Devices based on photon-assisted tunnelling could harvest energy from nuclear power stations, chemical manufacturing facilities and other sources of waste heat.




73 years ago, the same scientists who had helped to begin the atomic age set a “doomsday clock” for humanity. It first appeared on the cover of the June 1947 issue of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists as a dire warning about the nuclear rivalry between the U.S. and the Soviet Union. At that moment, the Bulletin estimated that we stood at about 7 minutes to midnight, which represented nuclear apocalypse.
The Doomsday Clock wasn’t – and still isn’t – a precise countdown to the end of all things. It’s a metaphor for how dangerous the global situation seems to be at a given moment, in the very well-informed but also subjective opinion of the Bulletin’s board of directors. In June 1947, things looked dire. The U.S. had dropped a pair of atomic bombs on Japan less than two years before; when the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists first published the Doomsday Clock image, researchers were still studying the aftermath of those bombs. Meanwhile, the Soviet Union was hard at work on its own atomic program, and was just a couple of years away from testing its first atomic bomb in 1949.
Through the Cold War and in the decades since, the clock’s minute hand has moved about two dozen times. In September 1953, it stood at two minutes to midnight, following Russia’s August 1953 hydrogen bomb test – which in turn had followed a U.S. hydrogen bomb test in November 1952. Those tests meant the two feuding superpowers each had much more powerful new weapons with which to destroy each other; the tests also heightened the sense of life-or-death competition that made it more likely that someone would decide to use those terrible new bombs.
Circa 2015
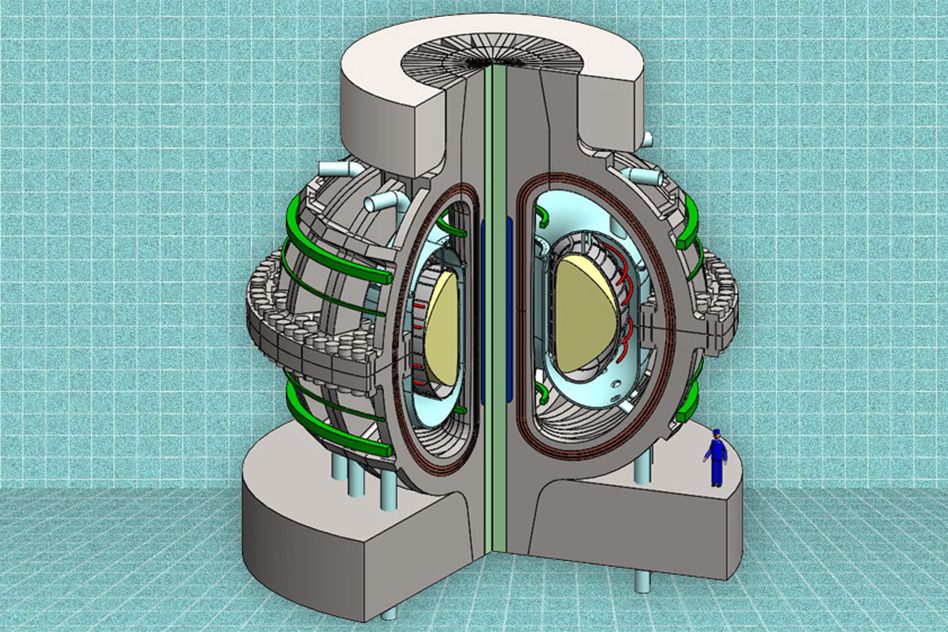
Fusion power can seem a bit like the last bus at night; it’s always coming, but never arrives. MIT is working to change that with a new compact tokamak fusion reactor design based on the latest commercially available magnetic superconductor technology. The ARC (affordable, robust, compact) reactor design promises smaller, cheaper reactors that could make fusion power practical within 10 years.
A commercially viable fusion reactor has been the Holy Grail of engineering since the 1950s, with the potential to turn almost all other major electricity sources into an historical footnote overnight. If perfected, it would essentially be an inexhaustible source of power, impacting on almost every aspect of life, from the environment to global politics. The trick is making it practical.
Put simply, fusion involves placing hydrogen atoms under very high heat and pressure until they fuse into helium atoms, which releases tremendous amounts of energy. The Sun does this as a matter of course, but reproducing those conditions on Earth outside of a hydrogen bomb has proven difficult.
Circa 2015
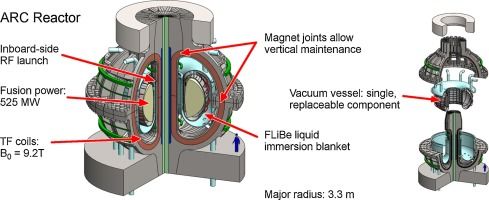
The affordable, robust, compact (ARC) reactor is the product of a conceptual design study aimed at reducing the size, cost, and complexity of a combined fusion nuclear science facility (FNSF) and demonstration fusion Pilot power plant. ARC is a ∼200–250 MWe tokamak reactor with a major radius of 3.3 m, a minor radius of 1.1 m, and an on-axis magnetic field of 9.2 T. ARC has rare earth barium copper oxide (REBCO) superconducting toroidal field coils, which have joints to enable disassembly. This allows the vacuum vessel to be replaced quickly, mitigating first wall survivability concerns, and permits a single device to test many vacuum vessel designs and divertor materials. The design point has a plasma fusion gain of Qp ≈ 13.6, yet is fully non-inductive, with a modest bootstrap fraction of only ∼63%. Thus ARC offers a high power gain with relatively large external control of the current profile. This highly attractive combination is enabled by the ∼23 T peak field on coil achievable with newly available REBCO superconductor technology. External current drive is provided by two innovative inboard RF launchers using 25 MW of lower hybrid and 13.6 MW of ion cyclotron fast wave power. The resulting efficient current drive provides a robust, steady state core plasma far from disruptive limits. ARC uses an all-liquid blanket, consisting of low pressure, slowly flowing fluorine lithium beryllium (FLiBe) molten salt. The liquid blanket is low-risk technology and provides effective neutron moderation and shielding, excellent heat removal, and a tritium breeding ratio ≥ 1.1. The large temperature range over which FLiBe is liquid permits an output blanket temperature of 900 K, single phase fluid cooling, and a high efficiency helium Brayton cycle, which allows for net electricity generation when operating ARC as a Pilot power plant.
Circa 2019
Scientists have longed to create the perfect energy source. Ideally, that source would eventually replace greenhouse gas-spewing fossil fuels, power cars, boats, and planes, and send spacecraft to remote parts of the universe. So far, nuclear fusion energy has seemed like the most likely option to help us reach those goals.
The big problem? It’s difficult to harness, and we’re nowhere near producing it at the scales we need in order to cause a seismic shift in energy policy. That’s why teams of researchers across the world are racing to improve our understanding of this reaction.
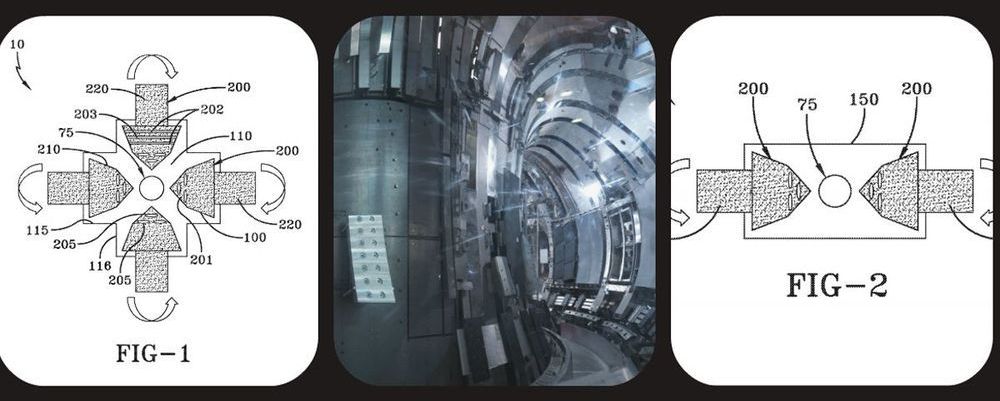
Now, the U.S. Navy has jumped into the game by filing a patent for a compact fusion reactor, according to exclusive reporting by The War Zone.


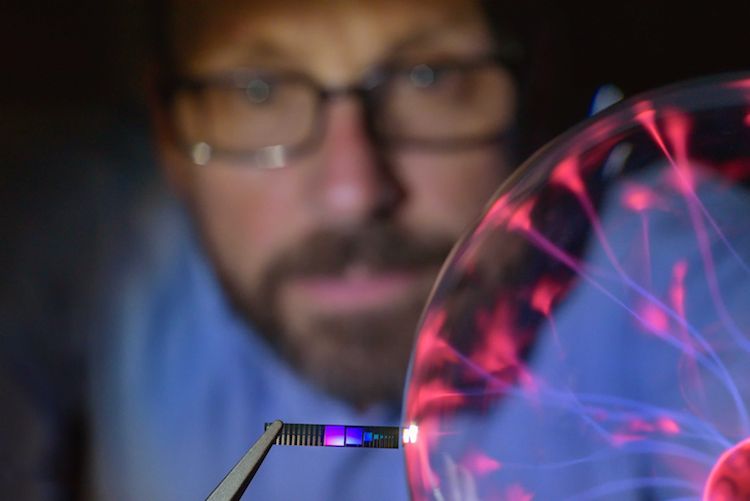
To just solve a puzzle or play a game, artificial intelligence can require software running on thousands of computers. That could be the energy that three nuclear plants produce in one hour.
A team of engineers has created hardware that can learn skills using a type of AI that currently runs on software platforms. Sharing intelligence features between hardware and software would offset the energy needed for using AI in more advanced applications such as self-driving cars or discovering drugs.
“Software is taking on most of the challenges in AI. If you could incorporate intelligence into the circuit components in addition to what is happening in software, you could do things that simply cannot be done today,” said Shriram Ramanathan, a professor of materials engineering at Purdue University.

EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: The US Department of Defense has been working with American companies for the past year on a project to develop a prototype for a portable nuclear microreactor, a device intended for use by the US military in security scenarios around the world. The US Department of Energy is also involved in the project, with the aim of providing electricity to remote sites that are difficult to link to the grid. The project thus represents a symbiosis between military and civilian technological development.
A symbiotic relationship between military and civilian aspects of technological development gained momentum in the US after the end of WWII. This was particularly visible among applications in the communication, computing, and aerospace fields, but was also present in the field of nuclear technology. Some technology projects were presented as dual-use in order to justify the cost of their development.
One example of nuclear energy symbiosis was the development of nuclear power-generating reactors. By 1956, more than a decade after the destruction of the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki by nuclear bombs, only the UK’s Calder Hall nuclear power plant, which had four reactors each producing 60 MW electricity (MWe), was in operation. However, as of December 2019, 443 nuclear power generators were operating worldwide, with a total output of 395 gigawatts electric (GWe)—an average output of nearly 900 MWe per reactor.

Eric Klien
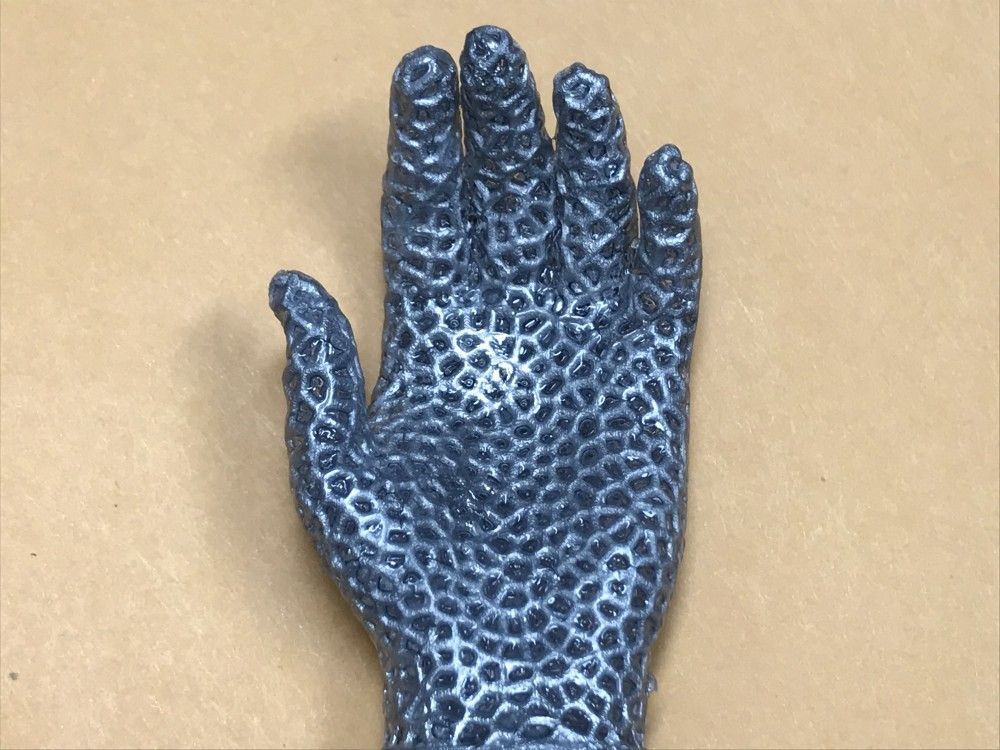
A liquid metal lattice that can be crushed but returns to its original shape on heating has been developed by Pu Zhang and colleagues at Binghamton University in the US. The material is held together by a silicone shell and could find myriad uses including soft robotics, foldable antennas and aerospace engineering. Indeed, the research could even lead to the creation of a liquid metal robot evoking the T-1000 character in the film Terminator 2.
The team created the liquid metal lattice using a special mixture of bismuth, indium and tin known as Field’s alloy. This alloy has the relatively unusual property of melting at just 62 °C, which means it can be liquefied with just hot water. Field’s alloy already has several applications – including as a liquid-metal coolant for advanced nuclear reactors.
Zhang and colleagues combined the alloy with a silicone shell through a complex hybrid manufacturing process that combines 3D printing, vacuum casting and so-called “conformal coating” – a technique normally used to coat circuit boards in a thin polymer layer to protect them against the environment. The silicone shell is what allows the lattice to “remember” a desired shape and restore such when the alloy is melted.