Inspired by the “Harry Potter” stories and the Disney Channel show “Wizards of Waverly Place,” 7-year-old Sabrina Corsetti emphatically declared to her parents one afternoon that she was, in fact, a wizard.
“My dad turned to me and said that, if I really wanted to be a wizard, then I should become a physicist. Physicists are the real wizards of the world,” she recalls.
That conversation stuck with Corsetti throughout her childhood, all the way up to her decision to double-major in physics and math in college, which set her on a path to MIT, where she is now a graduate student in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science.
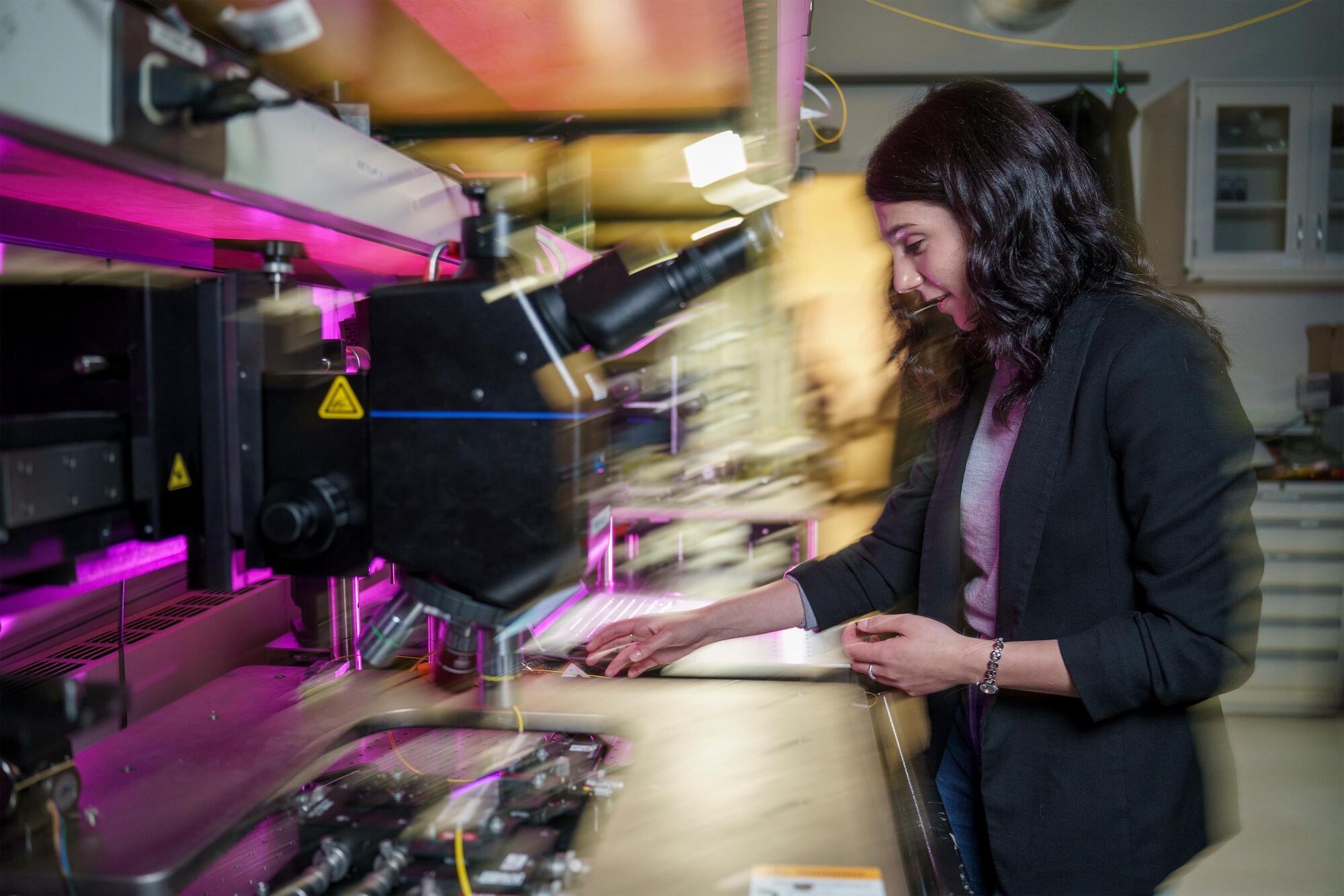
While her work may not involve incantations or magic wands, Corsetti’s research centers on an area that often produces astonishing results: integrated photonics. A relatively young field, integrated photonics involves building computer chips that route light instead of electricity, enabling compact and scalable solutions for applications ranging from communications to sensing.
MIT graduate student Sabrina Corsetti is exploring the cutting edge of integrated photonics, which involves building computer chips that route light instead of electricity. Her projects have included a chip-sized 3D printer and miniaturized optical systems for quantum computing.