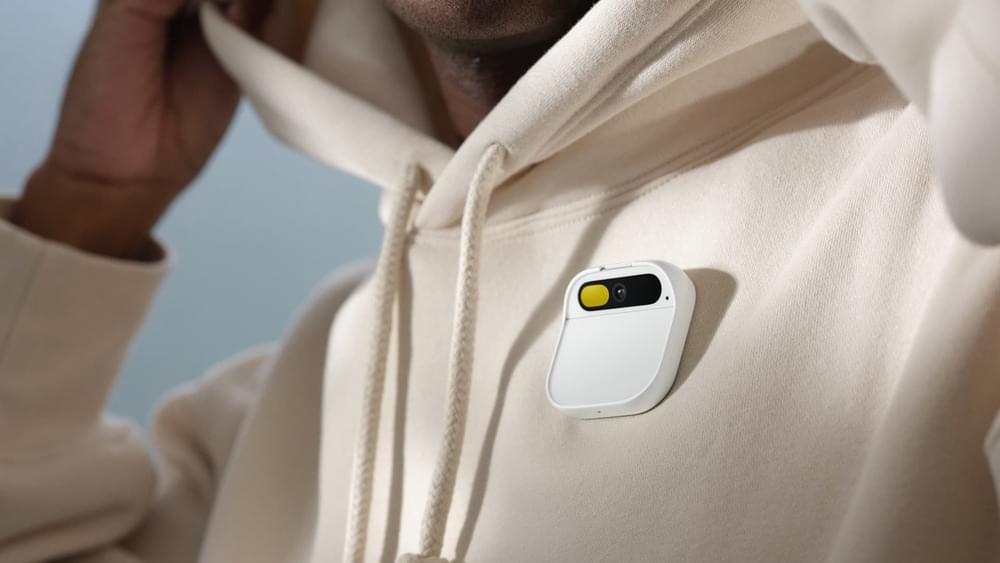
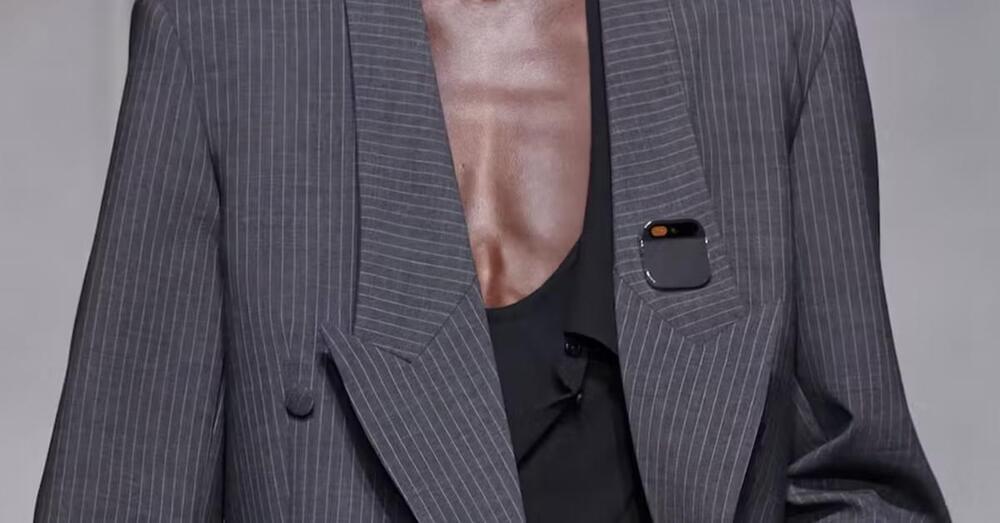
The Humane AI Pin is designed to replace your smartphone, allowing the user to make calls, send texts and look up information through voice controls. It also has a laser display, turning your palm into a mini screen that can show the time, date or what’s nearby.
“There are no wake words so it’s not always listening or always recording,” Chaudhri said at the beginning of a 10-minute launch video on the company’s website. “In fact, it doesn’t do anything until you engage with it, and your engagement comes through your voice, touch, gesture or the laser ink display.”
In addition to the upfront cost of the device, customers will have to pay a $24 monthly data subscription to T-Mobile, the company said. Having a separate phone number means that, unlike smart watches, the pin isn’t tethered to a smartphone.