Scientists created a map of an entire larval fruit fly brain that shows all 548,000 synapses in the organ.


The future of computing includes biology says an international team of scientists.
The time has come to create a new kind of computer, say researchers from John Hopkins University together with Dr. Brett Kagan, chief scientist at Cortical Labs in Melbourne, who recently led development of the DishBrain project, in which human cells in a petri dish learned to play Pong.
In an article published on February 27 in the journal Frontiers in Science, the team outlines how biological computers could surpass today’s electronic computers for certain applications while using a small fraction of the electricity required by today’s computers and server farms.


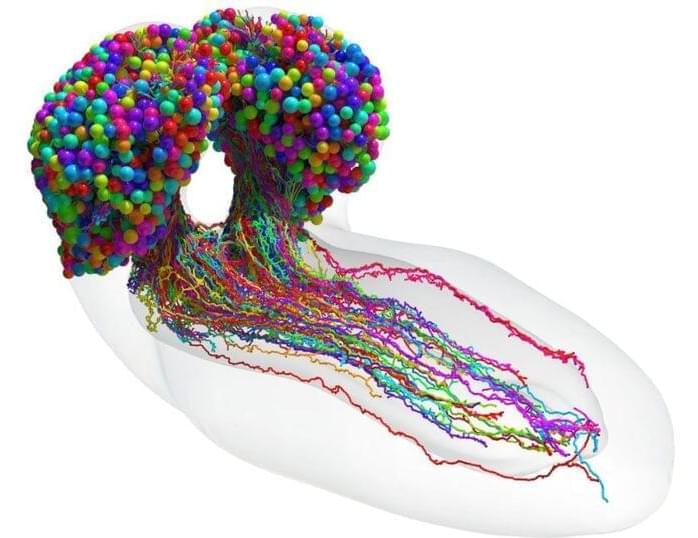
Summary: A newly constructed brain map shows every single neuron and how they are wired together in the brains of fruit fly larvae.
Source: UK Research and Innovation.
Researchers have built the first ever map showing every single neuron and how they’re wired together in the brain of the fruit fly larva.
A pilot trial by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, tested the nasal administration of the drug Foralumab, an anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody. Investigators found evidence that the drug dampened the inflammatory T cell response and decreased lung inflammation in patients with COVID-19. Further analysis showed the same gene expression modulation in patients with multiple sclerosis, who experienced decreased brain inflammation, suggesting that Foralumab could be used to treat other diseases. Their results are published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“We discovered a way to shut down inflammation not only seen in COVID-19, but also in a patient with multiple sclerosis as well as in healthy patients,” said lead author Thais Moreira, Ph.D., an assistant scientist at the Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases at BWH and an instructor in Neurology at Harvard Medical School. “This is very exciting because not only does our study suggest that this new monoclonal antibody drug is safe and can modulate the immune system without major side effects, but it can also decrease inflammation in multiple realms, so it may be useful for treating other diseases.”
“Inflammation is a major cause of many diseases,” said senior author Howard Weiner, MD, founder and director of the Brigham Multiple Sclerosis Center and co-director of the Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases. “Our center has spent decades looking for novel ways to treat disease where there is abnormal inflammation in a way that is safe and effective.”
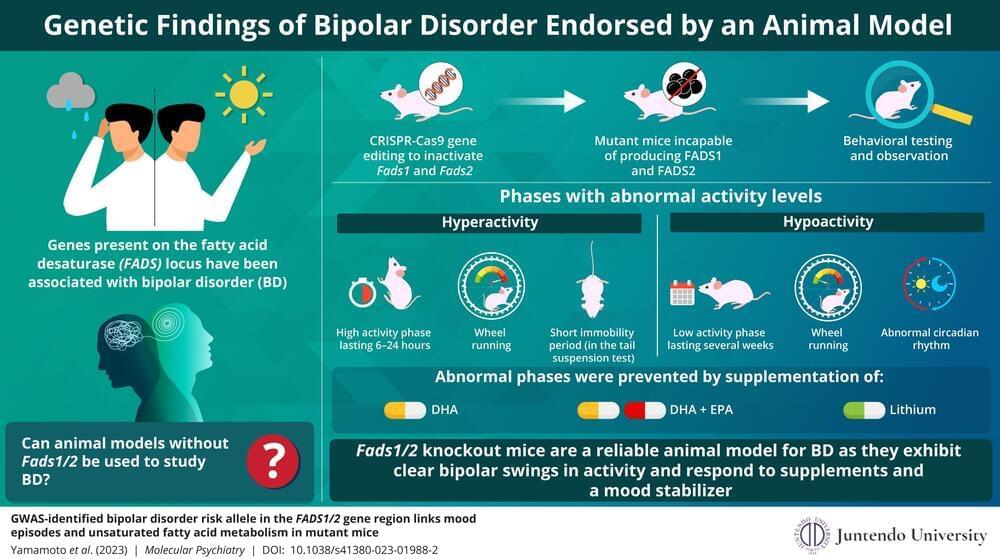
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a debilitating condition characterized by alternating states of depression (known as depressive episodes) and abnormal excitement or irritability (known as manic episodes). Large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have revealed that variations in the genes present on the fatty acid desaturase (FADS) locus are linked to an increased risk of BD.
Enzymes coded by FADS genes—FADS1 and FADS2—convert or “biosynthesize” omega-3 fatty acids into the different forms required by the human body. Omega-3 fatty acids like eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are crucial for the brain to function, and a reduction in the synthesizing activity of these molecules seems to increase susceptibility to bipolar mood swings.
Research on most diseases involves establishment of an animal model of the disease. So, keeping this knowledge in mind, a team of researchers including Dr. Takaoki Kasahara and Hirona Yamamoto from RIKEN Brain Science Institute and Dr. Tadafumi Kato from Juntendo University in Japan, used CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing to create mutant mice that lack both Fads1 and Fads2 genes.
Ziqiang zhang*, long zhou*, chengyi wang, sanyuan chen, yu wu, shujie liu, zhuo chen, yanqing liu, huaming wang, jinyu li, lei he, sheng zhao, furu wei.
Microsoft
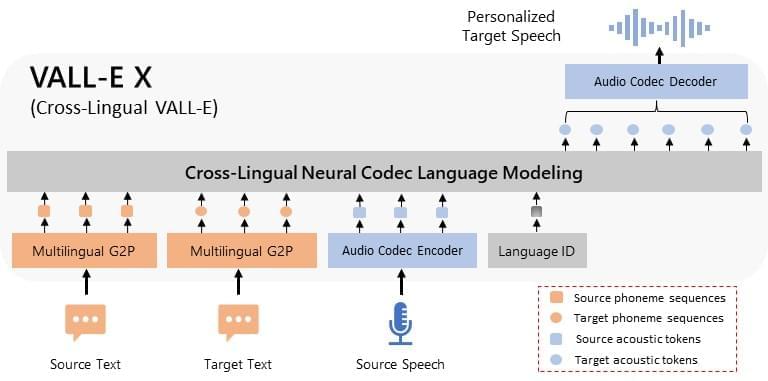
Abstract. We propose a cross-lingual neural codec language model, VALL-E X, for cross-lingual speech synthesis. Specifically, we extend VALL-E and train a multi-lingual conditional codec language model to predict the acoustic token sequences of the target language speech by using both the source language speech and the target language text as prompts. VALL-E X inherits strong in-context learning capabilities and can be applied for zero-shot cross-lingual text-to-speech synthesis and zero-shot speech-to-speech translation tasks. Experimental results show that it can generate high-quality speech in the target language via just one speech utterance in the source language as a prompt while preserving the unseen speaker’s voice, emotion, and acoustic environment. Moreover, VALL-E X effectively alleviates the foreign accent problems, which can be controlled by a language ID.
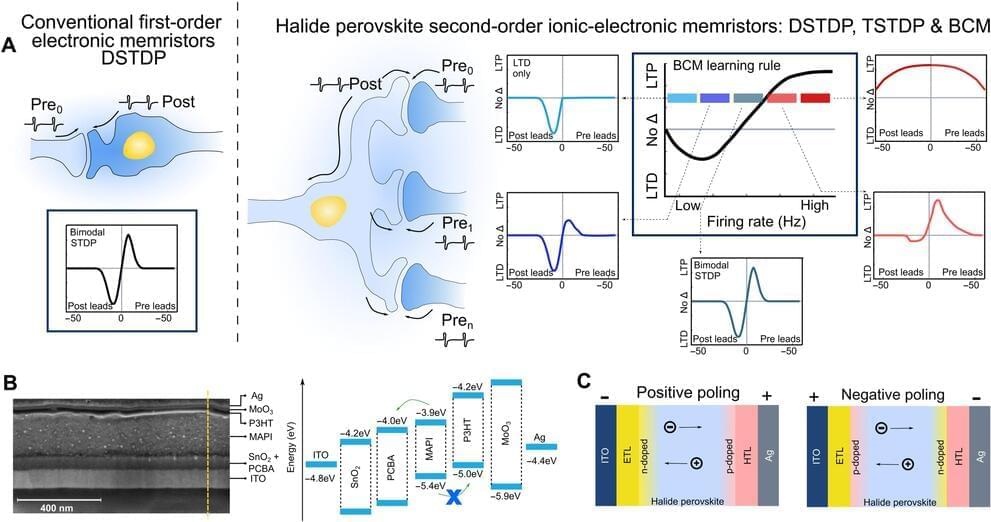
Researchers at Empa, ETH Zurich and the Politecnico di Milano are developing a new type of computer component that is more powerful and easier to manufacture than its predecessors. Inspired by the human brain, it is designed to process large amounts of data fast and in an energy-efficient way.
In many respects, the human brain is still superior to modern computers. Although most people can’t do math as fast as a computer, we can effortlessly process complex sensory information and learn from experiences, while a computer cannot—at least not yet. And, the brain does all this by consuming less than half as much energy as a laptop.
One of the reasons for the brain’s energy efficiency is its structure. The individual brain cells—the neurons and their connections, the synapses—can both store and process information. In computers, however, the memory is separate from the processor, and data must be transported back and forth between these two components. The speed of this transfer is limited, which can slow down the whole computer when working with large amounts of data.
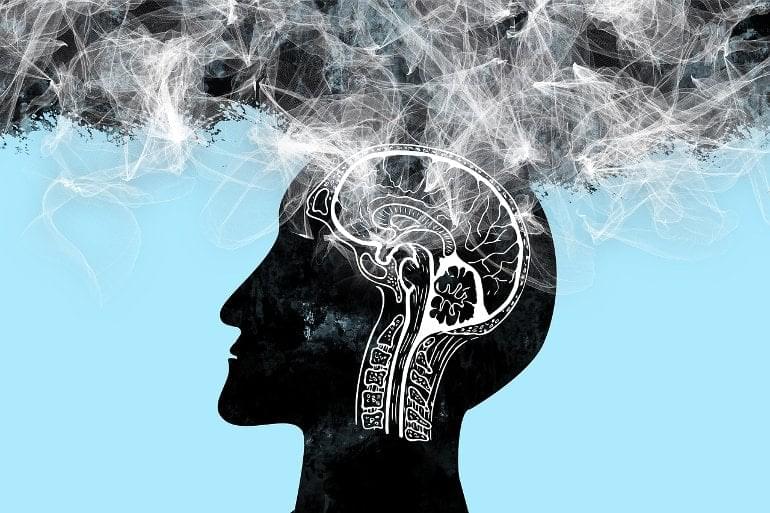

Summary: As the brain ages, microglia adopt dysfunctional states that increase the risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Source: TCD
Scientists from the Trinity Biomedical Sciences Institute (TBSI) have shed new light on aging processes in the brain. By linking the increased presence of specialised immune cells to conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and traumatic brain injury for the first time, they have unearthed a possible new target for therapies aimed at treating age-related neurological diseases.
Human enhancement has long been depicted as having the potential to help but also harm humanity. Brian Greene talks with Neuroscientists Takao Hensch, John Krakauer and Entrepreneur Brett Wingeier about their experiments using brain plasticity to heal illness, improve cognitive and athletic performance. They also raise warning flags about the race to build a more perfect human.
This program is part of the Big Ideas series, supported by the John Templeton Foundation.
Participants:
John Krakauer.
Takao Hensch.
Brett Wingeier.
Moderator:
Brian Greene.
SHARE YOUR THOUGHTS on this program through a short survey:
https://survey.alchemer.com/s3/7242995/Rewriting-the-Brain.
WSF Landing Page Link: https://www.worldsciencefestival.com/programs/rewiring-the-b…lasticity/