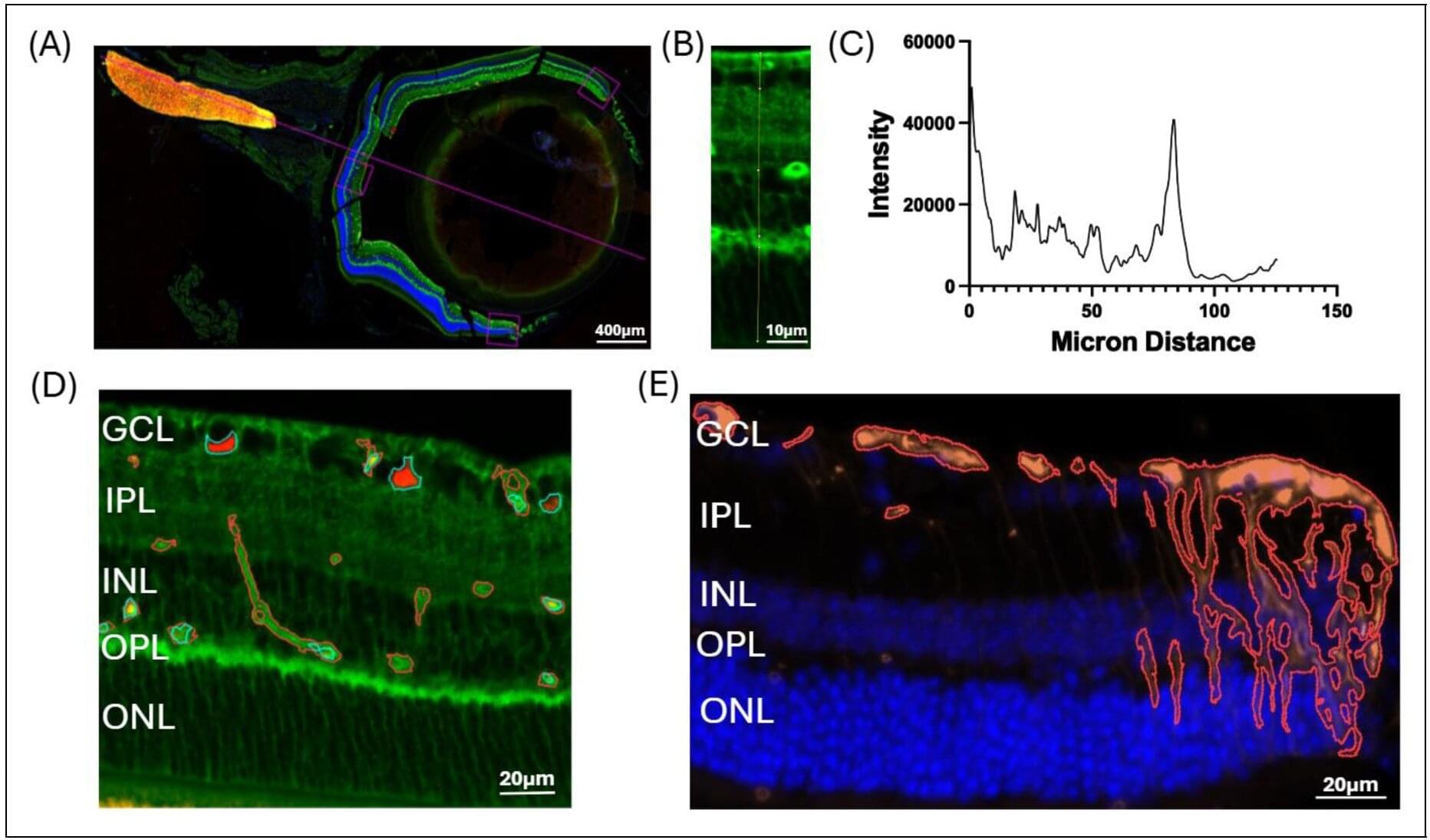
Periods of prolonged social isolation have long been associated with difficult emotions and, in some cases, with the emergence of psychiatric symptoms, such as depression, anxiety, and difficulties connecting with others. Some past psychology studies have suggested that chronic isolation during adolescence, the critical stage between childhood and adulthood, can disrupt the structure and functioning of a brain region known as the prefrontal cortex (PFC).
The PFC is known to play a critical role in various mental functions, including decision-making and the regulation of emotions. Disruptions to this brain region could thus explain the emotional and social difficulties experienced by many people after long periods of isolation.
Researchers at University of Electronic Science and Technology of China and other institutes recently carried out a study involving mice that investigated the potential of oxytocin (OXT), a hormone released when bonding or cuddling with others, as a therapeutic target for the mental health symptoms arising from chronic isolation. Their findings, published in Translational Psychiatry, suggest that this hormone could reverse some of the adverse effects of prolonged isolation.