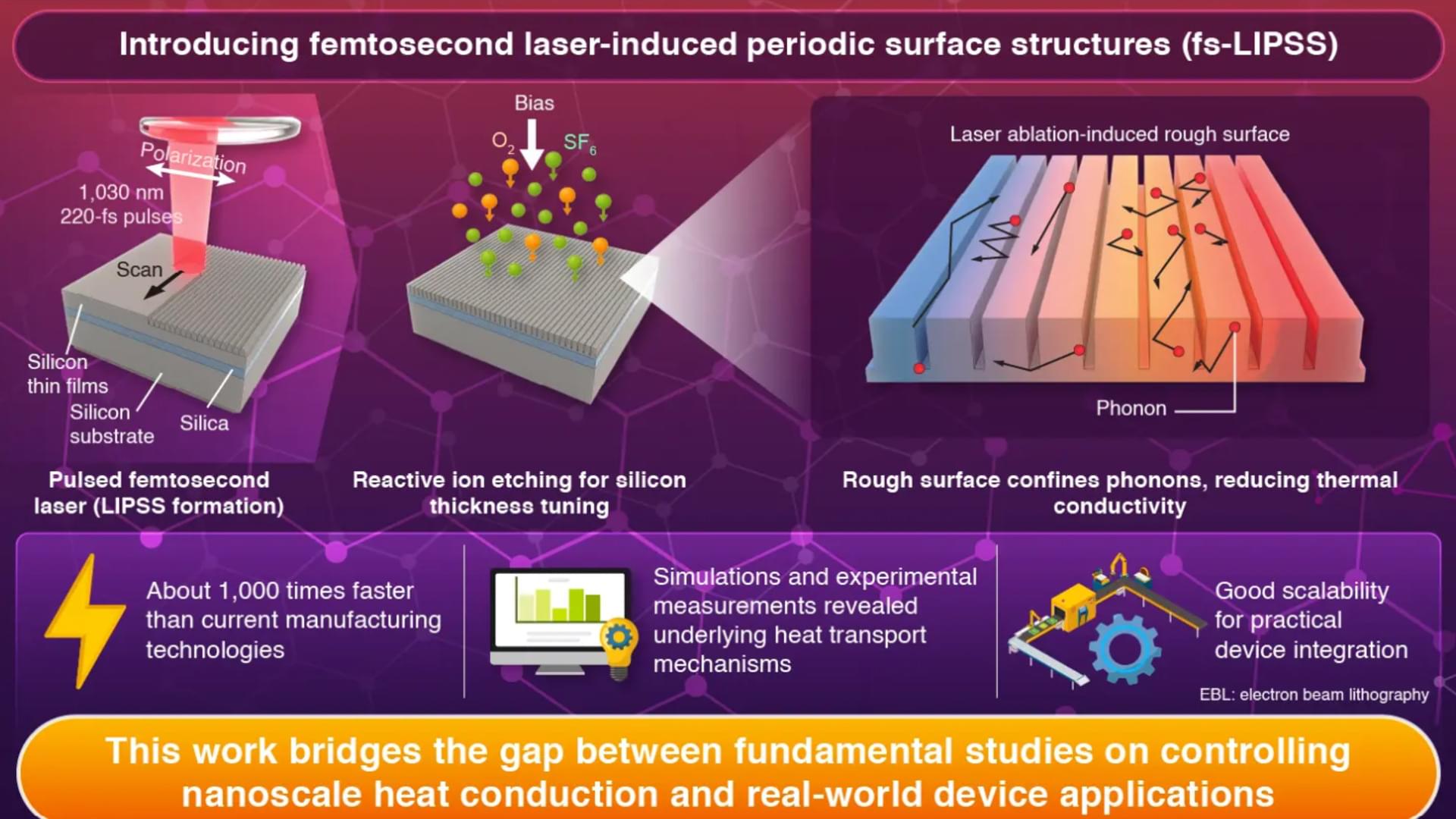
For AI hardware and quantum devices.


Collective behavior is an unusual phenomenon in condensed-matter physics. When quantum spins interact together as a system, they produce unique effects not seen in individual particles. Understanding how quantum spins interact to produce this behavior is central to modern condensed-matter physics.
Among these phenomena, the Kondo effect—the interaction between localized spins and conduction electrons—plays a central role in many quantum phenomena.
Yet in real materials, the presence of additional charges and orbital degrees of freedom make it difficult to isolate the essential quantum mechanism behind the Kondo effect. In these materials, electrons don’t just have spin, they also move around and can occupy different orbitals. When all these extra behaviors mix together, it becomes hard to focus only on the spin interactions responsible for the Kondo effect.
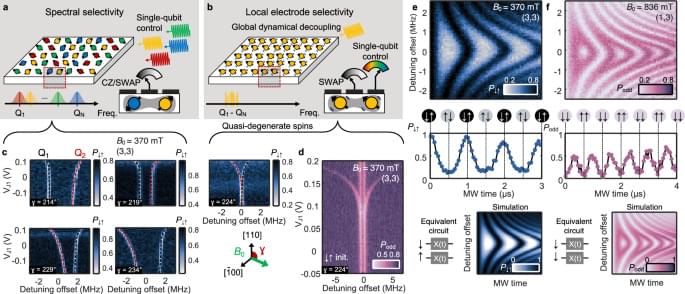
Global control of a qubits using a single microwave field is a promising strategy for scalable quantum computing. Here the authors demonstrate individual addressability vial local electrodes and two-qubit gates in an array of Si quantum dot spin qubits dressed by a global microwave field and driven on-resonance.


A team at Japan’s National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology (QST) has published a field-defining Perspective that places the societal payoff of quantum technologies front and center: earlier disease detection, faster drug development, and new routes to clean energy. Their paper has been published online in the journal ACS Nano on December 18, 2025.

From Dark till First Dawn of Universe Simulation: EWOG Quantum Gravity Theory.
🚀From Dark till First Dawn of Universe Simulation: Why EWOG is promising to the Cosmic Race! 🌌 https://lnkd.in/gFBNsKtq Ever wonder how the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) keeps finding massive, mature galaxies that “shouldn’t exist” yet? Standard cosmology (ΛCDM) is struggling to explain this without extreme fine-tuning. But Entanglement-Weighted Operator Gravity (EWOG) provides a first-principles answer. 🧩 The “Quantum Turbo” Effect In the dense early universe, high quantum entanglement between matter and geometry temporarily boosted gravity’s strength. The Core Idea: Gravity isn’t a constant; it’s an operator weighted by entanglement (Ŵ). * Curvature from Commutators: R̂ᵤᵥ = [∇̂ᵤ, ∇̂ᵥ] * The Boosted Coupling: G_eff(a, k) = G_N [1 + α₀(1 — e⁻ᵐʳ)ℱ] This “turbo boost” allowed gas to collapse into stars 150,000 years earlier than standard models predict.
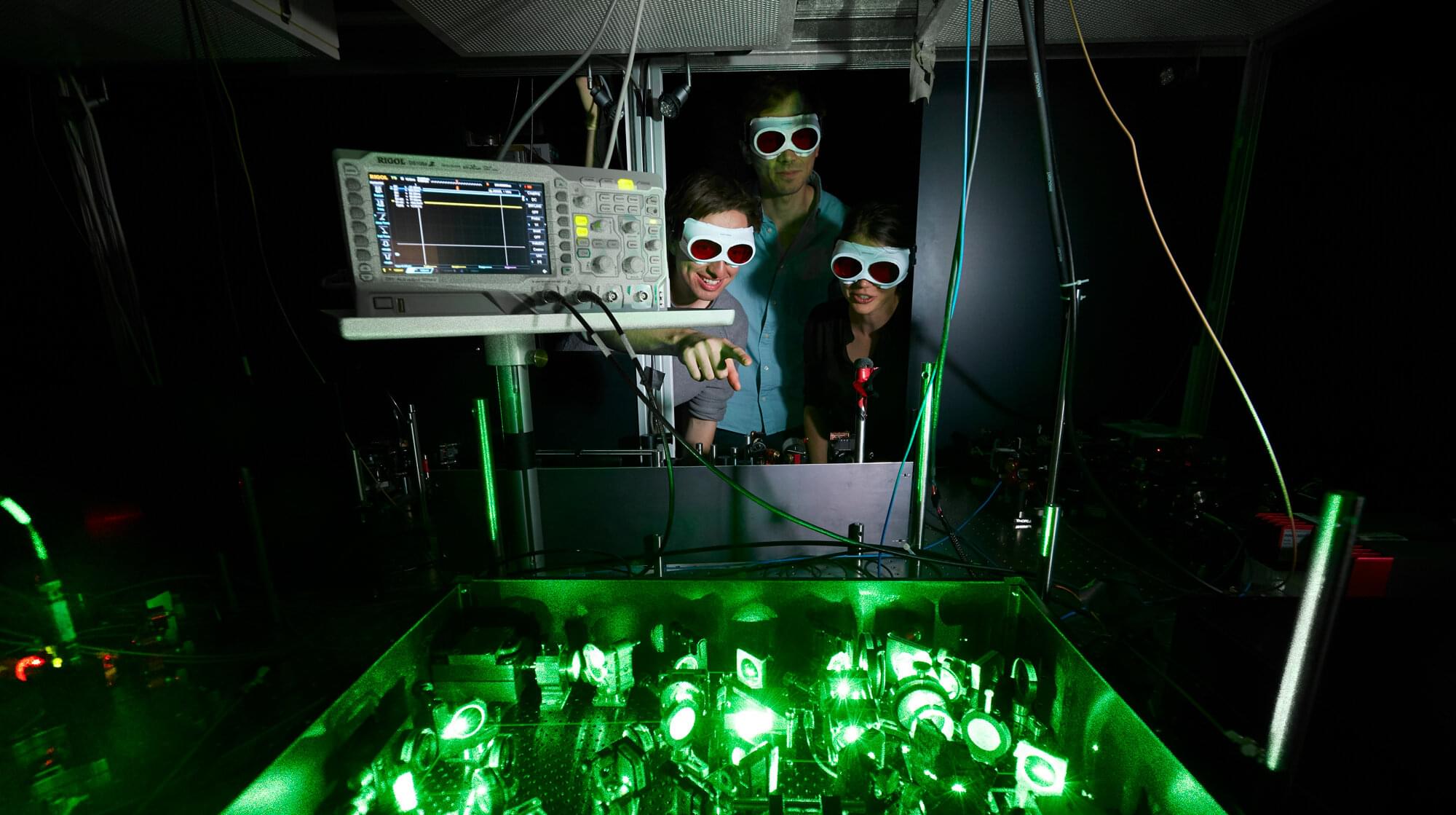


Physicists have uncovered a link between magnetism and a mysterious phase of matter called the pseudogap, which appears in certain quantum materials just above the temperature at which they become superconducting. The findings could help researchers design new materials with sought-after properties such as high-temperature superconductivity, in which electric current flows without resistance.
Using a quantum simulator chilled to just above absolute zero, the researchers discovered a universal pattern in how electrons—which can have spin up or down—influence their neighbors’ spins as the system is cooled.
The findings represent a significant step toward understanding unconventional superconductivity, and were the result of a collaboration between experimentalists at the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics in Germany and theoretical physicists, including Antoine Georges, director of the Center for Computational Quantum Physics (CCQ) at the Simons Foundation’s Flatiron Institute in New York City.
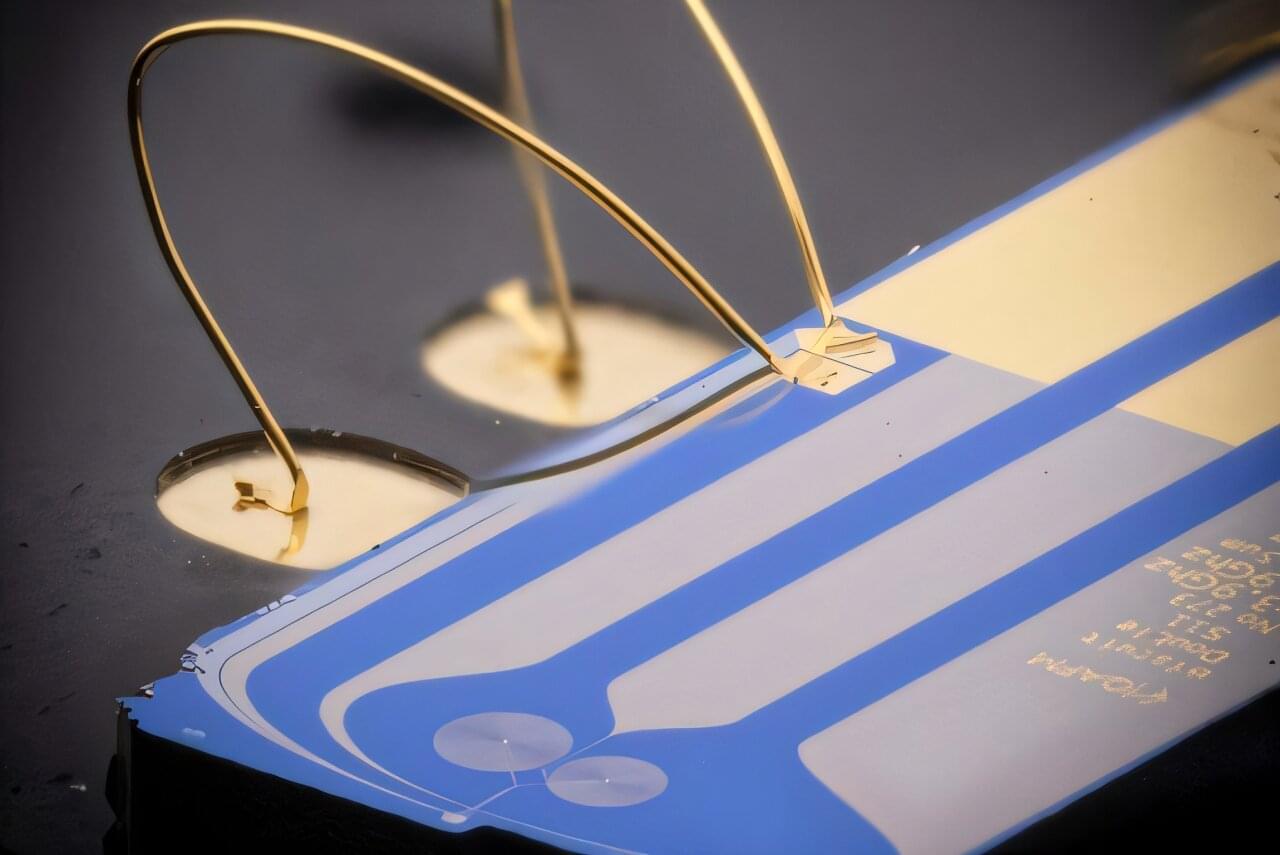
Nanomechanical systems developed at TU Wien have now reached a level of precision and miniaturization that will allow them to be used in ultra-high-resolution atomic force microscopes in the future. Their new findings are published in the journal Advanced Materials Technologies.
A major leap in measurement technology begins with a tiny gap of just 32 nanometers. This is the distance between a movable aluminum membrane and a fixed electrode, together forming an extremely compact parallel-plate capacitor—a new world record. This structure is intended for use in highly precise sensors, such as those required for atomic force microscopy.
But this world record is more than just an impressive feat of miniaturization—it is part of a broader strategy. TU Wien is developing various hardware platforms to make quantum sensing easier to use, more robust, and more versatile. In conventional optomechanical experiments, the motion of tiny mechanical structures is read out using light. However, optical setups are delicate, complex, and difficult to integrate into compact, portable systems. TU Wien therefore relies on other types of oscillations that are better suited for compact sensors.
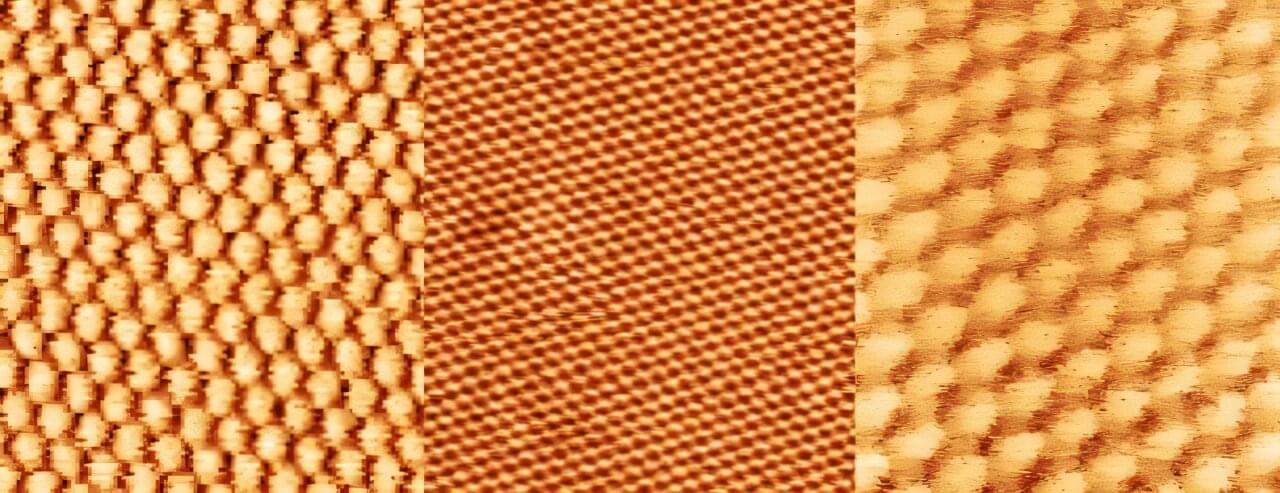

Exciting electronic characteristics emerge when scientists stack 2D materials on top of each other and give the top layer a little twist.
The twist turns a normal material into a patterned lattice and changes the quantum behavior of the material. These twisted materials have shown superconductivity—where a material can conduct electricity without energy loss—as well as special quantum effects. Researchers hope these “twistronics” could become components in future quantum devices.
But creating these extremely thin stacked structures, called moiré superlattices, is difficult to do. Scientists usually peel off single layers of material using Scotch tape and then carefully stick those layers together. However, the method has a very low success rate, often leaves behind contamination between layers and produces tiny samples smaller than the width of a human hair.