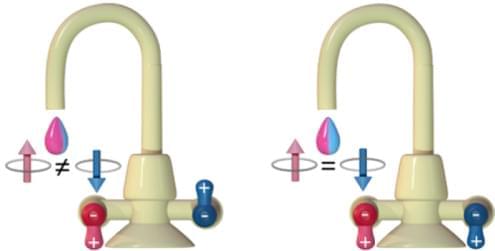
Altermagnets are arguably the hottest objects in magnetism right now (see Viewpoint: Altermagnetism Then and Now). Over the past year, researchers have delivered experimental evidence for this new type of magnet, but they have yet to harness the behavior for applications. Now three independent groups have proposed methods for electrically tuning the properties of altermagnets [1– 3]. If implemented, the findings could allow the use of altermagnets in next-generation spintronics devices.
Altermagnets can be thought of as a cross between antiferromagnets and ferromagnets. Like antiferromagnets the materials lack net magnetization—the magnetic spins of the atomic lattice are aligned in opposing directions. Like ferromagnets they have magnetically sensitive energy levels and display electronic band structures that are split into spin-up and spin-down bands. This splitting can be used to polarize an electronic current, as one spin state will flow through the material more easily. The combination of these properties could allow researchers to create spintronics devices that operate more rapidly and with greater efficiency than those currently in use, but for that, they first need a way to manipulate the spin properties of an altermagnet.
The proposed methods of the three teams (a group led by Tong Zhou of the Eastern Institute of Technology, Ningbo, China; Libor Šmejkal of the Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems, Germany; and a group led by Qihang Liu of the Southern University of Science and Technology, China) all use electric fields for this switching. Controlling magnetism with electricity is particularly attractive because electric fields are much easier to manipulate and integrate into modern electronic devices than magnetic fields. Electrical tuning is potentially also faster (subnanosecond) and could use less energy, two crucial properties for the development of high-speed, low-power spintronic devices.