A cutting-edge X-ray method reveals the 3D orientation of nanoscale material structures, offering fresh insights into their functionality.
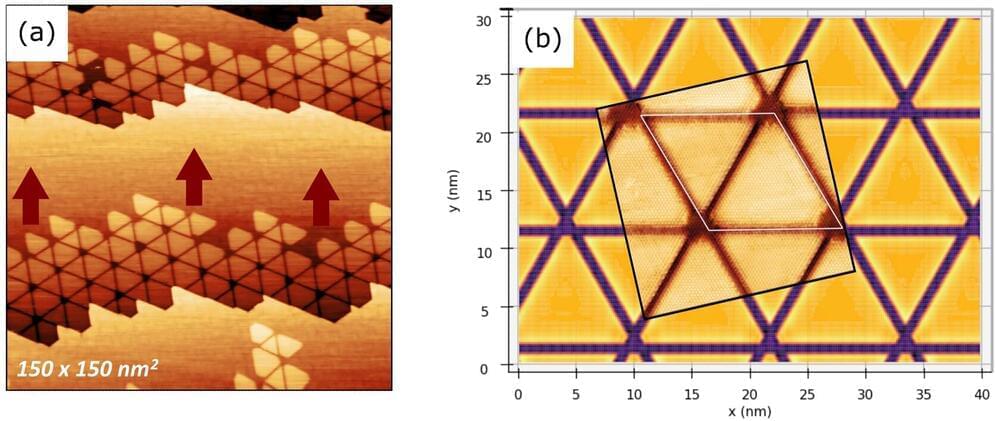
Researchers at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) have developed a groundbreaking technique called X-ray linear dichroic orientation tomography (XL-DOT). This method reveals the three-dimensional arrangement of a material’s structural building blocks at the nanoscale. Its first application focused on a polycrystalline catalyst, enabling scientists to visualize crystal grains, grain boundaries, and defects—critical features that influence catalyst performance. Beyond catalysis, XL-DOT offers unprecedented insights into the structure of various functional materials used in information technology, energy storage, and biomedical applications.