Something about congenital blindness is shielding people from schizophrenia.


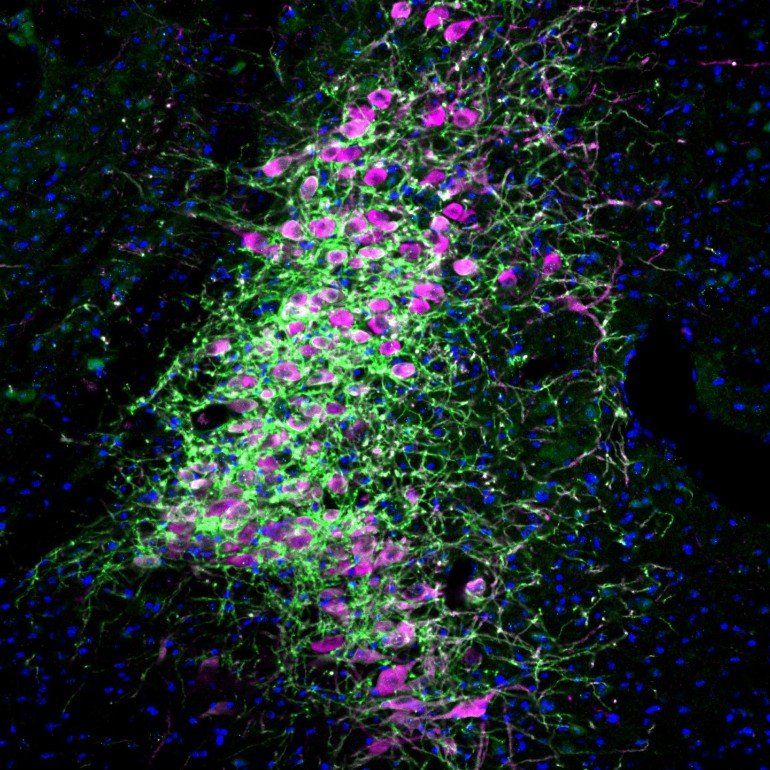
Summary: Study identifies a key role locus coeruleus neurons play in attentional control.
Source: picower institute of learning and memory.
The attentional control that organisms need to succeed in their goals comes from two abilities: the focus to ignore distractions and the discipline to curb impulses. A new study by MIT neuroscientists shows that these abilities are independent, but that the activity of norepinephrine-producing neurons in a single brain region, the locus coeruleus, controls both by targeting two distinct areas of the prefrontal cortex.
“It was a jaw-dropping moment, for us and for every scientist we told about this so far.”
But what if there’s more to the story? What if the electromagnetic fields generated by, but which are not identical to, the neuroanatomy of the brain, are in fact the primary seat of consciousness? The brain’s fields are generated by various physiological processes in the brain, but primarily by trans-membrane currents moving through neurons. These fields are always oscillating and they come in various speeds, clustered around certain bands, from delta on the lower end at 1–2.5 cycles (oscillations) per second (Hertz) up to gamma at 40–120 cycles per second.
Some neuroscientists have long considered the brain’s oscillating electromagnetic fields to be interesting but merely “epiphenomenal” features of the brain—like a train whistle on a steam-powered locomotive. Electromagnetic fields may just be noise that doesn’t affect the workings of the brain. Koch still seems to lean this way.
A closer look at Stentrode, the Brain Computer Interface that interacts with the brain via blood vessels. Recent paper demonstrating it working in 2 ALS patients.
Han from WrySci HX goes through the very interesting brain computer interface called Stentrode that can let you tweet with your mind. As a BCI, it’s a rival to Neuralink, Kernal, and Openwater. Find out about its background, how it works, why it’s the most unique BCI, and some results from its clinical trials. More below ↓↓↓
Subscribe! =]
Please consider supporting 🙏
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/wrysci_hx
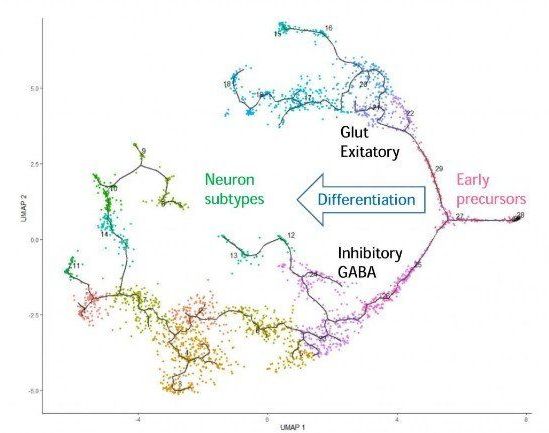
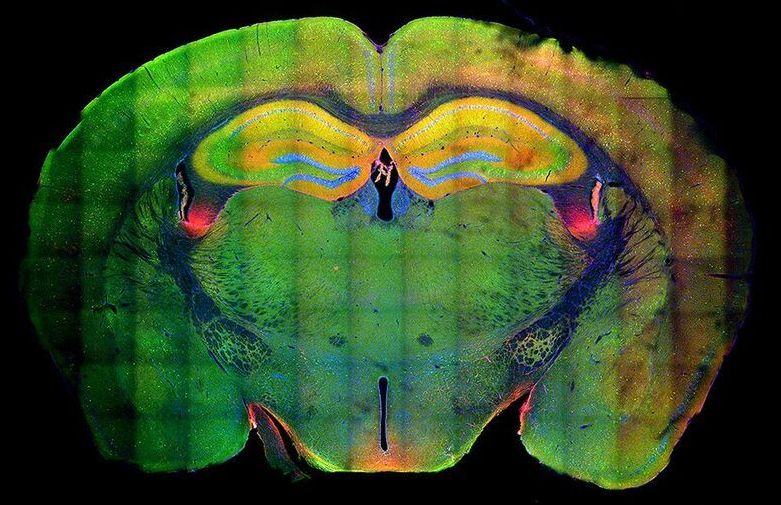
Summary: Study reveals how gene control mechanisms determine the identity of neurons in the embryonic brainstem. A failure in differentiation in developing brainstem neurons can lead to behavioral abnormalities, including ADHD.
Source: University of Helsinki
A recent study at the University of Helsinki reveals how gene control mechanisms define the identity of developing neurons in the brainstem. The researchers also showed that a failure in differentiation of the brainstem neurons leads to behavioural abnormalities, including hyperactivity and attention deficit.
Virgin Hyperloop, the transportation company owned by business magnate Richard Branson, has ambitious plans to build a vacuum tube transportation system that travels over 600 miles per hour.
But before it does so, the company has made the reasonable decision to figure out what traveling that quickly might to do the brain. To wit, scientists at West Virginia’s Rockefeller Neurosciences Institute (RNI) will find out what to expect when launching passengers at 78 percent the speed of sound.
Hold on to your brains!
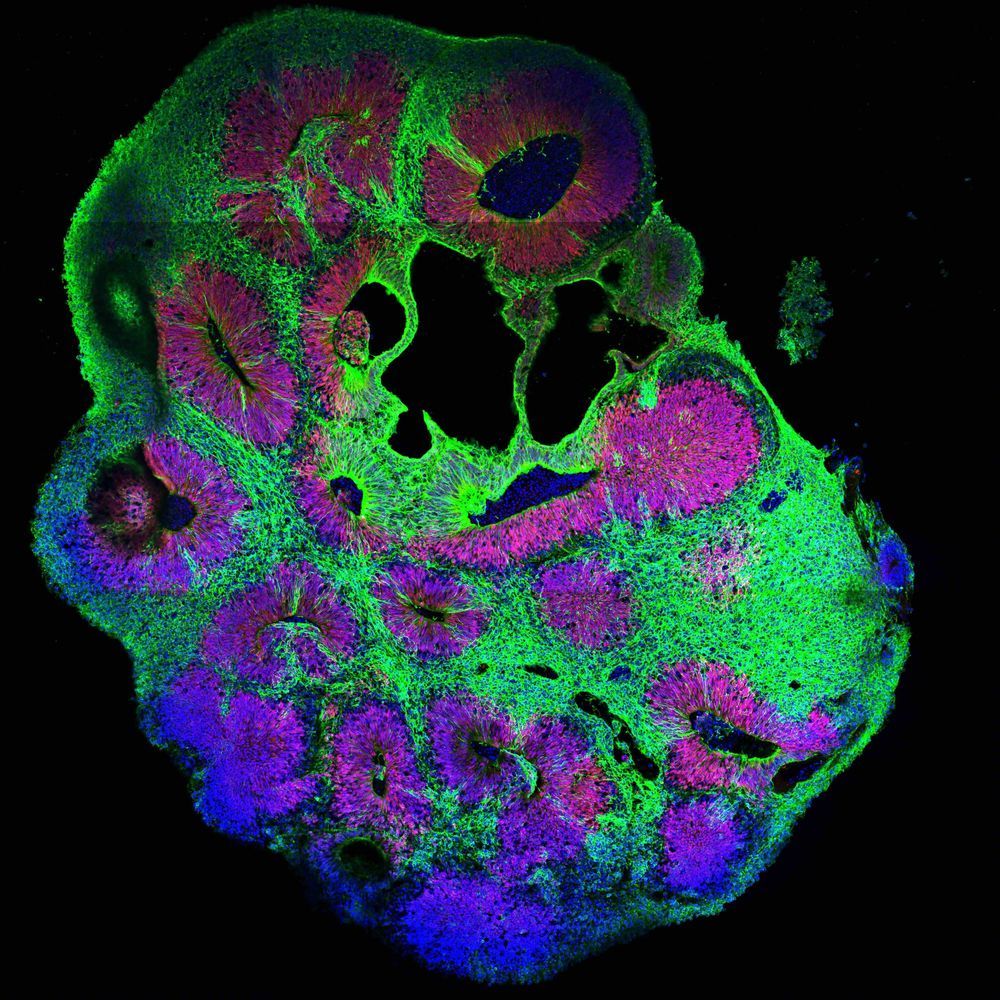
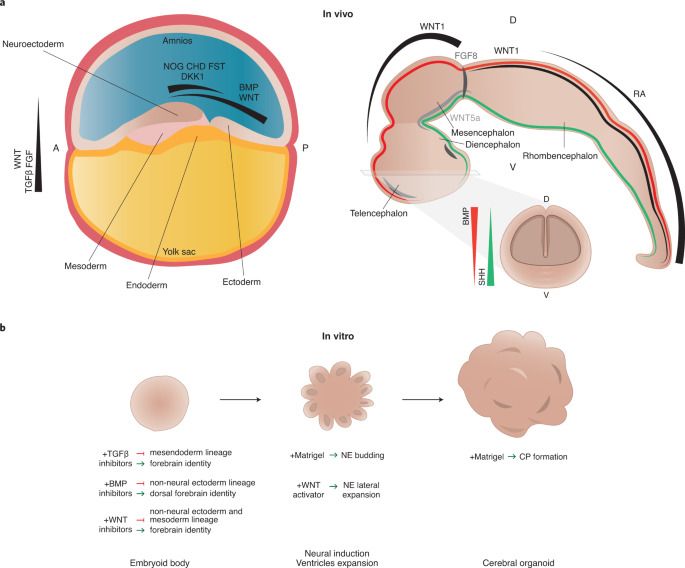
Many of the fundamental principles in biology and essentially all pathways regulating development were identified in so-called genetics screens. Originally pioneered in the fruit fly Drosophila and the nematode C. elegans, genetic screens involve inactivation of many genes one by one. By analyzing the consequences of gene loss, scientists can draw conclusions about its function. This way, for example, all genes required for formation of a brain can be identified.
Genetic screens can routinely be carried out in flies and worms. In humans, a wealth of knowledge exists about genetic disorders and the consequences of disease-relevant mutations, but their systematic analysis was impossible. Now, the Knoblich lab at IMBA has developed a groundbreaking technique allowing hundreds of genes to be analyzed in parallel in human tissue. They named the new technology CRISPR-LICHT and published their findings in the journal Science.
By using cerebral organoids, a 3D cell culture model for the human brain developed in Jürgen Knoblich’s group at IMBA, hundreds of mutations can now be analyzed for their role in the human brain using CRISPR-LICHT.

Article. I guess having implants directly on the brain isn’t the only way to have a brain to machine interface. The scientists involved in the study found an alternative by picking up signals through the blood vessels.
It’s not as information packed as a direct brain connection, but it’s not as invasive.
I think it would be a good alternative or even complementary to direct brain implants. Interesting. 😃
Electrodes threaded through the blood vessels that feed the brain let people control gadgets with their minds.