Taking inspiration from Mother Nature once again results in a new material with fantastic properties.


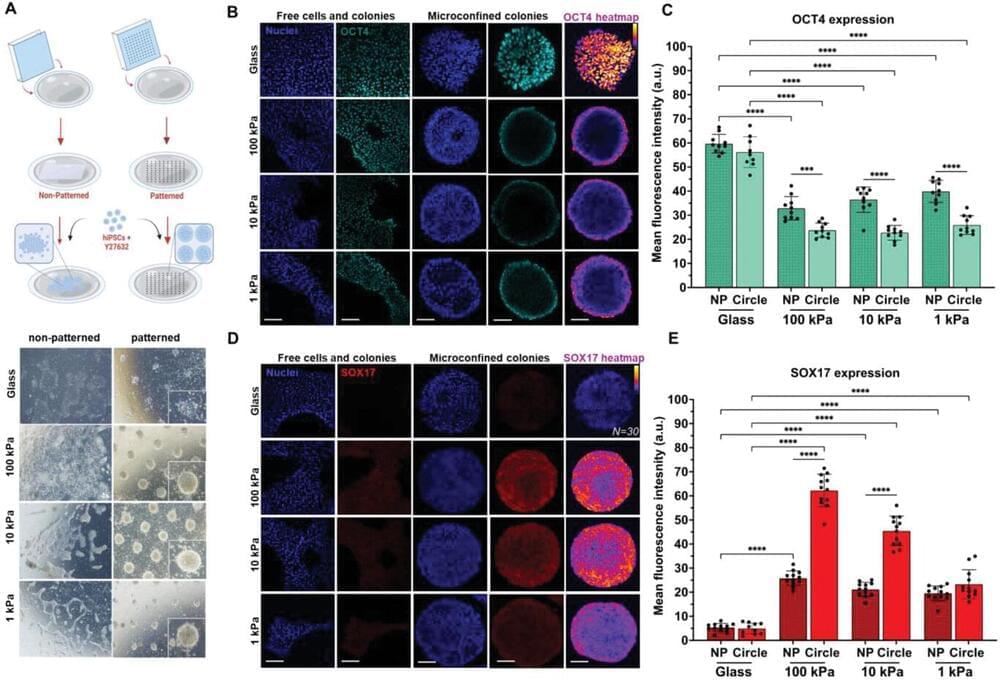
Materials scientists at UNSW Sydney have shown that human pluripotent stem cells in a lab can initiate a process resembling the gastrulation phase—where cells begin differentiating into new cell types—much earlier than occurs in mother nature.
For an embryo developing in the womb, gastrulation occurs at day 14. But in a dish in a lab at UNSW’s Kensington campus, Scientia Associate Professor Kris Kilian oversaw an experiment where a gastrulation-like event was triggered within two days of culturing human stem cells in a unique biomaterial that, as it turned out, set the conditions to mimic this stage of embryo development.
“Gastrulation is the key step that leads to the human body plan,” says A/Prof. Kilian.

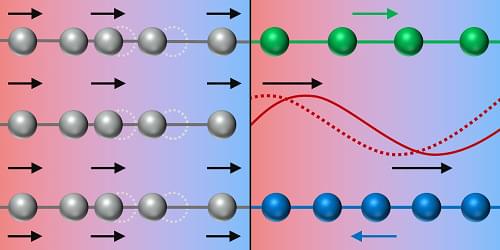
Heat-transport measurements and neutron-scattering spectroscopy probe a form of thermal conduction based on excitations called phasons.
The understanding of how substances conduct heat is of great significance in materials science. It is needed for many important technological applications—from heat management in electronics to temperature control in buildings [1]. Therefore, when an unusual form of thermal transport is identified, materials scientists take notice. Michael Manley of Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, and his colleagues have shown that excitations called phasons can provide the main contribution to thermal transport in a material known as fresnoite [2]. Phasons are collective lattice oscillations that occur in certain crystals with an aperiodic lattice structure—fresnoite being one of the best known. The researchers’ demonstration could pave the way for new heat-management strategies.
Thermal conductivity is a measure of a material’s ability to transfer heat. It is a property that we are all abruptly reminded of when we accidentally place our hand on a hot kitchen stove. The temperature gradient between our cooler skin and the hotter surface facilitates a transfer of energy into our hand, resulting in an unpleasant sensation. The notion that different materials conduct heat at different rates is similarly experienced when we perceive the cooling sensation of holding a metal spoon relative to a wooden one.
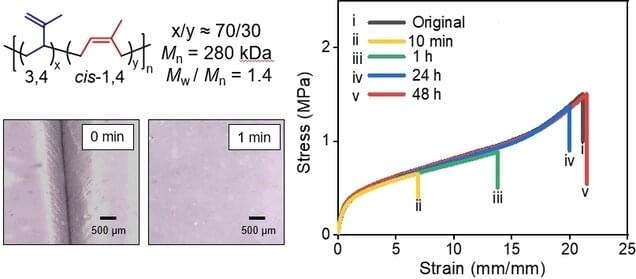
Material scientists at RIKEN have created a self-healing polymer by using an off-the-shelf compound for the first time. The strategy they used is promising for improving the durability and minimizing the environmental impact of various commercial polymers for a wide range of applications.
Polymers capable of healing themselves when damaged would last longer and thus reduce costs and the burden on the environment. Current strategies for producing self-healing polymers mainly employ reversible chemical reactions, but this usually entails complex synthesis processes. Furthermore, self-healing mechanisms based on chemical reactions may not work in certain environments such as in water and acidic and alkaline solutions.
Ideally, material scientists would like to produce polymers that self-heal under a wide range of conditions, from readily available materials, using simple synthesis processes.

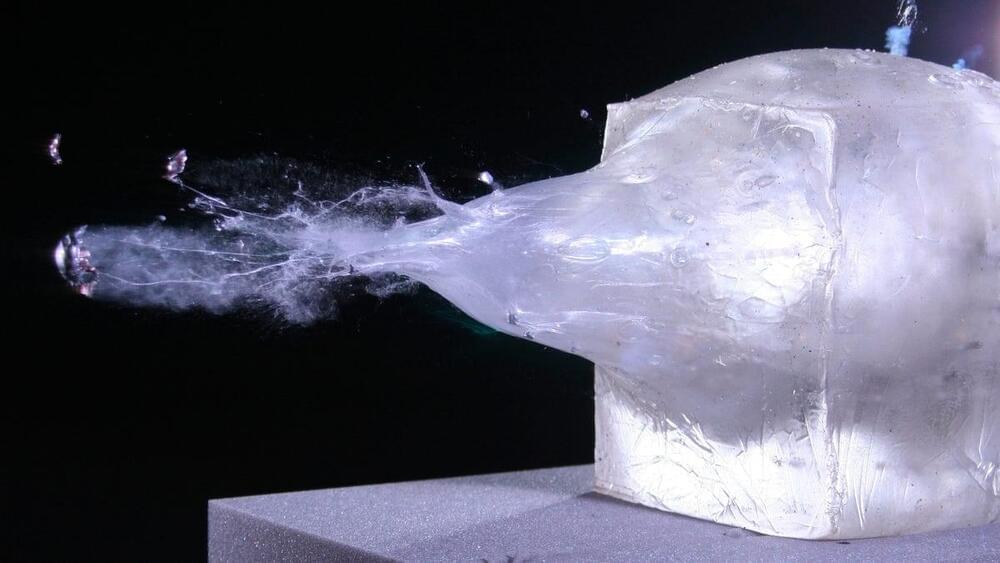
Scientists have measured the highest toughness ever recorded, of any material, while investigating a metallic alloy made of chromium, cobalt, and nickel (CrCoNi). Not only is the metal extremely ductile – which, in materials science, means highly malleable – and impressively strong (meaning it resists permanent deformation), its strength and ductility improve as it gets colder. This runs counter to most other materials in existence.
“In the same units, the toughness of a piece of silicon is one, the aluminum airframe in passenger airplanes is about 35, and the toughness of some of the best steels is around 100. So, 500, it’s a staggering number.” —

A research team from Skoltech, Aalto University, and Kurnakov Institute has recently developed a new, versatile and simple approach to using carbon nanotubes for manufacturing carbon nanotube-polymer nanocomposites. The method is reported in Carbon and involves making briquettes—dense packages of carbon nanotube powders. Nanocomposites made with briquettes perform equally well as those made from the more expensive masterbatches, which are also polymer-specific—that is, less versatile.
“We believe the use of dense briquettes of carbon nanotubes can significantly facilitate the development of the carbon nanotube composite industry. This technique is cheap and applicable to a broad variety of polymer matrices, without sacrificing any of the electrical and thermal properties of the final material,” the lead author of the study, Skoltech Ph.D. student Hassaan Butt, stated.
Carbon nanotubes have been intensively investigated for decades by researchers from academia and industry because of their unique combination of electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties. Meanwhile, polymer-based nanocomposites have come to be the largest carbon nanotube application and the one closest to widespread integration into everyday life. It is easy to understand why: The smallest amounts of nanotubes added to a polymer endow the material with fundamentally new properties, such as electrical conductivity and piezoresistivity, as well as crucially enhancing its thermal and mechanical properties.
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists are scaling up the production of vertically aligned single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) that could revolutionize diverse commercial products ranging from rechargeable batteries, automotive parts and sporting goods to boat hulls and water filters. The research appears in the journal Carbon.
Most CNT production today is used in bulk composite materials and thin films, which rely on unorganized CNT architectures. For many uses, organized CNT architectures such as vertically aligned forests provide important advantages for exploiting the properties of individual CNTs in macroscopic systems.
“Robust synthesis of vertically-aligned carbon nanotubes at large scale is required to accelerate deployment of numerous cutting-edge devices to emerging commercial applications,” said LLNL scientist and lead author Francesco Fornasiero. “To address this need, we demonstrated that the structural characteristics of single-walled CNTs produced at wafer scale in a growth regime dominated by bulk diffusion of the gaseous carbon precursor are remarkably invariant over a broad range of process conditions.”

This is number 22 on IE’s list of 22 best innovations, a look back at recycling for all plastics.
Two companies, Plastonix and Elemental Recycling have done what others could not: they have found technologies that recycle all types of plastic.
The monumental task of recycling the 380 million tons of plastic disposed of each year, that clog the ocean and beaches throughout the world, has eluded us. Around 80 percent of all plastic ends up in the oceans and landfills.
Ibrahim Can/Interesting Engineering.
This is a real innovation because up until now, there were practically no way to recycle most plastics, especially soft plastic, mixed plastics, and dirty or soiled plastics. That has all changed.
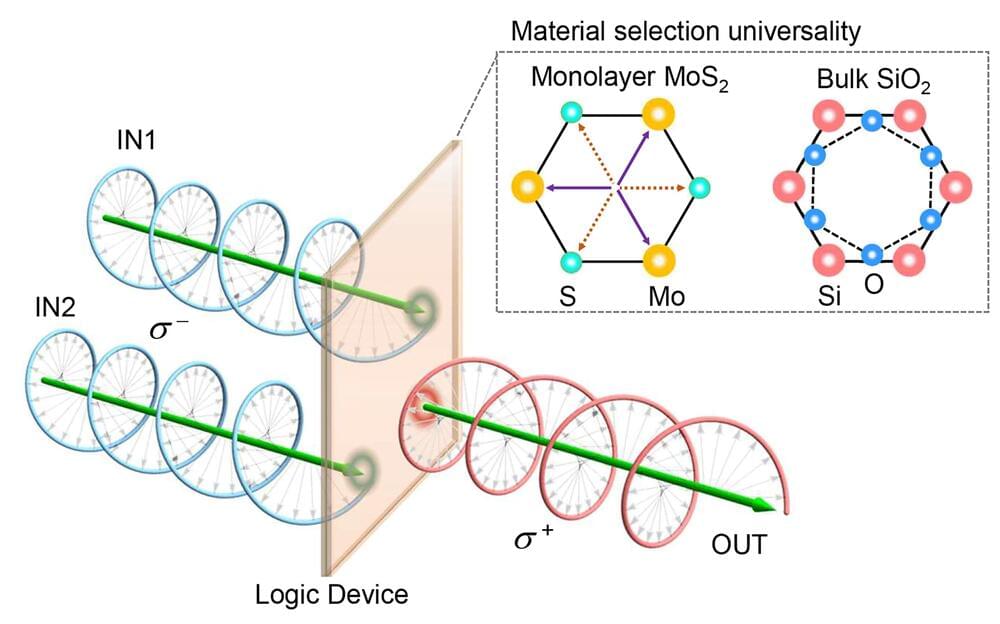
Logic gates are the fundamental components of computer processors. Conventional logic gates are electronic—they work by shuffling around electrons—but scientists have been developing light-based optical logic gates to meet the data processing and transfer demands of next-generation computing.
New optical chirality logic gates developed by researchers at Aalto University operate about a million times faster than existing technologies, offering ultrafast processing speeds.
The new approach uses circularly polarized light as the input signal. The logic gates are made from crystalline materials that are sensitive to the handedness of a circularly polarized light beam—that is, the light emitted by the crystal depends on the handedness of the input beams. This serves as the basic building block for one type of logic gate (XNOR), and the remaining types of logic gates are built by adding filters or other optical components.