Whether in the brain or in the muscles, wherever there are nerve cells, there are synapses. These contact points between neurons form the basis for the transmission of excitation, the communication between neurons. As in any communication process, there is a sender and a receiver: Nerve cell processes called axons generate and transmit electrical signals thereby acting as signal senders.
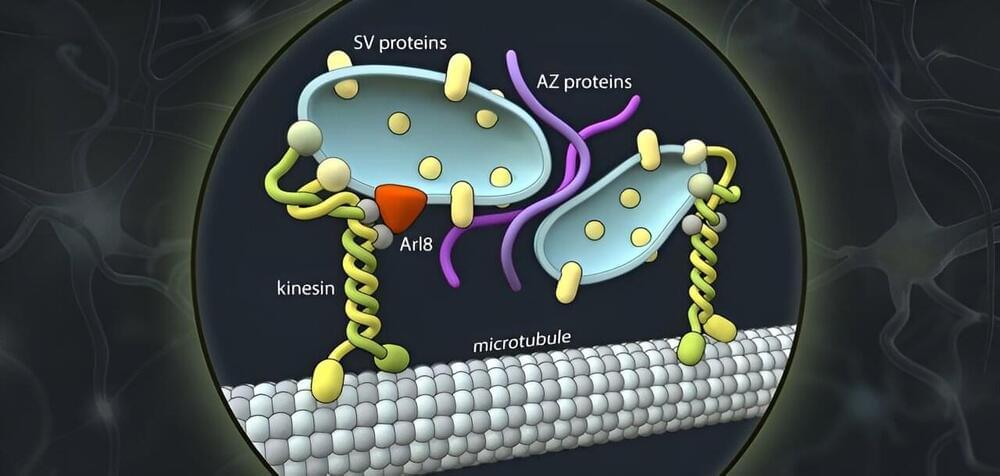
Synapses are points of contact between axonal nerve terminals (the pre-synapse) and post-synaptic neurons. At these synapses, the electrical impulse is converted into chemical messengers that are received and sensed by the post-synapses of the neighboring neuron. The messengers are released from special membrane sacs called synaptic vesicles.
As well as transmitting information, synapses can also store information. While the structure and function of synapses are comparably well understood, little is known about how they are formed.