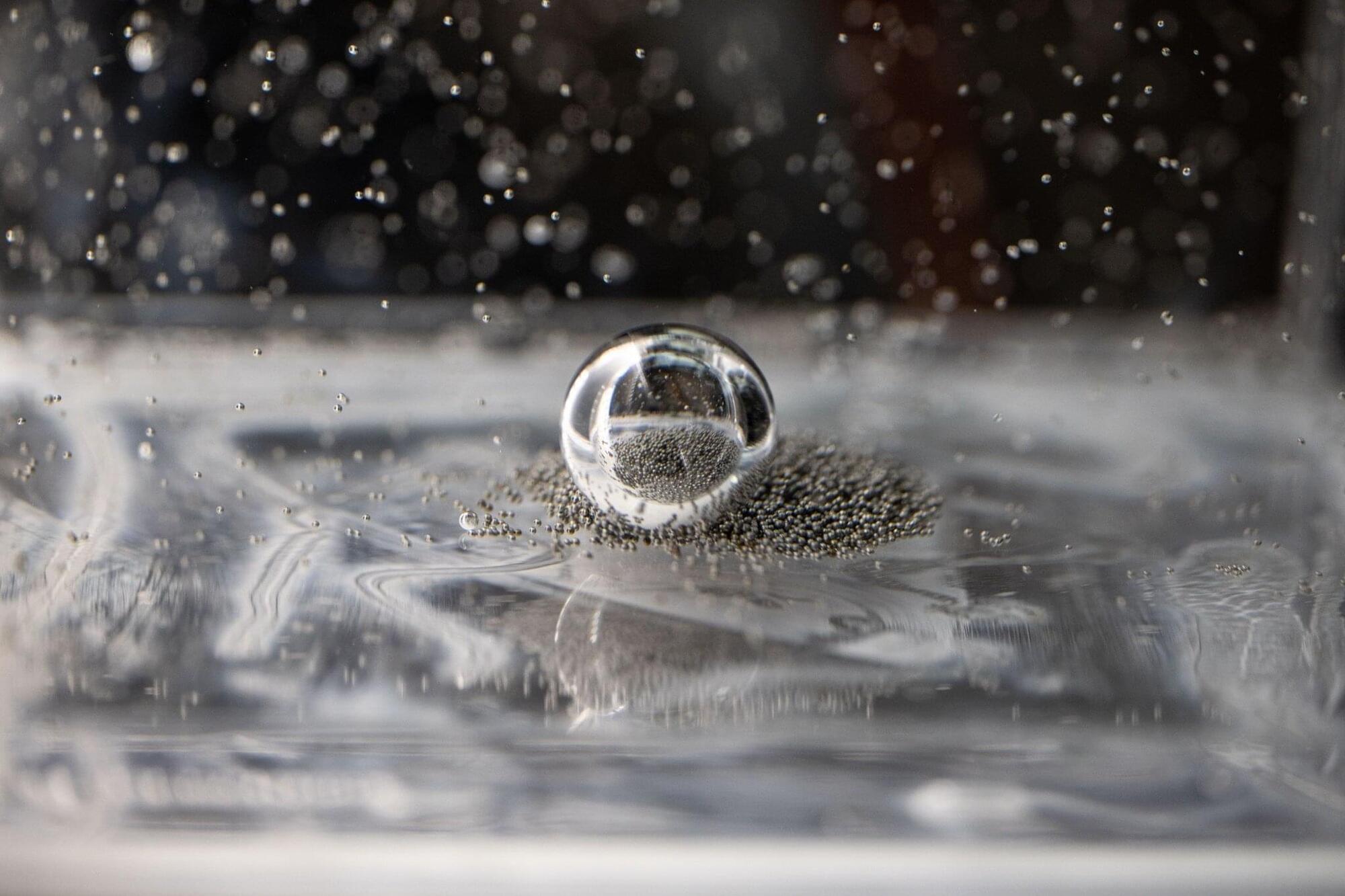
In this Oct. 20, 2025, photo, tiny ball bearings surround a larger central bearing during the Fluid Particles experiment, conducted inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) aboard the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory module.
A bulk container installed in the MSG, filled with viscous fluid and embedded particles, is subjected to oscillating frequencies to observe how the particles cluster and form larger structures in microgravity. Insights from this research may advance fire suppression, lunar dust mitigation, and plant growth in space. On Earth, the findings could inform our understanding of pollen dispersion, algae blooms, plastic pollution, and sea salt transport during storms.
In addition to uncovering potential benefits on Earth, research done aboard the space station helps inform long-duration missions like Artemis and future human expeditions to Mars.