The immersive tech could eventually allow park visitors to interact with Mickey Mouse and Elsa as images, not cast members in costume.
Disney is joining the metaverse party.
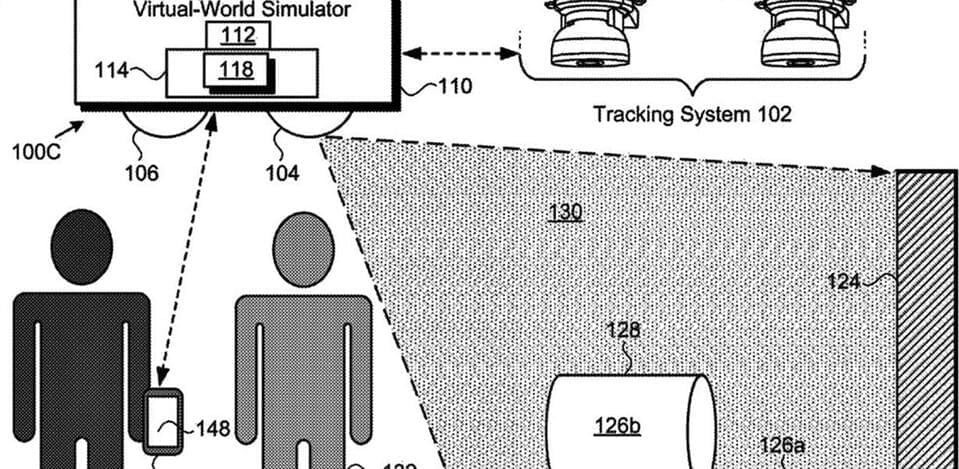
We aren’t talking online gigs or business meetings with avatars. Disney wants to enhance the virtual dimension of its theme parks with its Virtual World Simulator, new technology for which it was granted a patent in the U.S. on December 28.
The system could be used as follows: a user enters a venue or ride in which images are projected onto flat and curved surfaces, creating an immersive virtual environment. The user’s movements are tracked and the projections change accordingly, maintaining the sense of a complex, coherent world. Their shifting viewpoint is gauged with a technique called Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, or SLAM.