A nearby star-forming region may explain the mystery of tiny grains from beyond the solar system.


Researchers in Singapore and at CalTech have developed a 3D printed fabric with an interesting property: it is generally flexible but can stiffen on demand. You can see a video about the new fabric, below.
The material consists of nylon octahedrons interlocked. The cloth is enclosed in a plastic envelope and vacuum-packed. Once in a vacuum, the sheet becomes much stiffer and can hold many times its own weight.
Presumably, the idea would be to allow the material to flex in the plastic envelope until there was a need for the increased rigidity, and then remove the air. Of course, there are a lot of practical problems with that. If the envelope is no longer air tight, for example, the operation will fail. It is also hard to rapidly remove the air from the bag to make, say, something like Batman’s cape which was a comparison the researchers drew.
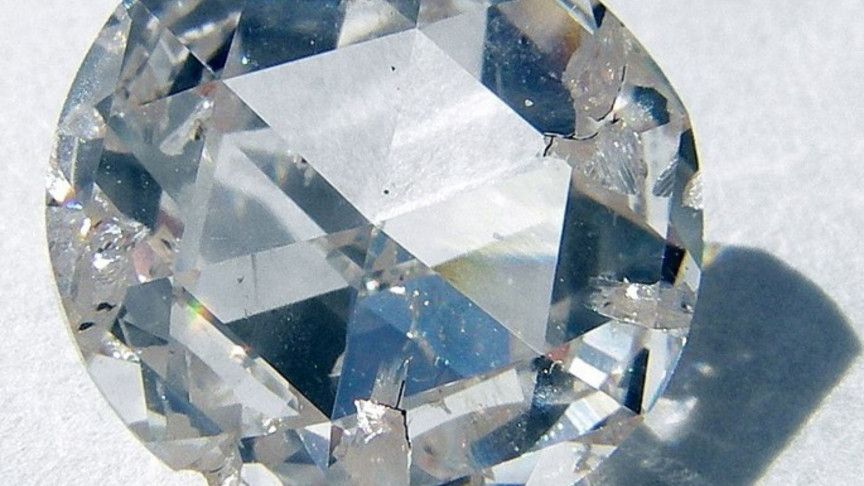

A team of researchers in northern China developed the world’s hardest glassy material, the transparent, yellow-tinted AM-III, which is capable of leaving a deep scratch on the surface of a diamond, a report from South China Morning Post explains.
The material, which is made entirely of carbon, reached a 113 gigapascals (GPa) on the Vickers hardness test. As a point of reference, natural diamonds usually score somewhere between 50 and 70 on the GPa scale.
The findings of the research, led by Professor Tian Yongjun of Yanshan University in Qinhuangdao, Hebei province, were published in the journal National Science Review. In 2,013 Tian and his team created the world’s hardest material that’s visible to the naked eye, a boron nitride crystal that is twice as hard as diamond at 200 GPa.
Scientists developed a material called AM-III which is tougher than diamond and is almost as efficient a semiconductor as silicon.

A freely moving diamond trapped inside another diamond was discovered in Siberia by Alrosa in 2019. The unusual diamond, nicknamed the “Matryoshka” after the traditional Russian nesting dolls, attracted widespread interest in how this feature formed The 0.62 ct flat octahedral diamond, a twinned macle, was recently examined by the New York laboratory. Flat-bottom trigon etch pits were well developed on the face {111} (figure 1). The crystal showed a clear green bodycolor, with small dark green radiation stains in shallow fractures along the edges when viewed from the top of the crystal. Two etch channels on opposite sides of the edges had rectangular openings about 0.2 mm in width. The channels extended into the internal enclosed cavity. These features made this diamond unique. Trapped in the cavity was a small, flat diamond crystal with a hexagonal outline. The small diamond, covered with some green radiation stains on the surface, is entirely detached from its host crystal and can move freely inside. The surface of the small diamond was covered with groups of straight parallel striations following the diamond crystal symmetry. No etched trigons were observed on the surfaces of the small diamond (figure 2). Except for tiny foreign-material contaminations at the two entrances of the open channels, no other inclusions were observed in this crystal (figure 3).
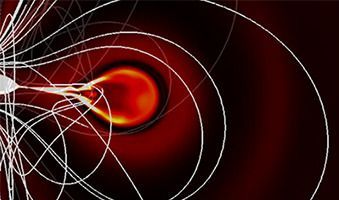

A new way to probe exotic matter aids the study of atomic and particle physics.
Physicists have created a new way to observe details about the structure and composition of materials that improves upon previous methods. Conventional spectroscopy changes the frequency of light shining on a sample over time to reveal details about them. The new technique, Rabi-oscillation spectroscopy, does not need to explore a wide frequency range so can operate much more quickly. This method could be used to interrogate our best theories of matter in order to form a better understanding of the material universe.
Though we cannot see them with the naked eye, we are all familiar with the atoms that make up everything we see around us. Collections of positive protons, neutral neutrons and negative electrons give rise to all the matter we interact with. However, there are some more exotic forms of matter, including exotic atoms, which are not made from these three basic components. Muonium, for example, is like hydrogen, which typically has one electron in orbit around one proton, but has a positively charged muon particle in place of the proton.
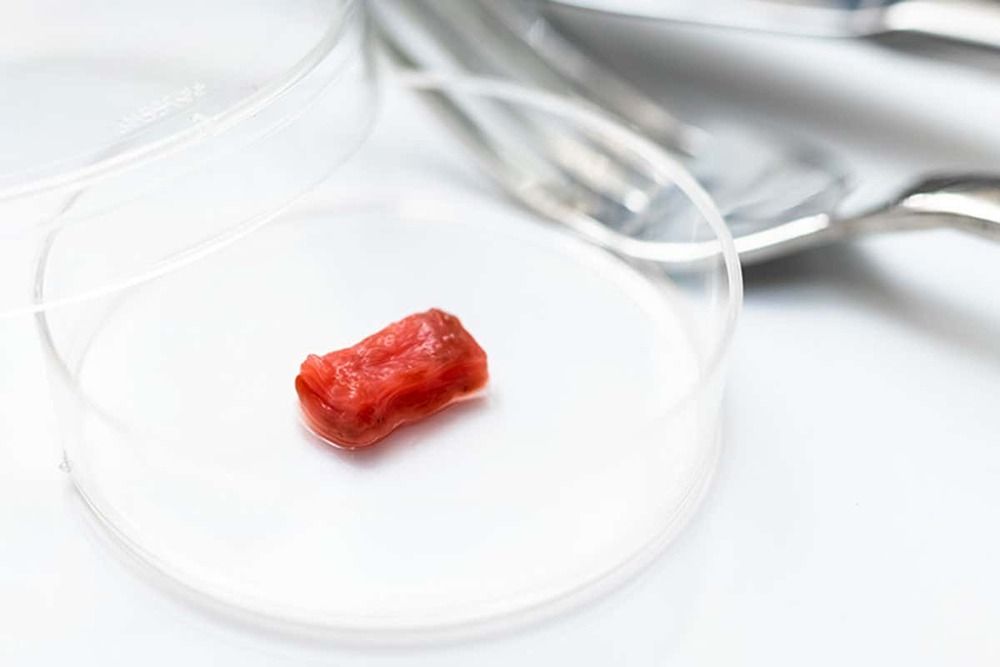

Many researchers are working to develop lab-grown meat, partly to reduce the environmental impact of meat production, and partly because of ethical concerns about the treatment of livestock. While some substitutes use plant-based materials to mimic meat, others aim to grow animal cells in culture to create true artificial meat.
So far, this kind of artificial meat doesn’t match the structure of the real thing. It is missing the complex layers of muscle, fat and sinew. The result is mince that can be used to make burgers, like the one famously cooked at a press conference in 2013. Now, researchers are attempting to make something that mimics a steak or chop.
A team led by Shoji Takeuchi at the University of Tokyo in Japan has found a new way to grow cow muscle cells in culture. The cells arrange themselves into long strands, resembling real muscle fibres. “We have developed steak meat with highly aligned muscle fibres that are arranged in one direction,” says Takeuchi.

This could prove helpful. 😀
Design graduate Kukbong Kim has developed a paint made from demolished concrete that is capable of absorbing 20 per cent of its weight in carbon.
Called Celour, the paint can sequester 27 grams of CO2 for every 135 grams of paint used.
“That is the same amount of carbon dioxide that a normal tree absorbs per day,” Kim said.

Seeing the environmental crises rising particularly because of the construction sector, more conscious choices regarding building materials need to be considered. Since the beginning of our craft, architects and constructors have been trying to utilize natural materials in buildings—either used in their raw form, like bamboo, or processed and incorporated into different materials. Hempcrete is one type of concrete incorporating natural materials; it is energy-saving and durable.
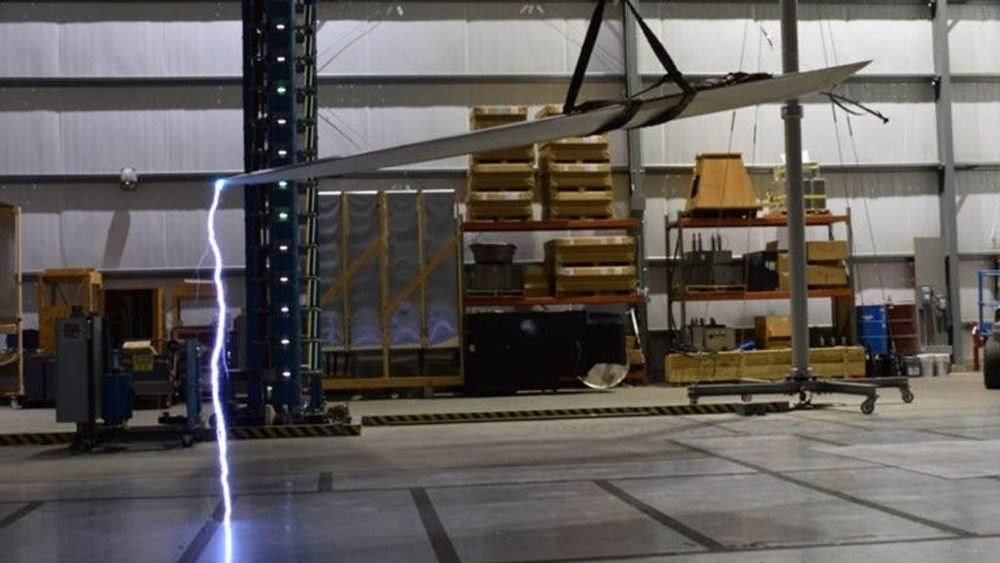

Standing hundreds of feet above ground, wind turbines — like tall trees, buildings, and telephone poles — are easy targets for lightning. Just by virtue of their height, they will get struck.
Lightning protection systems exist for conventional wind turbine blades. But protection was needed for blades made from a new type of material—thermoplastic resin composites — and manufactured using an innovative thermal (heat-based) welding process developed by scientists at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
Thermoplastic materials, like plastic bottles, can be more easily recycled than the thermoset materials commonly used to make wind turbine blades today. While thermoset materials need to be heated to cure, thermoplastics cure at room temperature, which reduces both blade manufacturing times and costs.