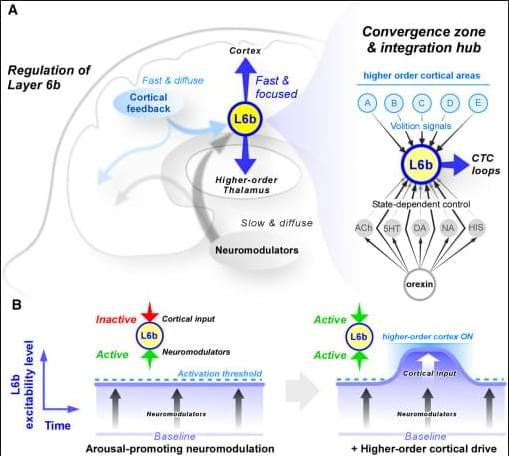
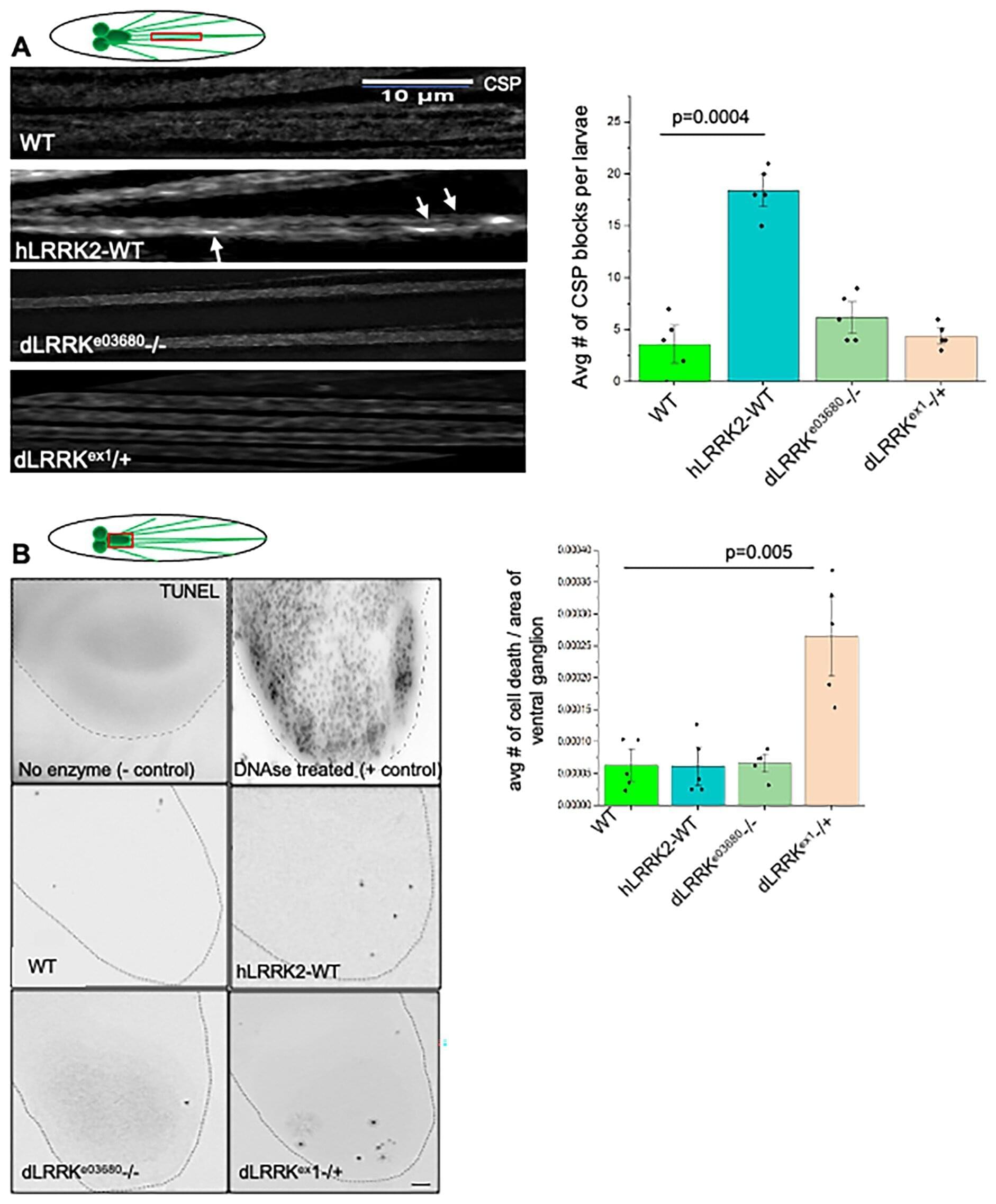
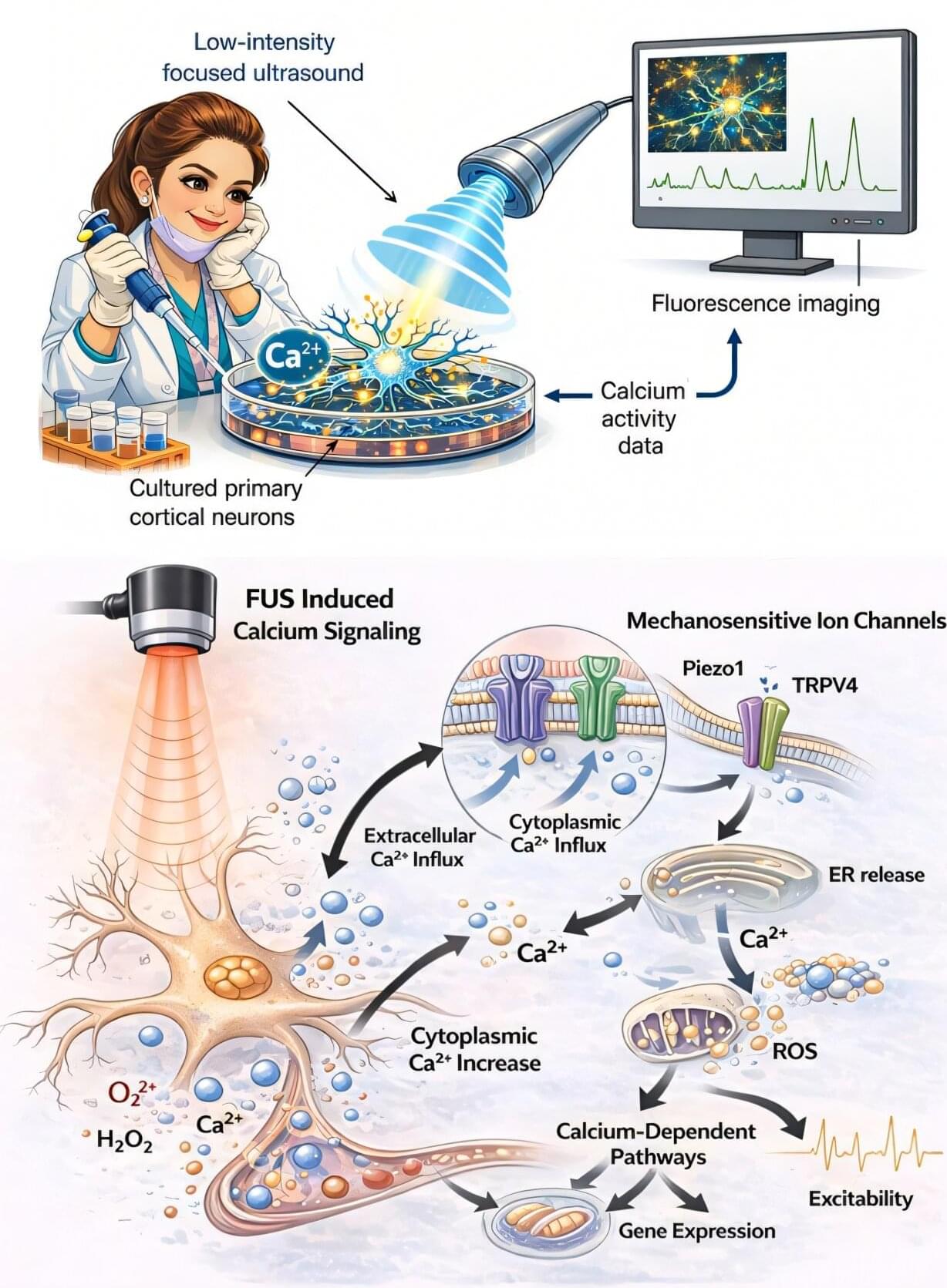
Although the technology has been around for several years, it has not yet become a standard tool in neuroscience research. Now, two researchers at MIT are preparing new experiments using the technique and have published a paper that serves as a detailed guide, or “roadmap,” for applying it to the study of consciousness.
“Transcranial focused ultrasound will let you stimulate different parts of the brain in healthy subjects, in ways you just couldn’t before,” says Daniel Freeman, an MIT researcher and co-author of the paper. “This is a tool that’s not just useful for medicine or even basic science, but could also help address the hard problem of consciousness. It can probe where in the brain are the neural circuits that generate a sense of pain, a sense of vision, or even something as complex as human thought.”
Unlike other brain stimulation methods, transcranial focused ultrasound does not require surgery. It can reach deeper areas of the brain with greater precision than techniques such as transcranial magnetic or electrical stimulation.