An Israeli startup is using over-the-phone voice analysis to detect atrial fibrillation, a common heart condition that is hard to find on a standard screening ECG.
Category: mobile phones – Page 117

AI With a Human Eye — Possibilities Are Endless
Possibilities Are Endless — iHLS.
This post is also available in:  עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
A new type of technology has recently been developed. AI technology that mimics the human eye. Researchers at the University of Central Florida have created a device for AI that replicates the retina of the eye. This new discovery can lead to AI that can immediately identify objects, such as automated descriptions of photos captured with a camera or a phone. This technology can potentially be used in autonomous robots and self-driving cars as well.
Scidaily.com reports that this technology performs better than the eye in terms of the range of wavelengths it can perceive, from ultraviolet to visible light and on to the infrared spectrum. The technology expands upon previous work by the research team that created brain-like devices that can enable AI to work in remote regions and space.
Review: Hands-free flight with EEGSmart’s mind-controlled UDrone
Circa 2019 😀 What a fun mind controlled toy drone 😗
How much more fun could drones be if you got fiddly hand controllers out of the way and flew them with your mind? That’s the question EEGSmart poses with its UDrone mini-quad, which responds to brainwaves and head movements instead of thumbsticks. It’s not perfect, but it does give a glimpse of a mind-controlled future.
The Udrone itself is fairly unremarkable; it’s a lightweight mini-quadcopter with 2-inch props, nice plastic bumpers to save it from damage when it bumps into a wall, and an 8-megapixel, 1080p-capable camera. You can fly it using your mobile phone, in which case it works like most similar small quads, but also has some smarts under its belt with face tracking, subject tracking and gesture recognition.
It flies for six or seven minutes on a battery, which is about right for this size of thing. The camera isn’t anything to write home about, but it streams video back to your phone in real time as long as you’re within Wi-Fi range. So far, so ordinary.

Mobile Technology and Home Broadband 2021
Smartphone ownership (85%) and home broadband subscriptions (77%) have increased among American adults since 2019 – from 81% and 73% respectively. Though modest, both increases are statistically significant and come at a time when a majority of Americans say the internet has been important to them personally. And 91% of adults report having at least one of these technologies.
A Pew Research Center survey of U.S. adults conducted from Jan. 25 to Feb. 8, 2021, also finds that some Americans have difficulties when trying to go online. Some 30% of adults say they often or sometimes experience problems connecting to the internet at home, including 9% who say such problems happen often. Still, a majority of Americans say these connection troubles occur rarely (41%) or never (21%).
While there has been slight growth in the share who say they subscribe to high-speed internet, about a quarter of the population still does not have a broadband internet connection at home. And broadband non-adopters continue to cite financial constraints as one of the most important reasons why they forgo these services. Among non-broadband users, 45% say a reason why they do not have broadband at home is that the monthly cost of a home broadband subscription is too expensive, while about four-in-ten (37%) say the same about the cost of a computer. Beyond cost barriers, a little fewer than half of non-users cite having other options for internet access or the fact that their smartphone does everything online they need as a reason why they do not have a high-speed internet connection at home.

DoD signaling demand for satellite support services in geostationary orbit
WASHINGTON — The Defense Innovation Unit is funding space projects that the agency hopes will spur commercial investments in satellite refueling technologies and support services for geostationary satellites.
“Imagine a world where every 18 to 24 months, you could simply upgrade the processor on a satellite in GEO the way that you upgrade your smartphone to take advantage of new processing power and new functionality,” said Steve “Bucky” Butow, director of the space portfolio at the Defense Innovation Unit.
DIU, based in Silicon Valley, is a Defense Department agency established in 2015 to help bring privately funded innovation into military programs.

New Android malware apps installed 10 million times from Google Play
A new batch of malicious Android apps filled with adware and malware was found on the Google Play Store that have been installed close to 10 million times on mobile devices.
The apps pose as image-editing tools, virtual keyboards, system optimizers, wallpaper changers, and more. However, their underlying functionality is to push intrusive ads, subscribe users to premium services, and steal victims’ social media accounts.
The discovery of these malicious apps comes from the Dr. Web antivirus team, who highlighted the new threats in a report published today.
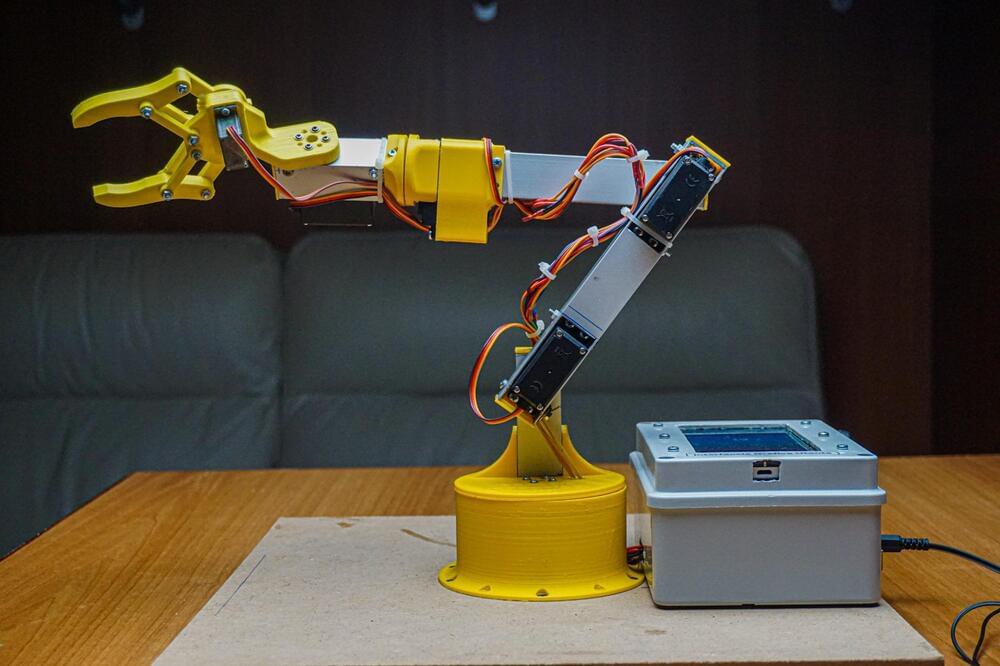
Move this custom robotic arm through a touchscreen interface
Normally, robotic arms are controlled by a GUI running on a host PC, or with some kind of analog system that maps human inputs to various degrees of rotation. However, Maurizio Miscio was able to build a custom robotic arm that is completely self-contained — thanks to a companion mobile app that resides on an old smartphone housed inside a control box.
Miscio started his project by making 3D models of each piece, most of which were 3D-printed. These included the gripper, various joints that each give a single axis of rotation, and a large circular base that acts as a stable platform on which the arm can spin. He then set to work attaching five servo motors onto each rotational axis, along with a single SG90 micro servo motor for the gripper. These motors were connected to an Arduino Uno that also had an HC-05 Bluetooth® serial module for external communication.
In order to operate the arm, Miscio developed a mobile app with the help of MIT App Inventor, which presents the user with a series of buttons that rotate a particular servo motor to the desired degree. The app even lets a series of motion be recorded and “played back” to the Uno over Bluetooth for repeated, accurate movements.
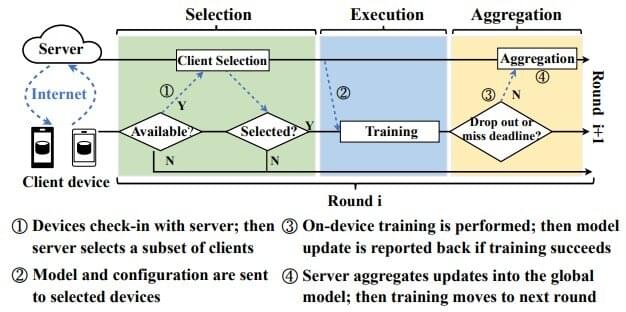
Open source platform enables research on privacy-preserving machine learning
The biggest benchmarking data set to date for a machine learning technique designed with data privacy in mind has been released open source by researchers at the University of Michigan.
Called federated learning, the approach trains learning models on end-user devices, like smartphones and laptops, rather than requiring the transfer of private data to central servers.
“By training in-situ on data where it is generated, we can train on larger real-world data,” explained Fan Lai, U-M doctoral student in computer science and engineering, who presents the FedScale training environment at the International Conference on Machine Learning this week.

Smart chip senses, stores, computes and secures data in one low-power platform
Digital information is everywhere in the era of smart technology, where data is continuously generated by and communicated among cell phones, smart watches, cameras, smart speakers and other devices. Securing digital data on handheld devices requires massive amounts of energy, according to an interdisciplinary group of Penn State researchers, who warn that securing these devices from bad actors is becoming a greater concern than ever before.
Led by Saptarshi Das, Penn State associate professor of engineering science and mechanics, researchers developed a smart hardware platform, or chip, to mitigate energy consumption while adding a layer of security. The researchers published their results on June 23 in Nature Communications.
“Information from our devices is currently stored in one location, the cloud, which is shared and stored in large servers,” said Das, who also is affiliated with the Penn State School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, the Materials Research Institute and the College of Earth and Mineral Sciences’ Department of Materials Science and Engineering. “The security strategies employed to store this information are extremely energy inefficient and are vulnerable to data breaches and hacking.”

The FBI Forced A Suspect To Unlock Amazon’s Encrypted App Wickr With Their Face
In November last year, an undercover agent with the FBI was inside a group on Amazon-owned messaging app Wickr, with a name referencing young girls. The group was devoted to sharing child sexual abuse material (CSAM) within the protection of the encrypted app, which is also used by the U.S. government, journalists and activists for private communications. Encryption makes it almost impossible for law enforcement to intercept messages sent over Wickr, but this agent had found a way to infiltrate the chat, where they could start piecing together who was sharing the material.
As part of the investigation into the members of this Wickr group, the FBI used a previously unreported search warrant method to force one member to unlock the encrypted messaging app using his face. The FBI has previously forced users to unlock an iPhone with Face ID, but this search warrant, obtained by Forbes, represents the first known public record of a U.S. law enforcement agency getting a judge’s permission to unlock an encrypted messaging app with someone’s biometrics.
According to the warrant, the FBI first tracked down the suspect by sending a request for information, via an unnamed foreign law enforcement partner, to the cloud storage provider hosting the illegal images. That gave them the Gmail address the FBI said belonged to Christopher Terry, a 53-year-old Knoxville, Tennessee resident, who had prior convictions for possession of child exploitation material. It also provided IP addresses used to create the links to the CSAM. From there, investigators asked Google and Comcast via administrative subpoenas (data requests that don’t have the same level of legal requirements as search warrants) for more identifying information that helped them track down Terry and raid his home.