Researchers found that prescription stimulants for ADHD act on brain networks that control wakefulness and reward, but not attention as previously thought.



Mass General Brigham investigators have developed a robust new artificial intelligence (AI) foundation model that is capable of analyzing brain MRI datasets to perform numerous medical tasks, including identifying brain age, predicting dementia risk, detecting brain tumor mutations and predicting brain cancer survival. The tool, known as BrainIAC, outperformed other, more task-specific AI models and was especially efficient when limited training data were available.
Results are published in Nature Neuroscience.
“BrainIAC has the potential to accelerate biomarker discovery, enhance diagnostic tools and speed the adoption of AI in clinical practice,” said corresponding author Benjamin Kann, MD, of the Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (AIM) Program at Mass General Brigham. “Integrating BrainIAC into imaging protocols could help clinicians better personalize and improve patient care.”
For decades, researchers have attempted to pinpoint the specific areas of the brain responsible for human intelligence. A new analysis suggests that general intelligence involves the coordination of the entire brain rather than the superior function of any single region. By mapping the connections within the human brain, or connectome, scientists found that distinct patterns of global communication predict cognitive ability.
The research indicates that intelligent thought relies on a system-wide architecture optimized for efficiency and flexibility. These findings were published in the journal Nature Communications.
General intelligence represents the capacity to reason, learn, and solve problems across a variety of different contexts. In the past, theories often attributed this capacity to specific networks, such as the areas in the frontal and parietal lobes involved in attention and working memory. While these regions are involved in cognitive tasks, newer perspectives suggest they are part of a larger story.

Ciaran O’Hare scribbles symbols using colored markers across his whiteboard like he’s trying to solve a crime—or perhaps planning one. He bounces around the edges of the board, slowly filling it with sharp angles and curling letters. I watch on, and when he senses I’m losing track, he pauses intermittently, allowing my brain to catch up. Ciaran speaks with an easy to understand British inflection, but the language on the whiteboard might as well be hieroglyphics.
Ciaran’s whiteboard doesn’t lay out a crime, but a mystery in the language of physics. In plain language, the mystery goes like this: everything we can see—with our eyes or elaborate telescopes—makes up only around 5% of the matter in our universe. There’s an invisible something out there that seems to bind the fabric of spacetime together. We don’t know what it is, but we know it’s there because of the force it exerts on the things we can see such as gigantic galaxies. The “something” is a phantom presence that touches our reality.
Scientists call it dark matter.

We’ve all heard the best approach to solve a problem is to “sleep on it.” It turns out there may be more truth to this adage than previously thought. While stories abound of eureka moments surfacing from dreams, scientific evidence has remained elusive, due to the challenge of systematically manipulating dreams.
A new study by neuroscientists at Northwestern University validates the possibility of influencing dreams and offers a crucial step to support the theory that dreams in REM sleep—the rapid eye movement phase of sleep in which lucid dreaming can occur—may be especially conducive to helping individuals come up with creative solutions to a problem.
The study has been published in the journal Neuroscience of Consciousness.
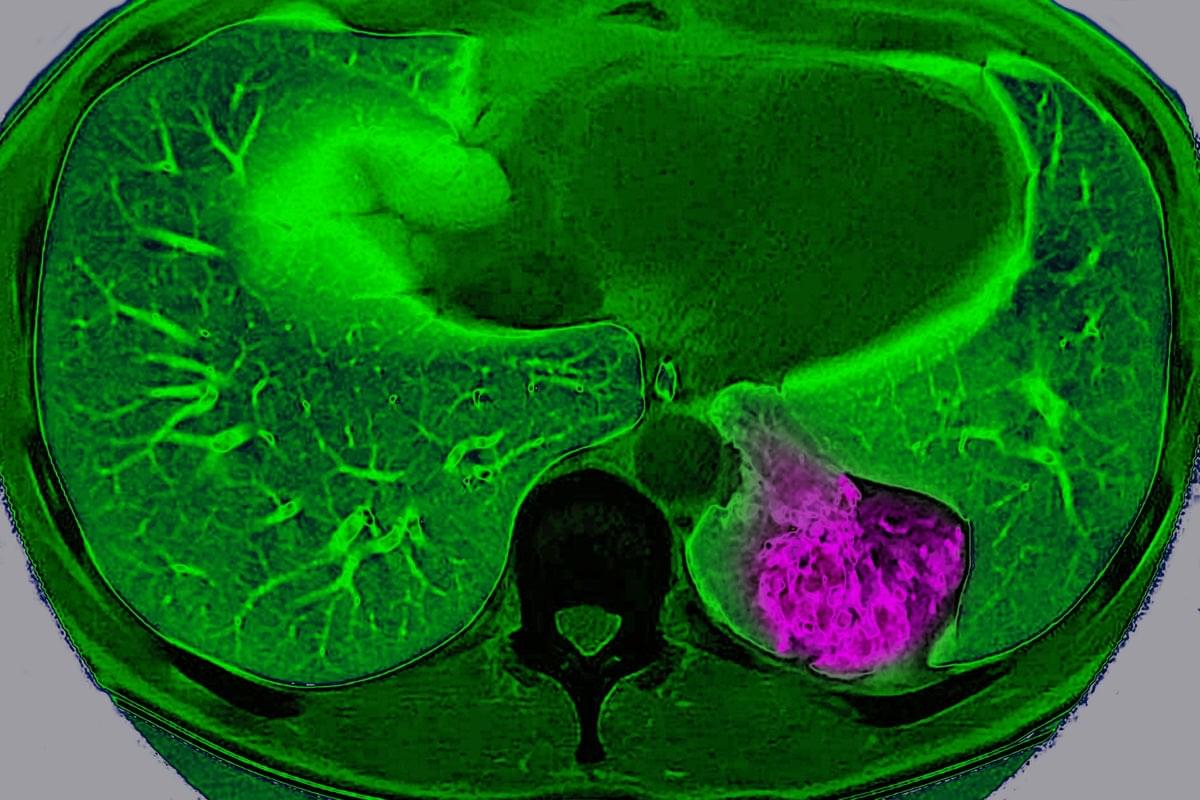
For years, scientists have viewed cancer as a localized glitch in which cells refuse to stop dividing. But a new study suggests that, in certain organs, tumors actively communicate with the brain to trick it into protecting them.
Scientists have long known that nerves grow into some tumors and that tumors containing lots of nerves usually lead to a worse prognosis. But they didn’t know exactly why. “Prior to our study, most of the focus has been this local interaction between the nerve [endings] and the tumor,” says Chengcheng Jin, an assistant professor of cancer biology at the University of Pennsylvania and a co-author of the study, which was published on Wednesday in Nature.
Jin and her colleagues discovered that lung cancer tumors in mice can use these nerve endings to communicate way beyond their close vicinity and send signals to the brain through a complex neuroimmune circuit. They also confirmed the circuit exists in humans.
✍️: Jacek Krywko 📸: BSIP/Universal Images Group via Getty Images.
Lung cancer tumor cells in mice communicate with the brain, sending signals to deactivate the body’s immune response, a study finds.
By Jacek Krywko edited by Tanya Lewis.
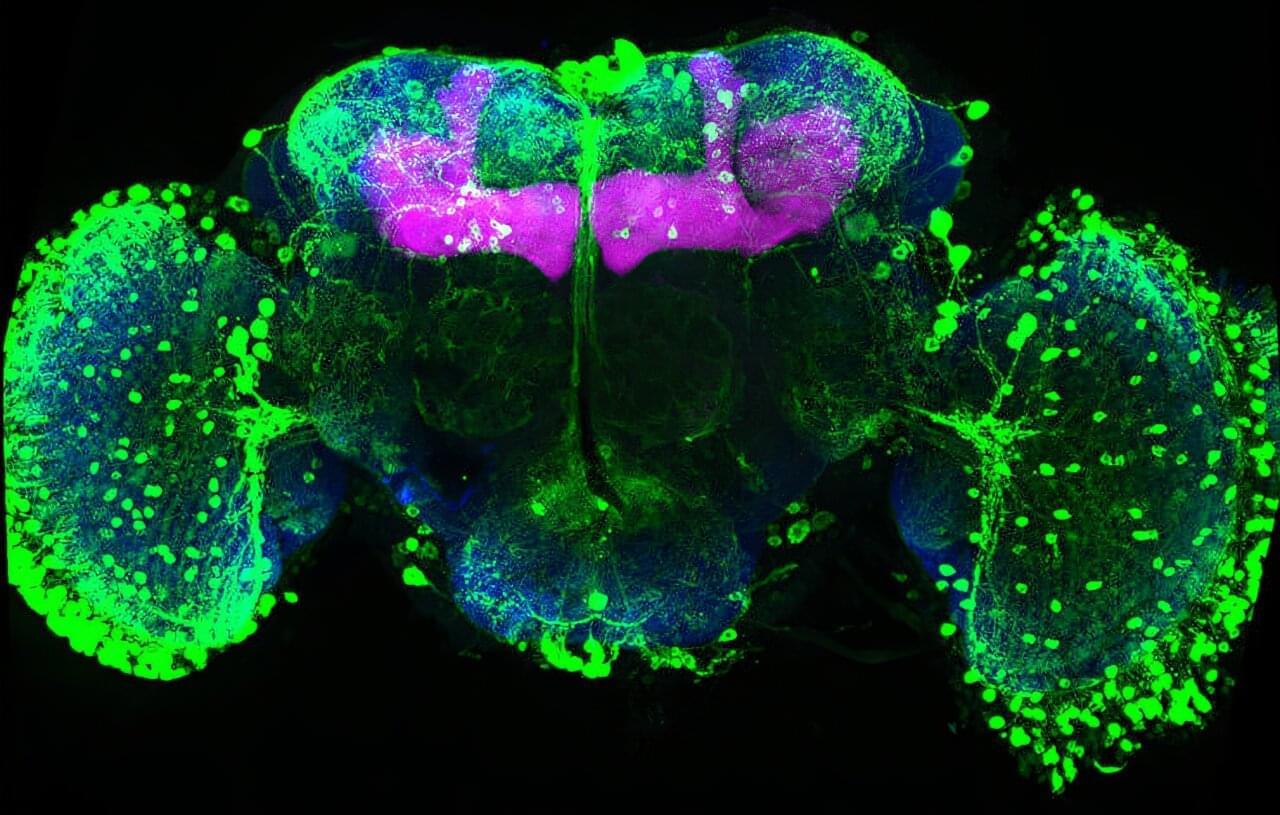
Memories must be flexible so animals can adapt when the world changes. FMI neuroscientists have found that in fruit flies, simply tasting a sugar reward again can weaken all previous associated memories. This process may inspire new ways to safely update harmful or unwanted memories. The paper is published in the journal Current Biology.
Memories help animals survive by guiding them on what to look for and what to avoid, such as remembering the smell of food or the warning signs of danger. But in a constantly changing world, those memories must also remain flexible. If a reward or threat no longer has the same meaning, the brain needs ways to update what it has learned without completely forgetting the past.
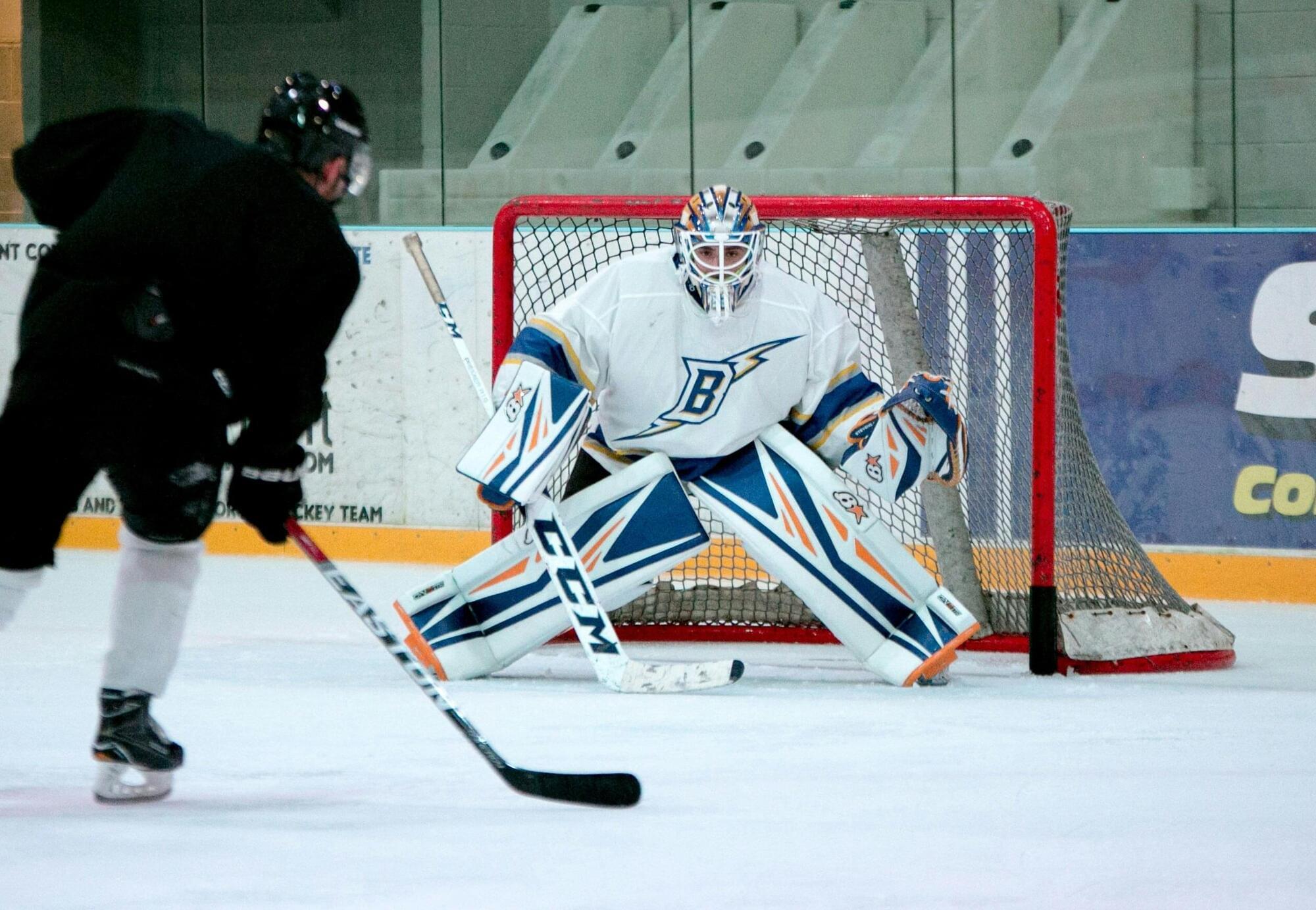

Olympic skiers, bobsledders and speed skaters all have to master one critical moment: when to start. As athletes prepare for the upcoming Winter Olympics, that split second is in the spotlight because when everyone is fast, strong and skilled, a moment of hesitation can separate gold from silver. Research from Carnegie Mellon University helps explain why that split-second pause happens and how the brain controls it, offering insight not only into elite athletic performance, but also how people make everyday decisions when the outcome isn’t clear.
Eric Yttri, associate professor of biological sciences, wanted to study how the brain decides when to act and when to wait, especially when the outcome is uncertain. He said to think about the moment the puck drops at a heated rivalry hockey game.
“Move too early, you get ejected from the faceoff. Move too late, and the puck is already gone. Having that sort of fine control on your ability to delay your action is really key,” Yttri said. “It’s a sword that cuts both ways.”