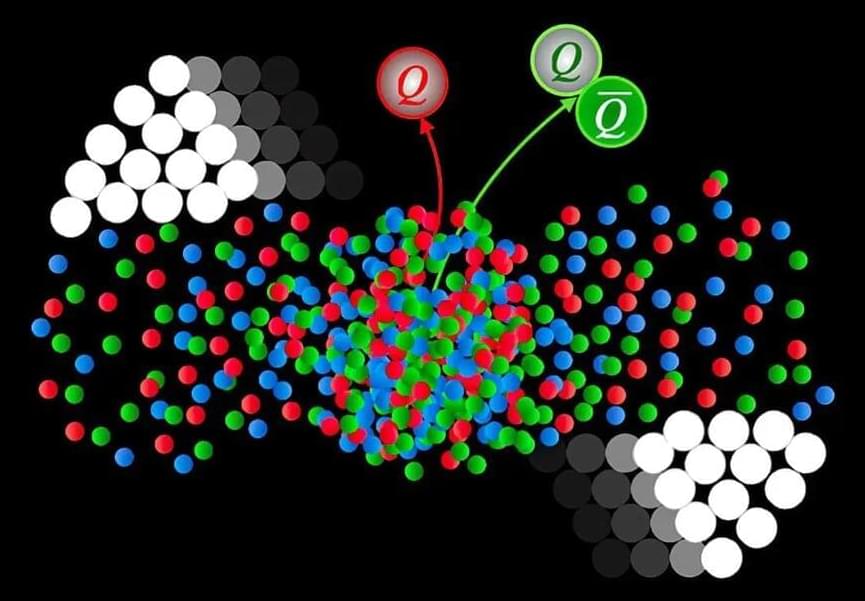
Scientists have taken a significant step forward in the study of the properties of quarks and gluons, the particles that make up atomic nuclei, by resolving a long-standing issue with a theoretical calculation method known as “axial gauge.” MIT
MIT is an acronym for the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It is a prestigious private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts that was founded in 1861. It is organized into five Schools: architecture and planning; engineering; humanities, arts, and social sciences; management; and science. MIT’s impact includes many scientific breakthroughs and technological advances. Their stated goal is to make a better world through education, research, and innovation.