Regular use of math and reading skills could prevent cognitive decline with age, according to a new Science Advances study.
Cognitive skills of the population such as literacy and numeracy are important not only for individual incomes but also for the economic growth of nations (2–6). As a result, the aging of world populations presents an economic concern if the commonly assumed declines of these skills with age hold.
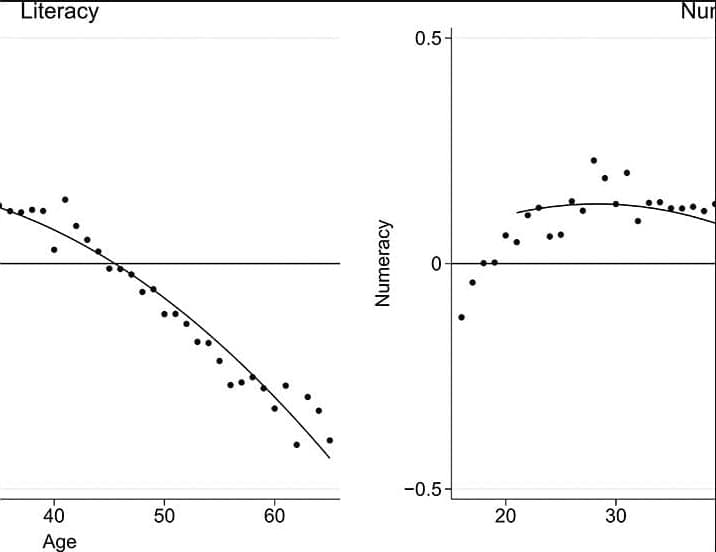
We use longitudinal variation in individual literacy and numeracy skills for a representative adult sample to create age-skill profiles that credibly separate age from cohort effects. The pure age component that we derive provides a different perspective on the impacts of aging populations. Overall, our results are not consistent with a view that a natural law dictates an inevitable decline in these skills with age. Potential cognitive declines only occur at later ages and are not inevitable with usage of skills.
This is consolation for countries with aging populations, but avoidance of skill losses is not automatic and appears related to stimulation from skill usage. These results thus suggest that age-skill relationships of adults deserve policy attention, consistent with concerns about the necessity of lifelong learning.