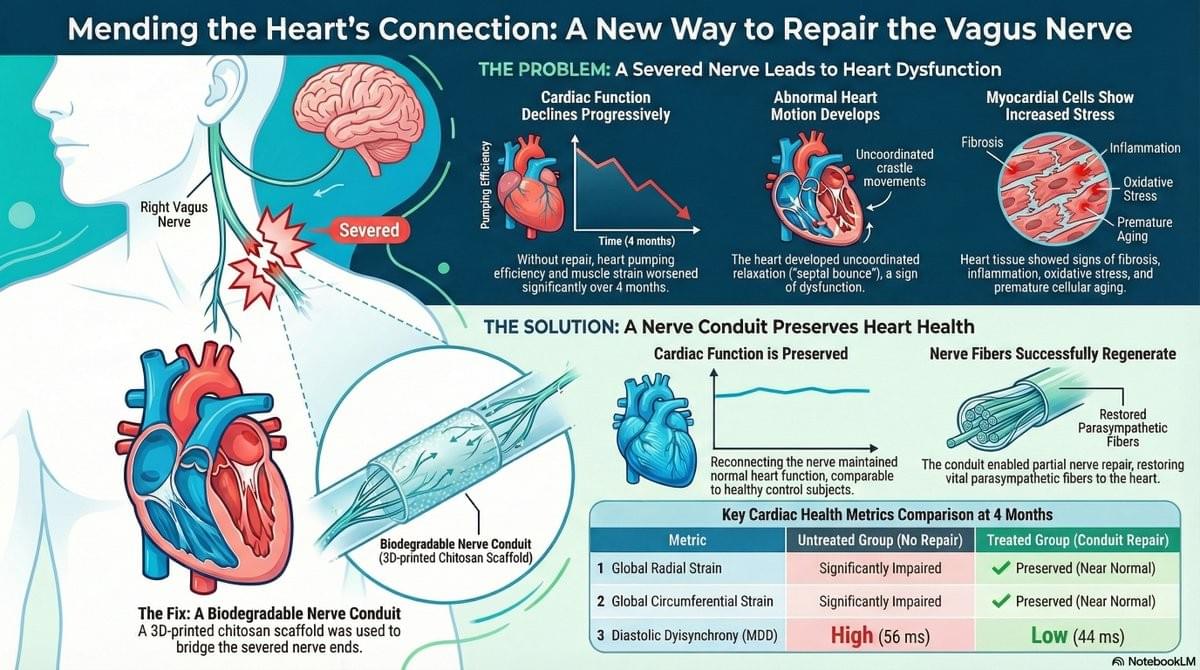
The secret to a healthier and “younger” heart lies in the vagus nerve. A recent study published in Science Translational Medicine has shown that preserving bilateral cardiac vagal innervation is an anti-aging factor. In particular, the right cardiac vagus nerve emerges as a true guardian of cardiomyocyte health, helping to preserve the longevity of the heart independently of heart rate.
‘When the integrity of the connection to the vagus nerve is lost, the heart ages more rapidly,’ explains the senior author.
‘Even partial restoration of the connection between the right vagus nerve and the heart is sufficient to counteract the mechanisms of remodelling and preserve effective cardiac contractility,’ adds another author.
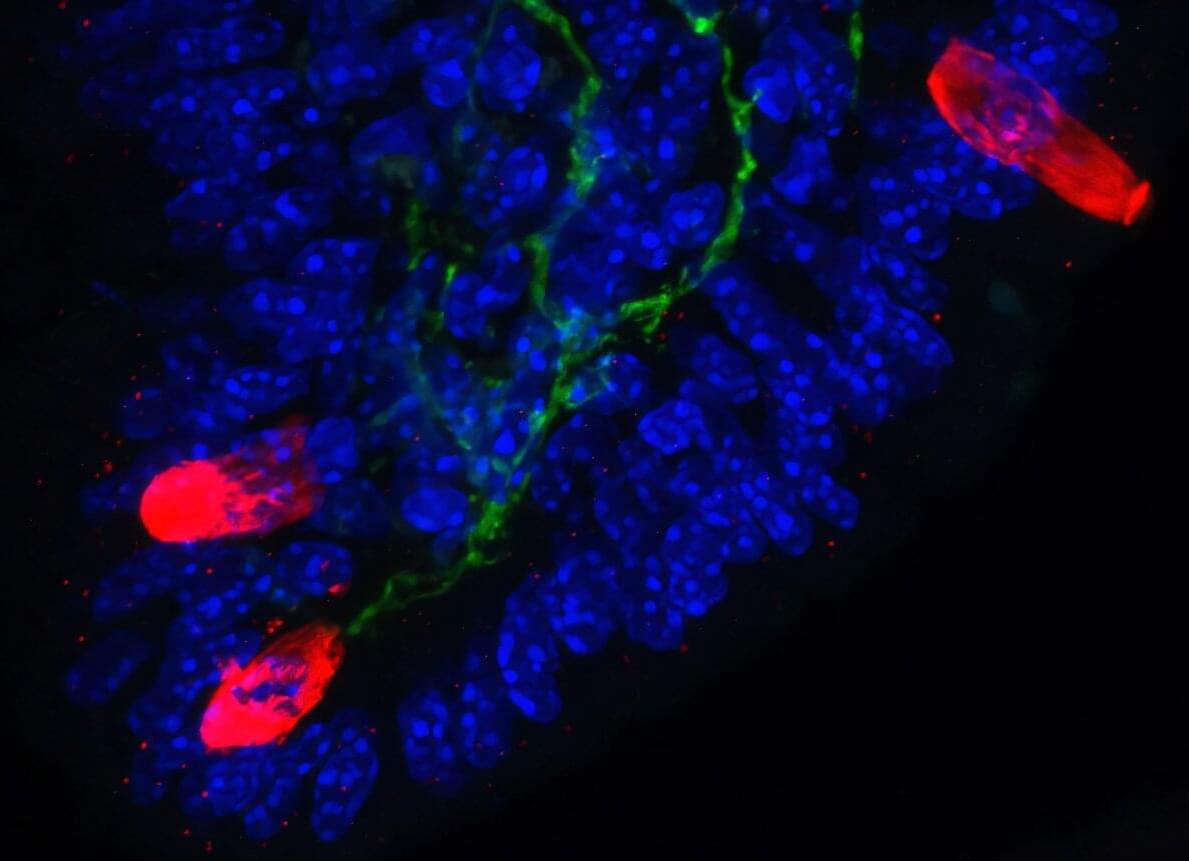
‘We have developed an implantable bioabsorbable nerve conduit designed to promote and guide the spontaneous regeneration of the thoracic vagus nerve at the cardiac level,’ explains a co-author.
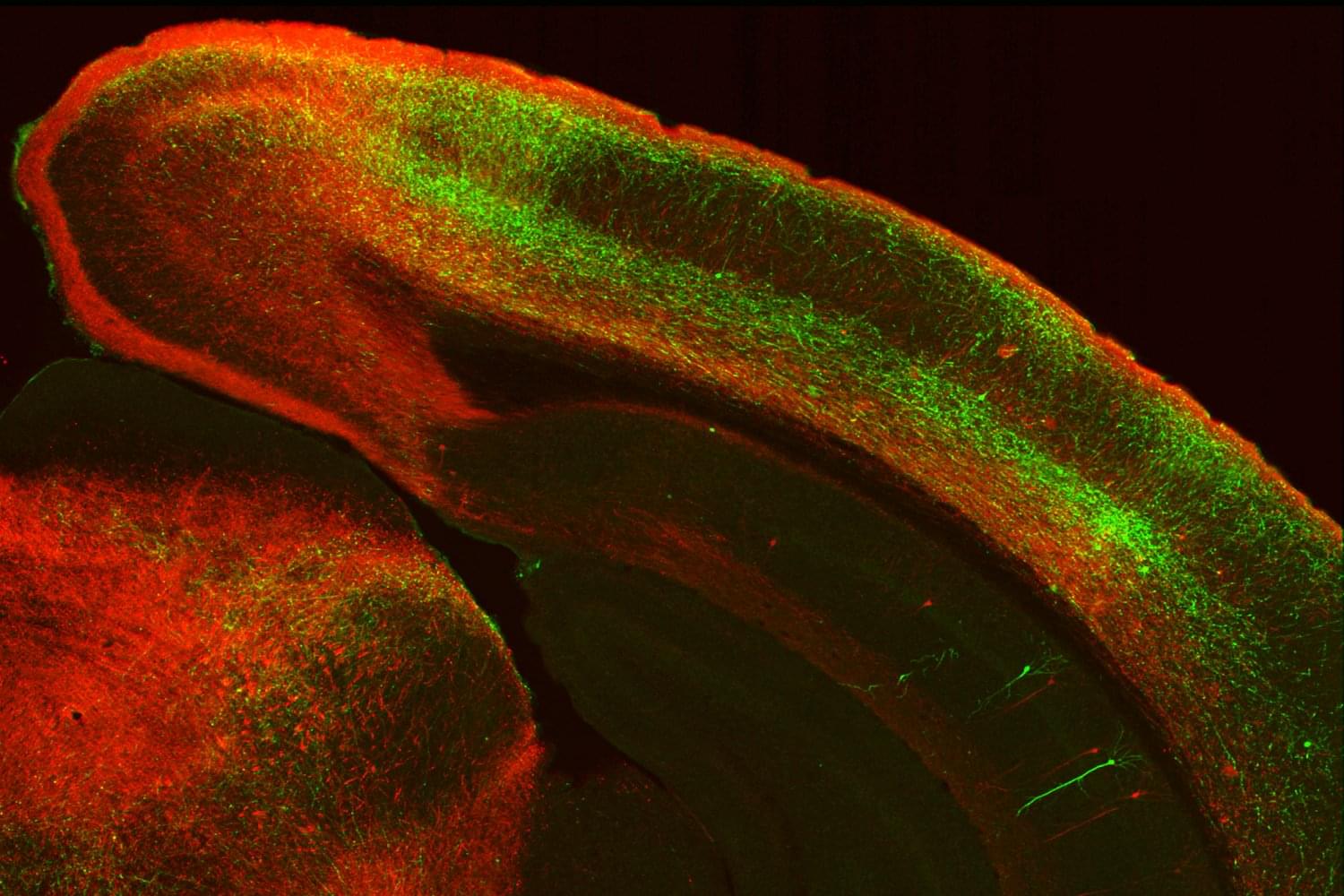
Treated adult male minipigs displayed improved global circumferential, longitudinal, and radial strains and reduced diastolic dyssynchrony. Histological analysis revealed partial repair with about 20% viable vagal fascicles, restoration of myocardial parasympathetic fibers, normalization of oxidative stress and aging markers, and prevention of interstitial fibrosis.