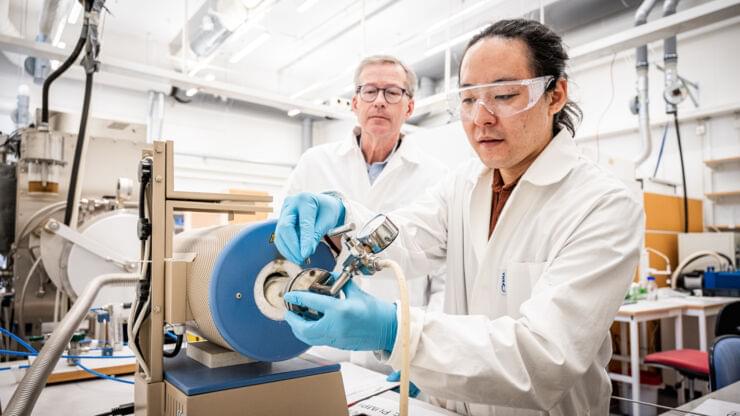
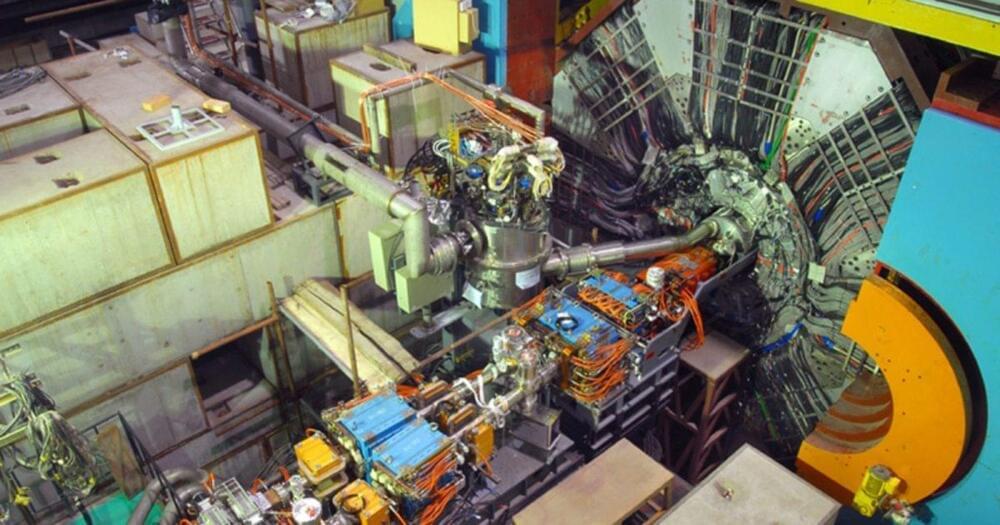
Argonne National Laboratory scientists have used anomaly detection in the ATLAS collaboration to search for new particles, identifying a promising anomaly that could indicate new physics beyond the Standard Model.
Scientists used a neural network, a type of brain-inspired machine learning algorithm, to sift through large volumes of particle collision data in a study that marks the first use of a neural network to analyze data from a collider experiment.
Particle physicists are tasked with mining this massive and growing store of collision data for evidence of undiscovered particles. In particular, they’re searching for particles not included in the Standard Model of particle physics, our current understanding of the universe’s makeup that scientists suspect is incomplete.