Curtin University-led research has discovered a rare dust particle trapped in an ancient extra-terrestrial meteorite that was formed by a star other than our sun.
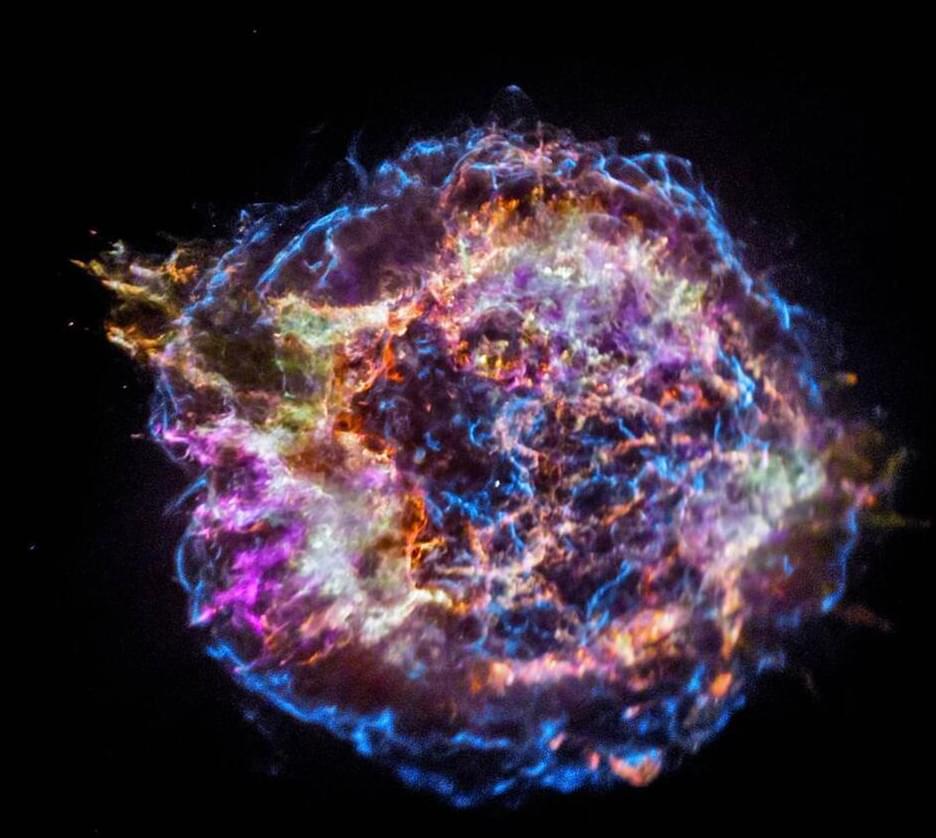


Curtin University-led research has discovered a rare dust particle trapped in an ancient extra-terrestrial meteorite that was formed by a star other than our sun.


Gravitons, the particles thought to carry gravity, have never been seen in space – but something very similar has been detected in a semiconductor.
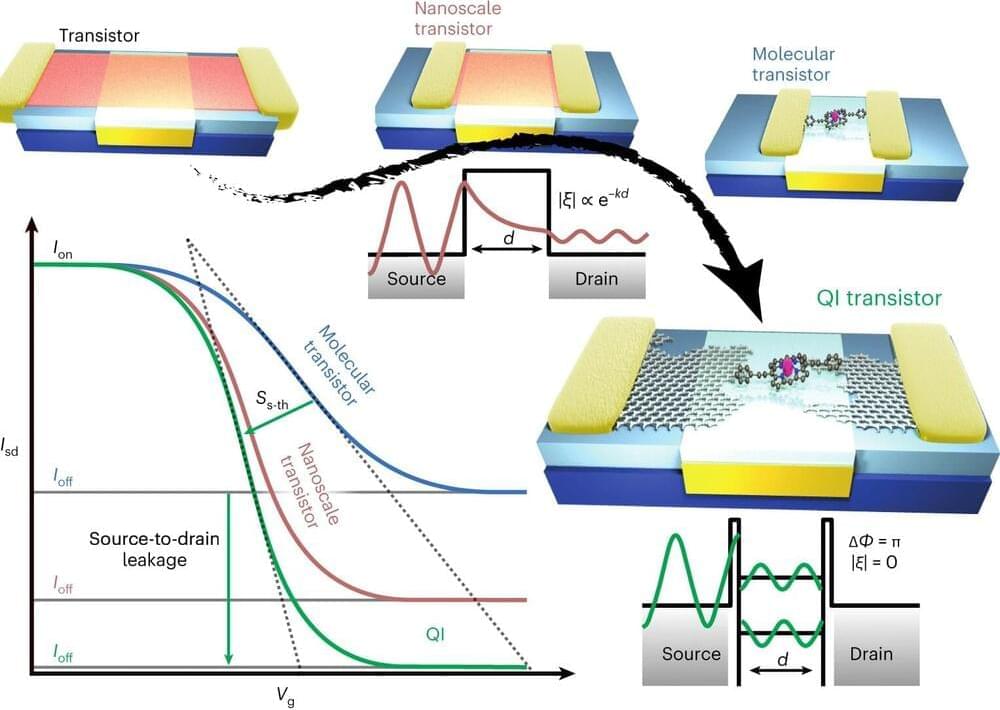
As transistors get smaller, they become increasingly inefficient and susceptible to errors, as electrons can leak through the device even when it is supposed to be switched off, by a process known as quantum tunneling. Researchers are exploring new types of switching mechanisms that can be used with different materials to remove this effect.
In the nanoscale structures that Professor Jan Mol, Dr. James Thomas, and their group study at Queen Mary’s School of Physical and Chemical Sciences, quantum mechanical effects dominate, and electrons behave as waves rather than particles. Taking advantage of these quantum effects, the researchers built a new transistor.
The transistor’s conductive channel is a single zinc porphyrin, a molecule that can conduct electricity. The porphyrin is sandwiched between two graphene electrodes, and when a voltage is applied to the electrodes, electron flow through the molecule can be controlled using quantum interference.
There’s a specter haunting the tunnels of a particle accelerator at CERN.
In the Super Proton Synchrotron, physicists have finally measured and quantified an invisible structure that can divert the course of the particles therein, and create problems for particle research.
It’s described as taking place in phase space, which can represent one or more states of a moving system. Since four states are required to represent the structure, the researchers view it as four-dimensional.
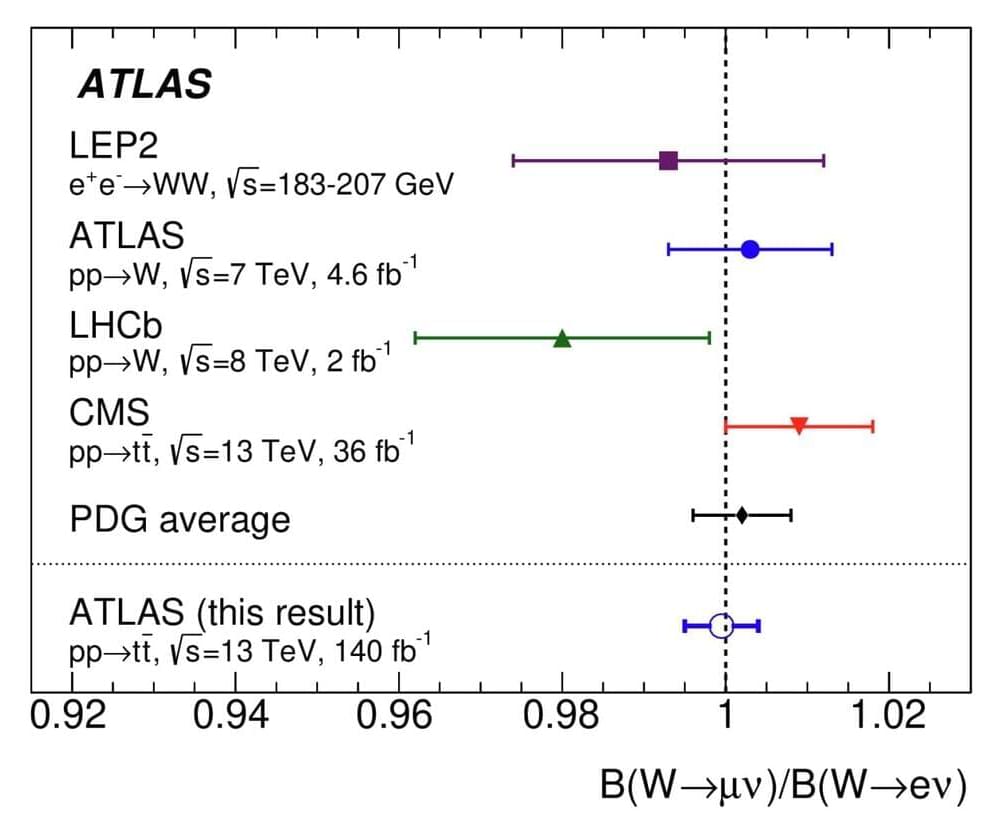
In a talk at the ongoing Rencontres de Moriond conference, the ATLAS collaboration presented the result of its latest test of a key principle of the Standard Model of particle physics known as lepton flavor universality. The precision of the result is the best yet achieved by a single experiment in decays of the W boson and surpasses that of the current experimental average.

Several thousand sensors distributed over a square kilometer near the South Pole are tasked with answering one of the large outstanding questions in physics: does quantum gravity exist? The sensors monitor neutrinos—particles with no electrical charge and almost without mass—arriving at the Earth from outer space. A team from the Niels Bohr Institute (NBI), University of Copenhagen, has contributed to developing the method that exploits neutrino data to reveal if quantum gravity exists.
If as we believe, quantum gravity does indeed exist, this will contribute to unite the current two worlds in physics. Today, classical physics describes the phenomena in our normal surroundings such as gravity, while the atomic world can only be described using quantum mechanics.
The unification of quantum theory and gravitation remains one of the most outstanding challenges in fundamental physics. It would be very satisfying if we could contribute to that end, says Tom Stuttard, Assistant Professor at NBI.
Scientists have advanced the field by stabilizing exciton-polaritons in semiconductor photonic gratings, achieving long-lived and optically configurable quantum fluids suitable for complex system simulations.
Researchers from CNR Nanotec in Lecce and the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw used a new generation of semiconductor photonic gratings to optically tailor complexes of quantum droplets of light that became bound together into macroscopic coherent states. The research underpins a new method to simulate and explore interactions between artificial atoms in a highly reconfigurable manner, using optics. The results have been published in the prestigious journal Nature Physics.
Quantum Simulation Technologies
Researchers have developed methods to entangle large numbers of particles, improving the precision and speed of quantum measurements. These advancements could revolutionize quantum sensors and atomic clocks, with potential applications in fundamental physics research.
Opening new possibilities for quantum sensors, atomic clocks, and tests of fundamental physics, JILA researchers have developed new ways of “entangling” or interlinking the properties of large numbers of particles. In the process they have devised ways to measure large groups of atoms more accurately even in disruptive, noisy environments.
The new techniques are described in a pair of papers published in Nature.[1] JILA is a joint institute of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Colorado Boulder.
