Astronomers found evidence that dark matter and neutrinos may interact, hinting at a “fundamental breakthrough” that challenges our understanding of how the universe evolved.
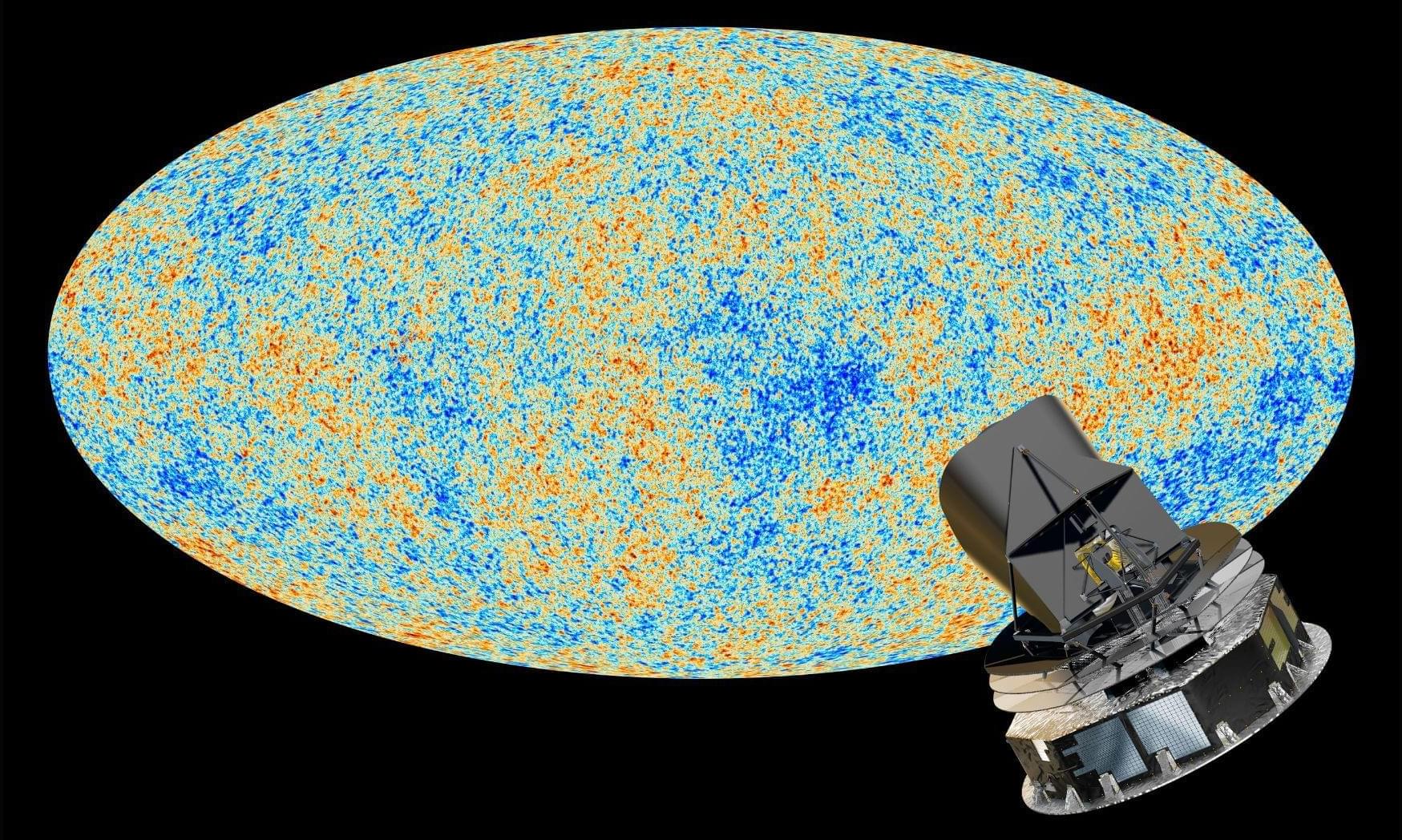

After years of trying, scientists have finally created a stable superatom of copper, a long-sought-after chemical breakthrough that could revolutionize how we deal with carbon emissions.
Copper is a cheap and common metal, and because of its ability to bind carbon atoms together (C-C coupling), scientists have wanted to use it to turn carbon dioxide into products like ethylene for plastics and fuels. However, it corrodes or falls apart almost immediately when exposed to air or harsh industrial conditions.
A superatom is a cluster of atoms that behaves like a single atom, but with greater stability. In this new study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, scientists from Tsinghua University in Beijing built a nanocluster made from 45 copper atoms (Cu45).


One candidate for dark matter is a subatomic particle carrying a tiny electric charge many times smaller than that of the electron. This so-called millicharged dark matter would presumably interact with Earth’s magnetic field, generating potentially observable time variations in the magnetic field on Earth’s surface. A new study of archived data looked for this signal but came up empty [1]. The research has thus placed strict limits on the properties that a millicharged dark-matter particle could have if it has a small mass (in the range of 10–18 to 10–15 eV/c2).
Dark matter can’t have a typical electric charge, as it would interact too strongly with normal matter. But a small charge is possible and could produce features in-line with dark-matter models. Astrophysicists have looked for evidence of millicharged dark matter in stellar evolution data, as such particles could cause stars to cool faster than expected. No such signal has been seen, ruling out a large portion of millicharged-dark-matter parameter space.
Lei Wu from Nanjing Normal University in China and colleagues have explored another potential signal in the geomagnetic field. According to the team’s calculations, low-mass millicharged particles could annihilate each other in the presence of the planet’s magnetic-field background, producing an effective electric current that would generate its own magnetic field. This dark-matter-induced field would be small (roughly a million times less than Earth’s field), but it might be detectable owing to its peculiar time variation (at frequencies less than 1 Hz). The researchers failed to find such a signal in previously collected geomagnetic observations. The absence rules out low-mass dark-matter charges in a large range down to 10−30 times the electron charge. Such a small charge may seem implausible, but “nature sometimes surprises us,” Wu says.
Recent research has demonstrated that a rhodium (Rh) cluster of an optimal, intermediate size—neither too small nor too large—exhibits the highest catalytic activity in hydroformylation reactions. Similar to the concept of finding the “just right” balance, the study identifies this so-called “Goldilocks size” as crucial for maximizing catalyst efficiency. The study is published in the journal ACS Catalysis and was featured as the cover story.
Led by Professor Kwangjin An from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, in collaboration with Professor Jeong Woo Han from Seoul National University, the research demonstrates that when Rh exists as a cluster —comprising about 10 atoms—it outperforms both single-atom and nanoparticle forms in reaction speed and activity.
Hydroformylation is a vital industrial process used for producing raw materials for plastics, detergents, and other chemicals. Currently, many Rh catalysts are homogeneous—dissolved in liquids—which complicates separation and recycling. This challenge has driven efforts to develop solid, heterogeneous Rh catalysts that are easier to recover and reuse.
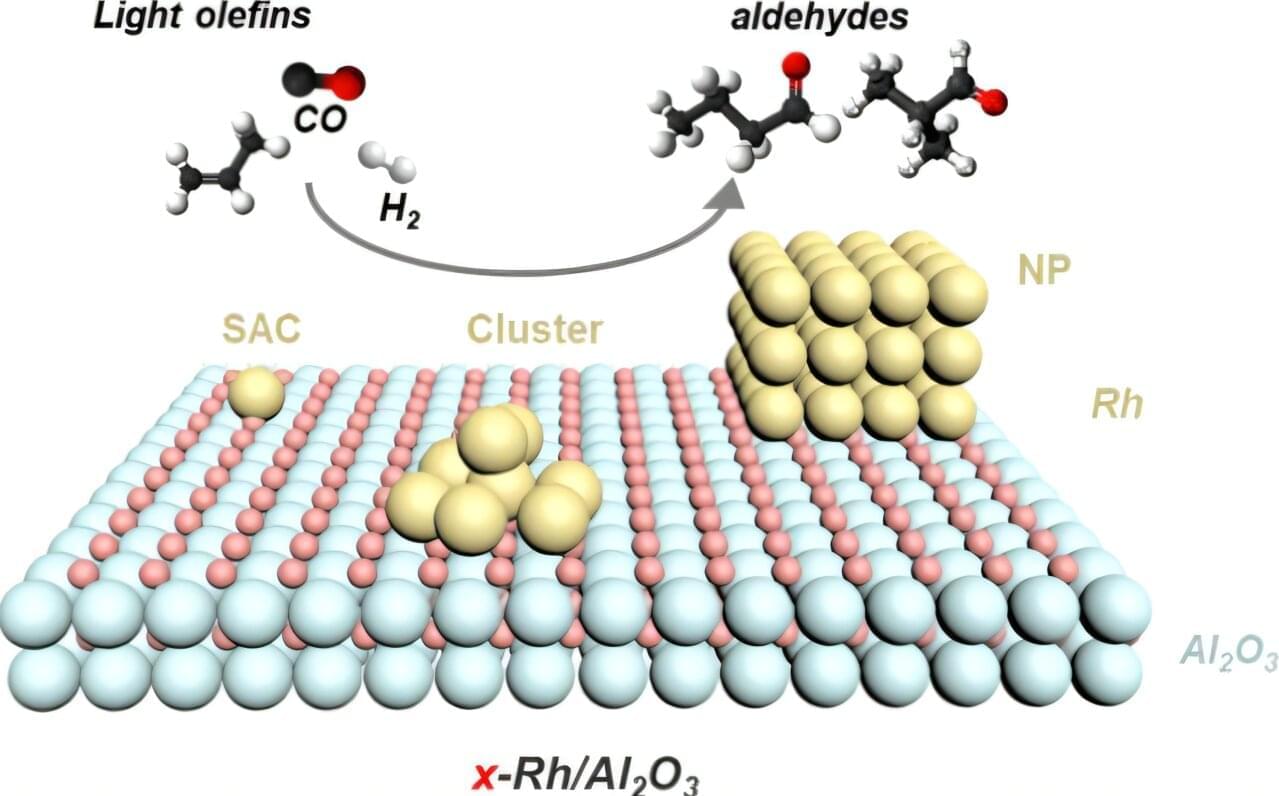
Quantum computing represents a potential breakthrough technology that could far surpass the technical limitations of modern-day computing systems for some tasks. However, putting together practical, large-scale quantum computers remains challenging, particularly because of the complex and delicate techniques involved.
In some quantum computing systems, single ions (charged atoms such as strontium) are trapped and exposed to electromagnetic fields including laser light to produce certain effects, used to perform calculations. Such circuits require many different wavelengths of light to be introduced into different positions of the device, meaning that numerous laser beams have to be properly arranged and delivered to the designated area. In these cases, the practical limitations of delivering many different beams of light around within a limited space become a difficulty.
To address this, researchers from The University of Osaka investigated unique ways to deliver light in a limited space. Their work revealed a power-efficient nanophotonic circuit with optical fibers attached to waveguides to deliver six different laser beams to their destinations. The findings have been published in APL Quantum.

When materials become just one atom thick, melting no longer follows the familiar rules. Instead of jumping straight from solid to liquid, an unusual in-between state emerges, where atomic positions loosen like a liquid but still keep some solid-like order. Scientists at the University of Vienna have now captured this elusive “hexatic” phase in real time by filming an ultra-thin silver iodide crystal as it melted inside a protective graphene sandwich.

Scientists have built a quantum “wire” where atoms collide endlessly—but energy and motion never slow down. Researchers at TU Wien have discovered a quantum system where energy and mass move with perfect efficiency. In an ultracold gas of atoms confined to a single line, countless collisions occur—but nothing slows down. Instead of diffusing like heat in metal, motion travels cleanly and undiminished, much like a Newton’s cradle. The finding reveals a striking form of transport that breaks the usual rules of resistance.
In everyday physics, transport describes how things move from one place to another. Electric charge flows through wires, heat spreads through metal, and water travels through pipes. In each case, scientists can measure how easily charge, energy, or mass moves through a material. Under normal conditions, that movement is slowed by friction and collisions, creating resistance that weakens or eventually stops the flow.
Researchers at TU Wien have now demonstrated a rare exception. In a carefully designed experiment, they observed a physical system in which transport does not degrade at all.
Several years ago, scientists discovered that a single microscopic particle could rock back and forth on its own under a steady electric field. The result was curious, but lonely. Now, Northwestern University engineers have discovered what happens when many of those particles come together. The answer looks less like ordinary physics and more like mystifying, flawlessly timed choreography.
The study appears in the journal Nature Communications.
In the work, the team found that groups of tiny particles suspended in liquid oscillate together, keeping time as though they somehow sense one another’s motion. Nearby particles fall into sync, forming clusters that appear to sway in unison—rocking back and forth with striking coordination.
Some things are easier to achieve if you’re not alone. As researchers from the University of Rostock, Germany have shown, this very human insight also applies to the most fundamental building blocks of nature.
At its very core, quantum mechanics postulates that everything is made out of elementary particles, which cannot be split up into even smaller units. This made Ph.D. candidate Vera Neef, first author of the recent publication “Pairing particles into holonomies,” wonder: “What can two particles only accomplish if they work as a team? Can they jointly achieve something, that is impossible for one particle alone?”