The largest genetic study of delirium shows that APOE ε4 increases delirium susceptibility even without dementia. Researchers identified shared risk loci with Alzheimer’s disease and blood proteins that predict delirium up to 16 years earlier.



In a new study, published in JAMA Network Open, 295 participants report promising mental health benefits after reducing their social media usage for a week. The cohort consisted of young adults from the ages of 18 to 24—the age group commonly associated with the highest social media usage, as well as a heightened risk of mental health issues.
Although many self-reports have surfaced online indicating that reducing social media use has been beneficial in various ways, the scientific link between social media use and youth mental health is still debated, with past studies showing mixed results.

Researchers at Karolinska Institutet, Columbia University and the University of San Francisco, have uncovered a previously unknown mechanism by which dopamine, a key brain chemical vital for movement and motivation, can affect brain activity indirectly by boosting serotonin. The study was published in Science Advances.
Dopamine is a key chemical messenger that supports many essential brain functions, including motivation, movement, and learning. Although dopamine acts throughout the brain, it plays an especially central role in the basal ganglia, a network of interconnected regions responsible for selecting which behaviors we express.
The basal ganglia and dopamine are deeply involved in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases, and many widely used medications target this network.

Whether great minds think alike is up for debate, but the collaborating minds of two people working on a shared task process information alike, according to a study published in PLOS Biology by Denise Moerel and colleagues from Western Sydney University in Australia.
Humans rely on collaboration for everything from raising food to raising children. But to cooperate successfully, people need to make sure that they are seeing the same things and working within the same rules. We must agree that the red fruits are the ones that are ripe and that we will leave green fruits alone.
Behavioral collaboration requires that people think in the same way and follow the same instructions. To better understand people’s cognitive processes during a shared task, the authors of this study collected data from 24 pairs of people.
Researchers found that mothers with untreated or persistent thyroid hormone imbalance across pregnancy face a higher chance of having children diagnosed with autism.
The study also revealed that longer periods of imbalance led to higher autism rates in offspring. The results emphasize the importance of frequent thyroid monitoring.
Thyroid imbalance in pregnancy linked to higher autism risk.

Biomedical researchers at Texas A&M University may have discovered a way to stop or even reverse the decline of cellular energy production—a finding that could have revolutionary effects across medicine.
Dr. Akhilesh K. Gaharwar and Ph.D. student John Soukar, along with their fellow researchers from the Department of Biomedical Engineering, have developed a new method to give damaged cells new mitochondria, returning energy output to its previous levels and dramatically increasing cell health.
Mitochondrial decline is linked to aging, heart disease and neurodegenerative disorders. Enhancing the body’s natural ability to replace worn-out mitochondria could fight all of them.
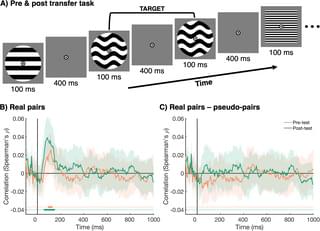
How do brains align during social interaction to support shared understanding? This study shows that interbrain information alignment emerges rapidly and strengthens with practice, with distinct neural processes supporting sensory synchrony during early alignment and shared cognitive representation in real pairs during late alignment.