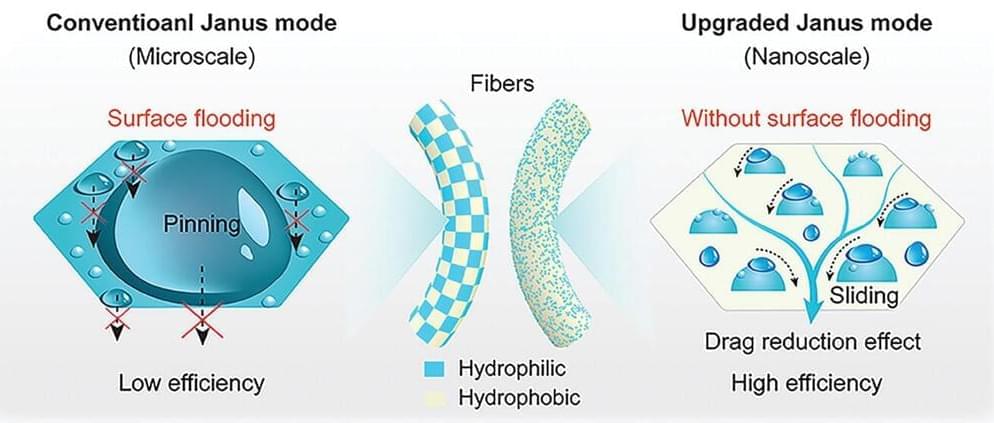
Researchers develop fibers with nanoscale surface modifications that significantly improve fog water collection rates, offering a promising solution for freshwater scarcity.


University of California, Irvine scientists recently discovered a one-dimensional nanoscale material whose color changes as temperature changes. The team’s results appeared in Advanced Materials (“Sensitive Thermochromic Behavior of InSeI, a Highly Anisotropic and Tubular 1D van der Waals Crystal”).
“We found that we can make really small and sensitive thermometers,” said Maxx Arguilla, UC Irvine professor of chemistry whose research group led the study. “It’s one of the most applied and translatable works to come out of our lab.”
Arguilla likened the thermometers to “nanoscale mood rings,” referring to the jewelry that changes color depending on the wearer’s body temperature. But instead of simply taking a qualitative temperature reading, the changes in the color of these materials “can be calibrated and used to optically take temperature readings at the nanoscale,” Arguilla said.
“This breakthrough helps us better understand and study the fascinating world of quantum physics,” he says.
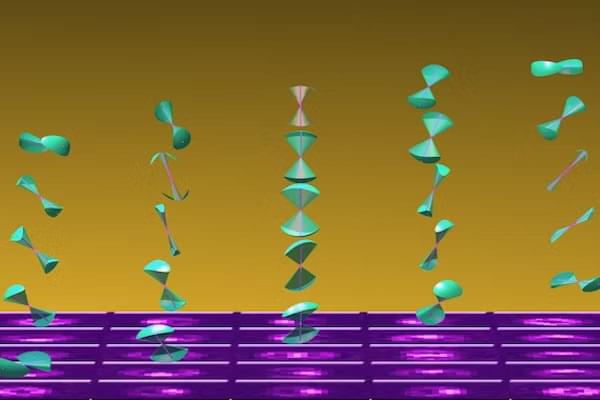
The fluorescent nanodiamonds, with an average diameter of about 750 nm, were produced through high-pressure, high-temperature synthesis. These diamonds were irradiated with high-energy electrons to create nitrogen-vacancy color centers, which host electron spin qubits.
When illuminated by a green laser, they emitted red light, which was used to read out their electron spin states. An additional infrared laser was shone at the levitated nanodiamond to monitor its rotation. Like a disco ball, as the nanodiamond rotated, the direction of the scattered infrared light changed, carrying the rotation information of the nanodiamond.
A new publication has discovered ways to reduce the toxicity of graphene oxide (GO), an ultra-thin sheet of nanomaterial derived from graphite, laying the groundwork to use it as a drug delivery system.
Professor Khuloud Al-Jamal, who led the study, said: “Researchers have been incredibly excited in the potential medical applications of graphene since experiments into the nanomaterial were recognised with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010. However, concerns around toxicity have remained a consistent obstacle.”
Graphene oxide (GO) is an ultra-thin sheet derived from graphite. It is similar to pencil lead but includes attached oxygen atoms, making it compatible with water. Its unique physical and chemical properties mean it has a high capacity for carrying antibiotics and anticancer drugs, among others, as well as targeting specific cells, making it a potentially effective drug delivery system.

Nanomaterials, with their distinctive physical and chemical properties, hold significant promise for revolutionizing the housing construction industry. By enabling the development of stronger, more durable, efficient, and sustainable structures, nanotechnology offers solutions to challenges such as climate change and global urbanization.
The use of nanomaterials in construction began in the mid-1980s with the advent of carbon-based structures. Since then, their application has become more widespread, driving innovations in the sector. Today, advances in nanotechnology are leading to the creation of increasingly sophisticated, selective, and efficient nanomaterials, broadening the scope of construction capabilities.
This study explored the application of various nanomaterials—titanium dioxide, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), nanosilica, nanocellulose, nanoalumina, and nanoclay—in residential construction. These materials were chosen for their potential to enhance the structural integrity, thermal performance, and overall functionality of building materials used in housing.

With inventions like a nanomaterial-based battery for IoT and nanoscale transistors, the future of nanotechnology in this field seems to have potential. For now, any large-scale applications are likely years away. Companies must overcome technical, cost, and implementation hurdles before progressing to mass-market applications.
However, numerous nanoscale-sized discoveries and inventions will likely emerge in the coming years. As the value of nanotechnologies and IoT continue increasing, more investors, business owners, and researchers will explore possible use cases. While their inventions may not hit shelves for years, their development speed will surely accelerate.
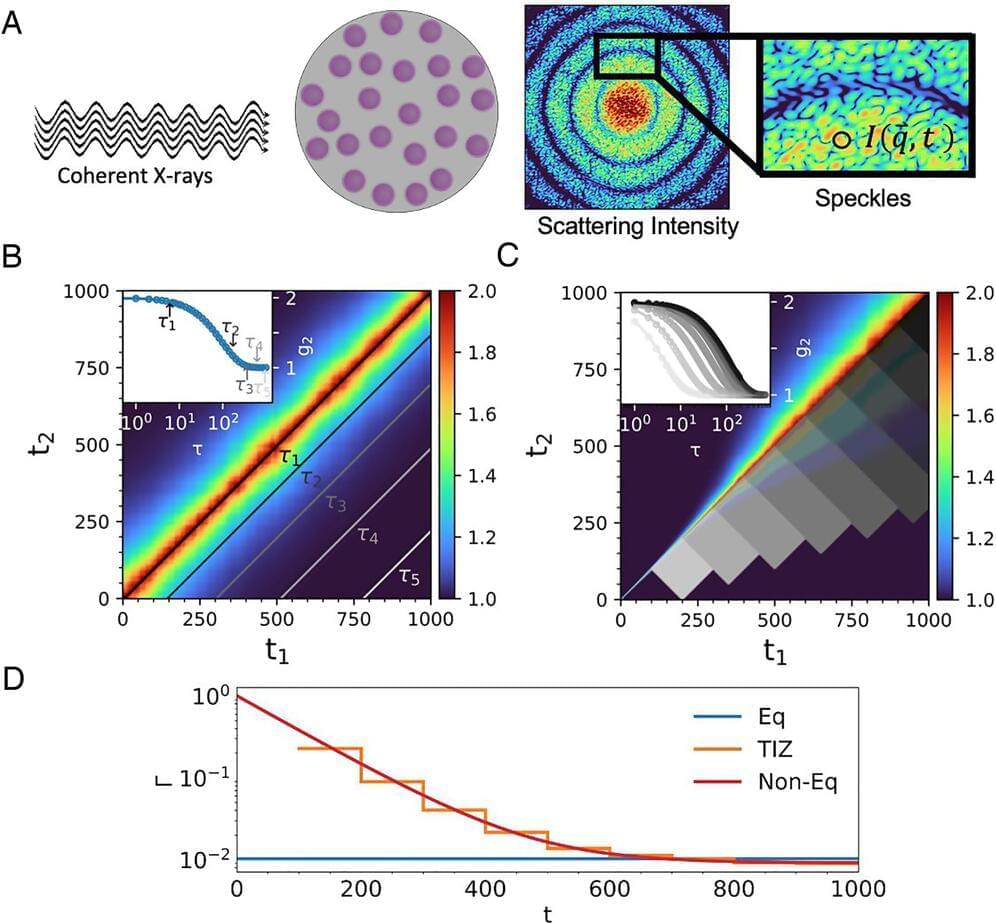
While new technologies, including those powered by artificial intelligence, provide innovative solutions to a steadily growing range of problems, these tools are only as good as the data they’re trained on. In the world of molecular biology, getting high-quality data from tiny biological systems while they’re in motion – a critical step for building next-gen tools – is something like trying to take a clear picture of a spinning propeller. Just as you need precise equipment and conditions to photograph the propeller clearly, researchers need advanced techniques and careful calculations to measure the movement of molecules accurately.
Matthew Lew, associate professor in the Preston M. Green Department of Electrical & Systems Engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, builds new imaging technologies to unravel the intricate workings of life at the nanoscale. Though they’re incredibly tiny – 1,000 to 100,000 times smaller than a human hair – nanoscale biomolecules like proteins and DNA strands are fundamental to virtually all biological processes.
Scientists rely on ever-advancing microscopy methods to gain insights into these systems work. Traditionally, these methods have relied on simplifying assumptions that overlook some complexities of molecular behavior, which can be wobbly and asymmetric. A new theoretical framework developed by Lew, however, is set to shake up how scientists measure and interpret wobbly molecular motion.
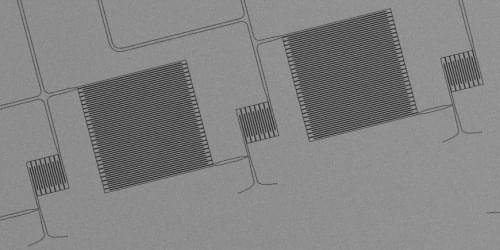
Single-photon detectors built from superconducting nanowires have become a vital tool for quantum information processing, while their superior speed and sensitivity have made them an appealing option for low-light imaging applications such as space exploration and biophotonics. However, it has proved difficult to build high-resolution cameras from these devices because the cryogenically cooled detectors must be connected to readout electronics operating at room temperature. Now a research team led by Karl Berggren at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology has demonstrated a superconducting electronics platform that can process the single-photon signals at ultracold temperatures, providing a scalable pathway for building megapixel imaging arrays [1].
The key problem with designing high-resolution cameras based on these superconducting detectors is that each of the sensors requires a dedicated readout wire to record the single-photon signals, which adds complexity and heat load to the cryogenic system. Researchers have explored various multiplexing techniques to reduce the number of connections to individual detectors, yielding imaging arrays in the kilopixel range, but further scaling will likely require a signal-processing solution that can operate at ultralow temperatures.
Berggren and his collaborators believe that the answer lies in devices called nanocryotrons (nTrons), which are three-terminal structures made from superconducting nanowires, just like the single-photon detectors are. Although nTrons do not deliver the same speed and power of superconducting electronics based on Josephson junctions, the researchers argue that these shortcomings are not a critical problem in photon-sensing applications, where the detectors are similarly limited in speed and power. The nTrons also offer several advantages over Josephson junctions: they operate over a wider range of cryogenic temperatures, they don’t require magnetic shielding, and they exploit the same fabrication process as that used for the detectors, allowing for easy on-chip integration.