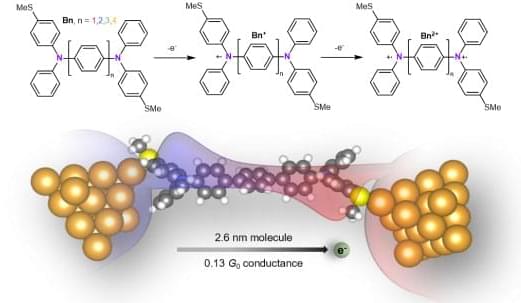
Under the direction of Latha Venkataraman, associate professor of applied physics at Columbia Engineering, researchers have designed a new technique to create a single-molecule diode, and, in doing so, they have developed molecular diodes that perform 50 times better than all prior designs. Venkataraman’s group is the first to develop a single-molecule diode that may have real-world technological applications for nanoscale devices. Their paper, “Single-Molecule Diodes with High On-Off Ratios through Environmental Control,” is published May 25 in Nature Nanotechnology.
“Our new approach created a single-molecule diode that has a high (250) rectification and a high “on” current (~ 0.1 micro Amps),” says Venkataraman. “Constructing a device where the active elements are only a single molecule has long been a tantalizing dream in nanoscience. This goal, which has been the ‘holy grail’ of molecular electronics ever since its inception with Aviram and Ratner’s 1974 seminal paper, represents the ultimate in functional miniaturization that can be achieved for an electronic device.”
With electronic devices becoming smaller every day, the field of molecular electronics has become ever more critical in solving the problem of further miniaturization, and single molecules represent the limit of miniaturization. The idea of creating a single-molecule diode was suggested by Arieh Aviram and Mark Ratner who theorized in 1974 that a molecule could act as a rectifier, a one-way conductor of electric current. Researchers have since been exploring the charge-transport properties of molecules. They have shown that single-molecules attached to metal electrodes (single-molecule junctions) can be made to act as a variety of circuit elements, including resistors, switches, transistors, and, indeed, diodes. They have learned that it is possible to see quantum mechanical effects, such as interference, manifest in the conductance properties of molecular junctions.