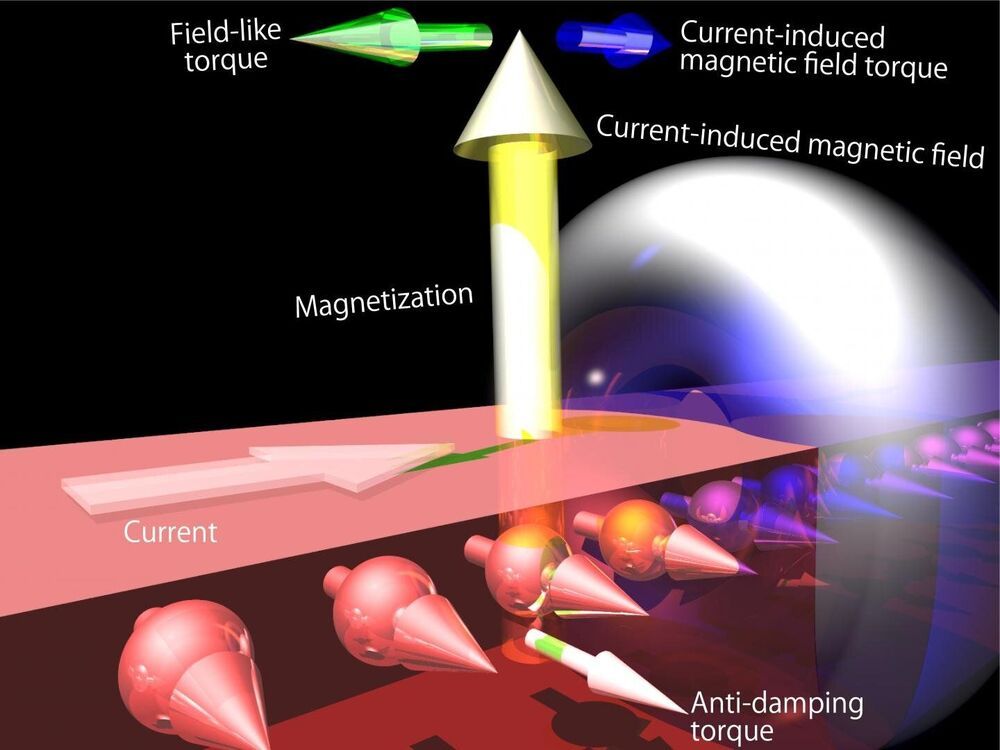
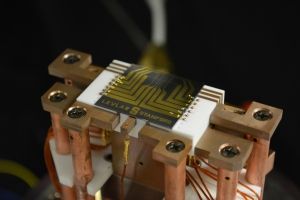
Researchers are a step closer to realizing a new kind of memory that works according to the principles of spintronics which is analogous to, but different from, electronics. Their unique gallium arsenide-based ferromagnetic semiconductor can act as memory by quickly switching its magnetic state in the presence of an induced current at low power. Previously, such current-induced magnetization switching was unstable and drew a lot of power, but this new material both suppresses the instability and lowers the power consumption too.
The field of quantum computing often gets covered in the technical press; however, another emerging field along similar lines tends to get overlooked, and that is spintronics. In a nutshell, spintronic devices could replace some electronic devices and offer greater performance at far low power levels. Electronic devices use the motion of electrons for power and communication. Whereas spintronic devices use a transferable property of stationary electrons, their angular momentum, or spin. It’s a bit like having a line of people pass on a message from one to the other rather than have the person at one end run to the other. Spintronics reduces the effort needed to perform computational or memory functions.
Spintronic-based memory devices are likely to become common as they have a useful feature in that they are nonvolatile, meaning that once they are in a certain state, they maintain that state even without power. Conventional computer memory, such as DRAM and SRAM made of ordinary semiconductors, loses its state when it’s powered off. At the core of experimental spintronic memory devices are magnetic materials that can be magnetized in opposite directions to represent the familiar binary states of 1 or 0, and this switching of states can occur very, very quickly. However, there has been a long and arduous search for the best materials for this job, as magnetizing spintronic materials are no simple matter.