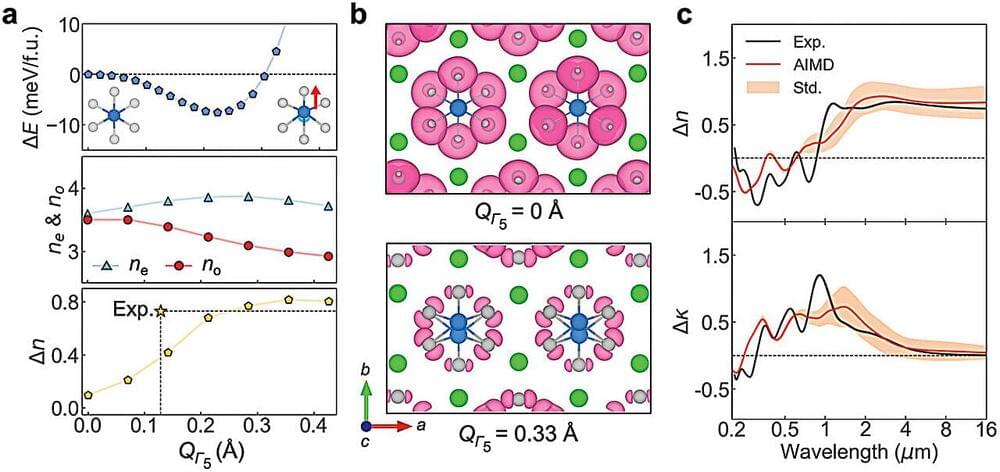
While we usually think of disorder as a bad thing, a team of materials science researchers led by Rohan Mishra, from Washington University in St. Louis, and Jayakanth Ravichandran, from the University of Southern California, have revealed that—when it comes to certain crystals—a little structural disorder might have big impacts on useful optical properties.
Engineers at Princeton and North Carolina State University have combined ancient paper-folding and modern materials science to create a soft robot that bends and twists through mazes with ease.
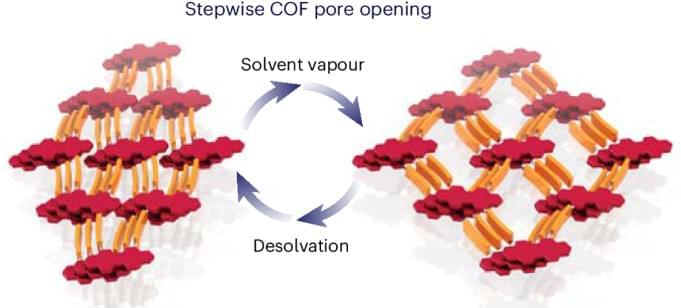
Two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (2D COFs) enable the construction of bespoke functional materials, but designing dynamic 2D COFs is challenging. Now it has been shown that perylene-diimide-based COFs can open and close their pores upon uptake or removal of guests, while fully retaining their crystalline long-range order. Moreover, the variable COF geometry enables stimuli-responsive optoelectronic properties.
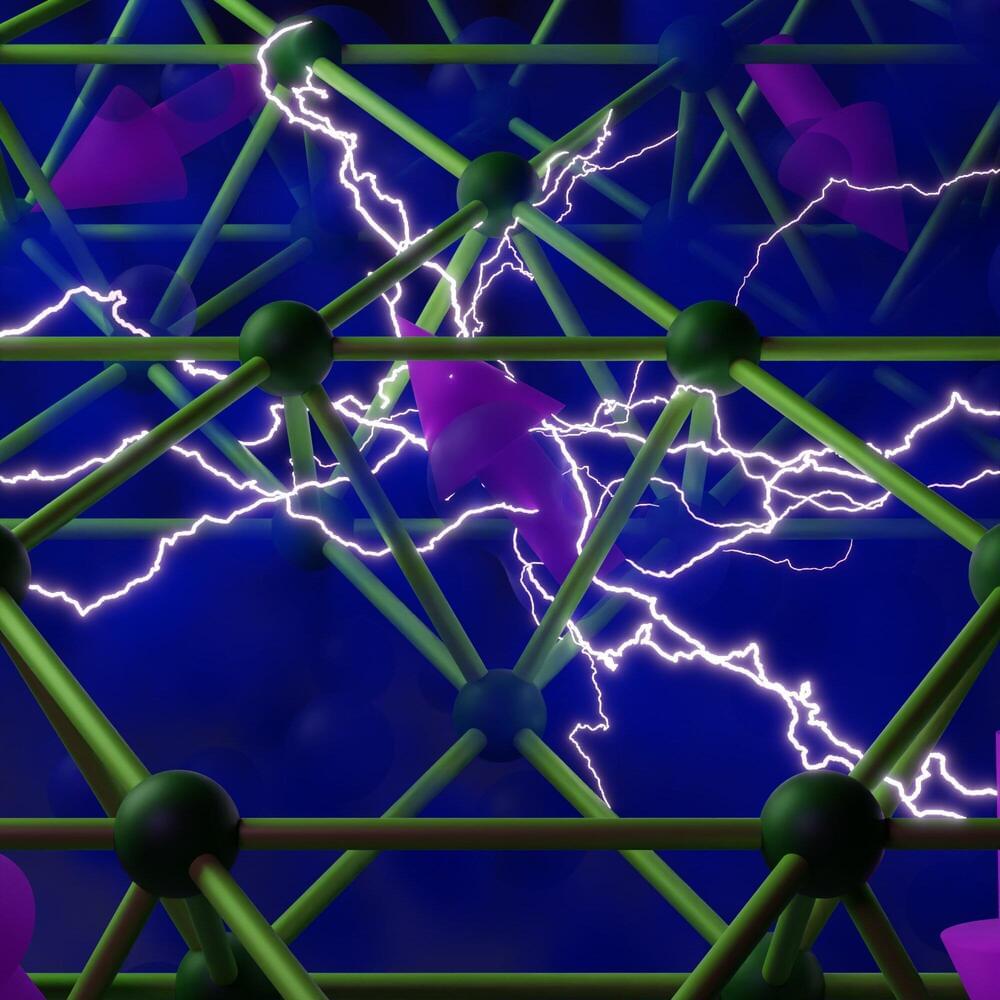

The work introduces a completely new way to create and study strange metals, whose electrons behave differently than those in a conventional metal like copper. “It is a potential new approach to designing these unusual materials,” says Joseph G. Checkelsky, lead principal investigator of the research and Associate Professor of Physics.
Linda Ye, MIT Ph.D. ‘21, is first author of a paper on the work published earlier this year in Nature Physics. “A new way of making strange metals will help us develop a unifying theory behind their behavior. That has been quite challenging to date, and could lead to a better understanding of other materials, including high-temperature superconductors,” says Ye, now an assistant professor at the California Institute of Technology.
The Nature Physics paper is accompanied by a News & Views article titled, “A strange way to get a strange metal.”
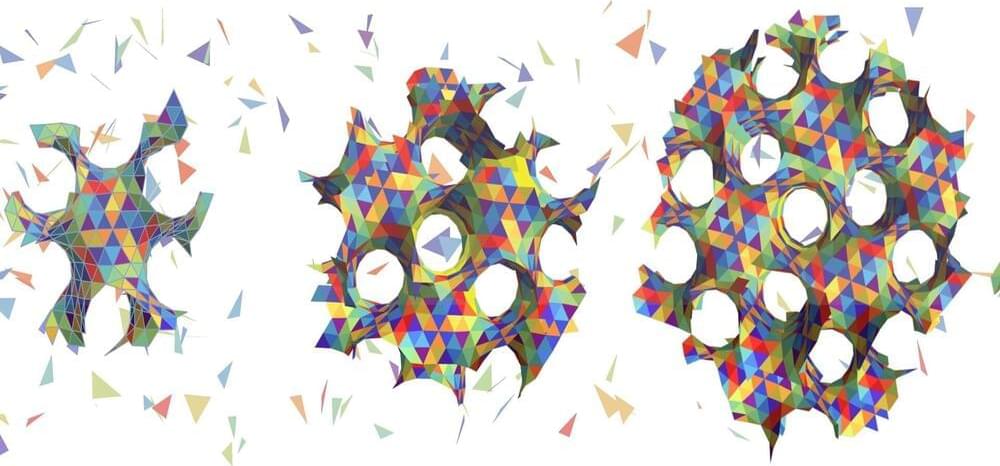

A team of researchers led by the University of Massachusetts Amherst has drawn inspiration from a wide variety of natural geometric motifs—including those of 12-sided dice and potato chips—in order to extend a set of well-known design principles to an entirely new class of spongy materials that can self-assemble into precisely controllable structures.