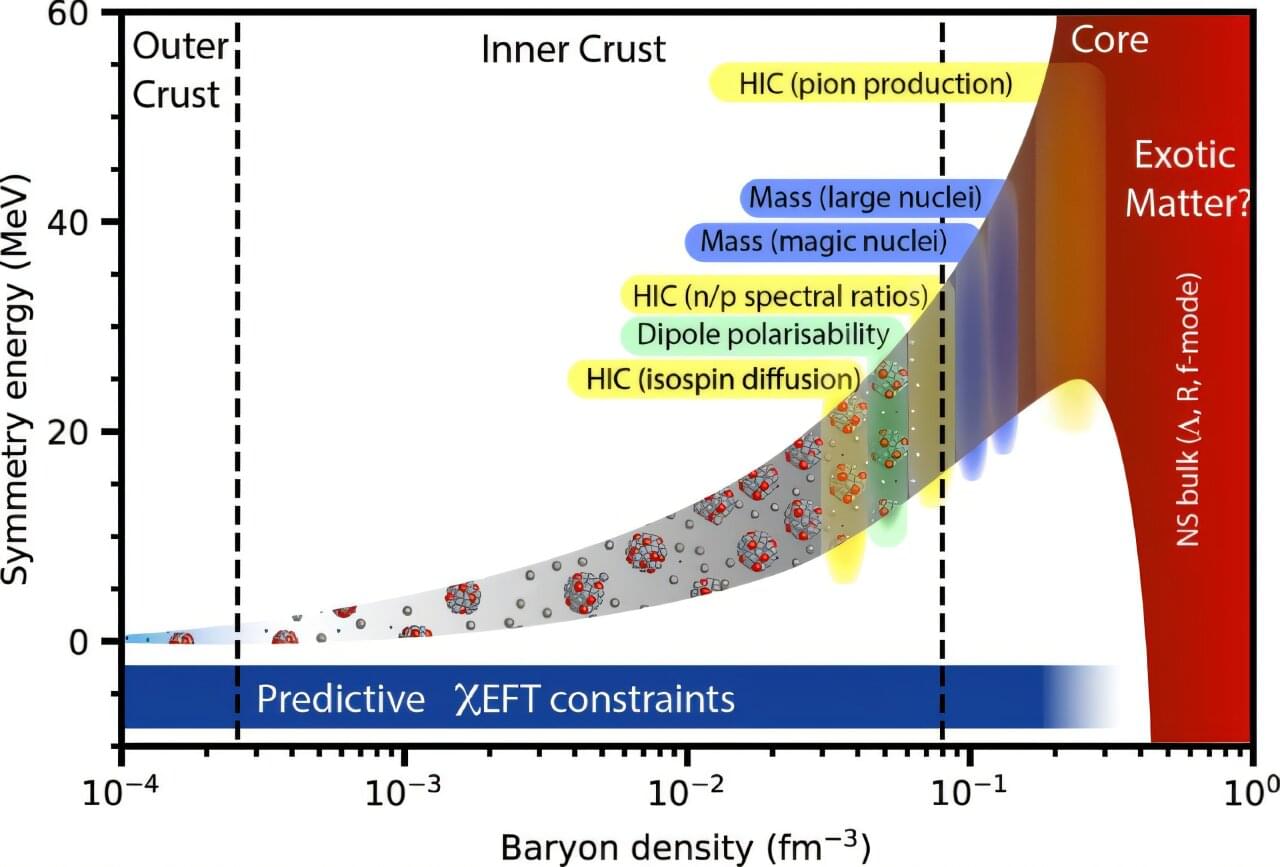
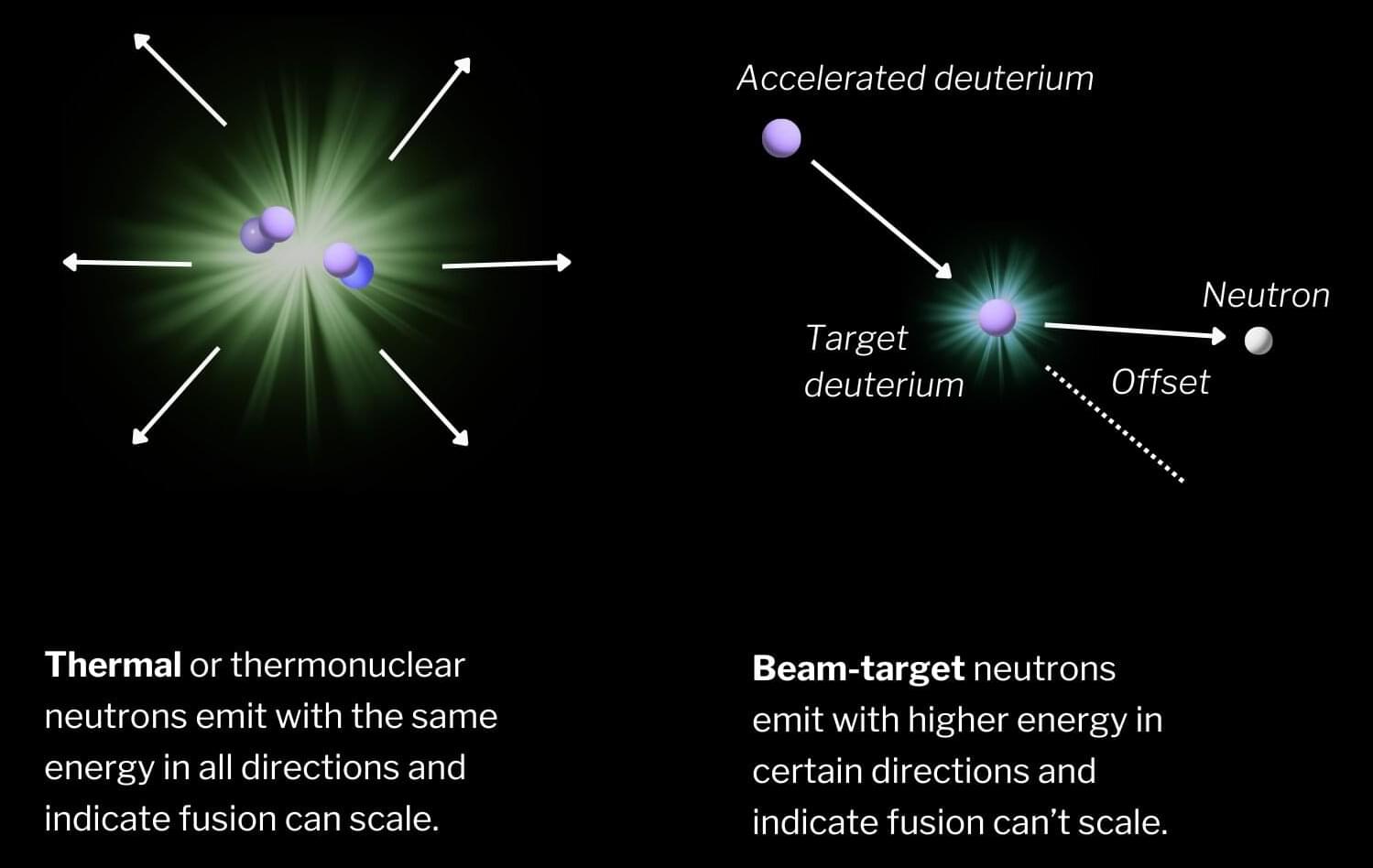
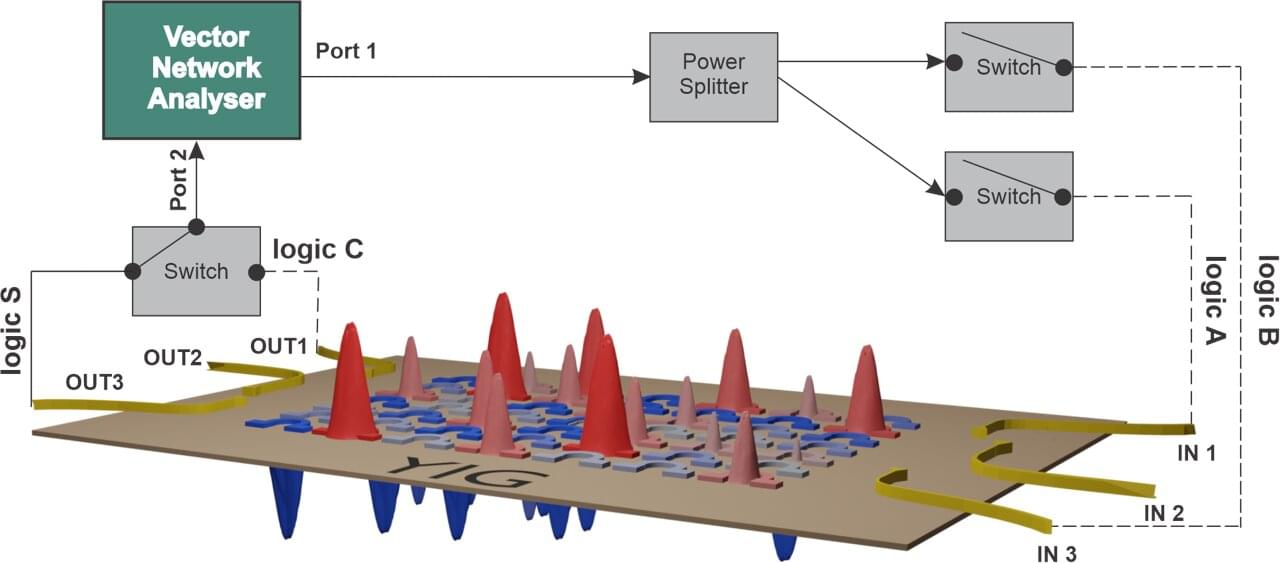
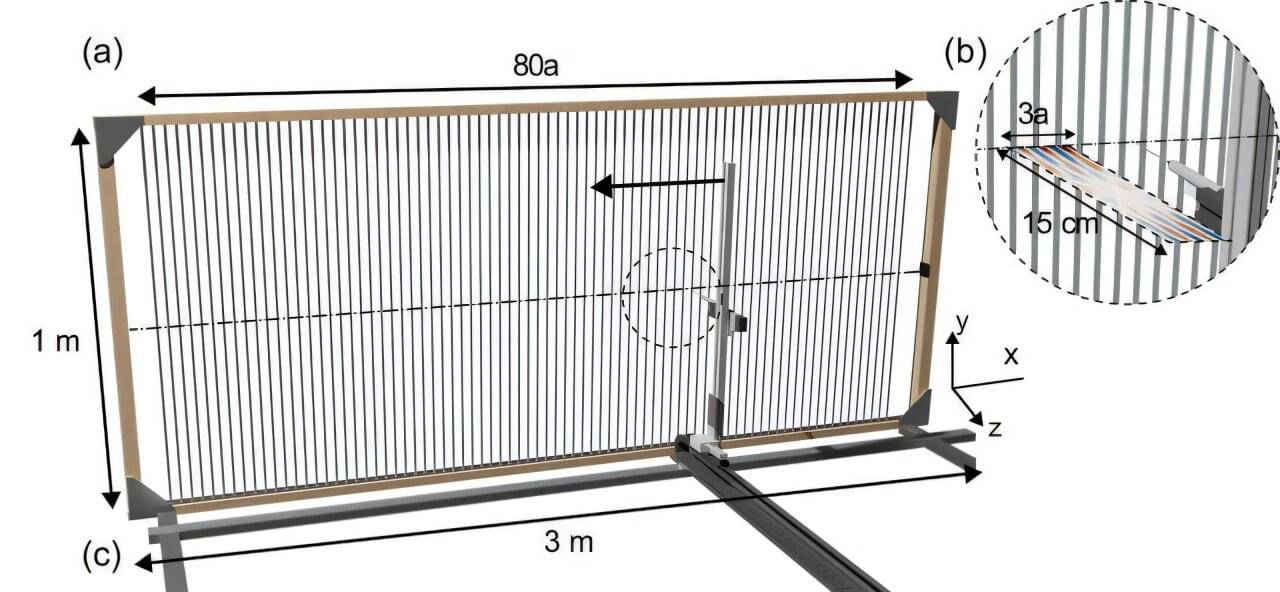
The study of ‘starquakes’ (like earthquakes, but in stars) promises to give us important new insights into the properties of neutron stars (the collapsed remnants of massive stars), according to new research led by the University of Bath in the UK.
Such explorations have the potential to challenge our current approaches to studying nuclear matter, with important impacts for the future of both nuclear physics and astronomy. Longer term, there may also be implications in the fields of health, security and energy.
The value of studying asteroseismology—as these vibrations and flares are known—has emerged from research carried out by an international team of physicists that includes Dr. David Tsang and Dr. Duncan Neill from the Department of Physics at Bath, along with colleagues from Texas A&M and the University of Ohio.