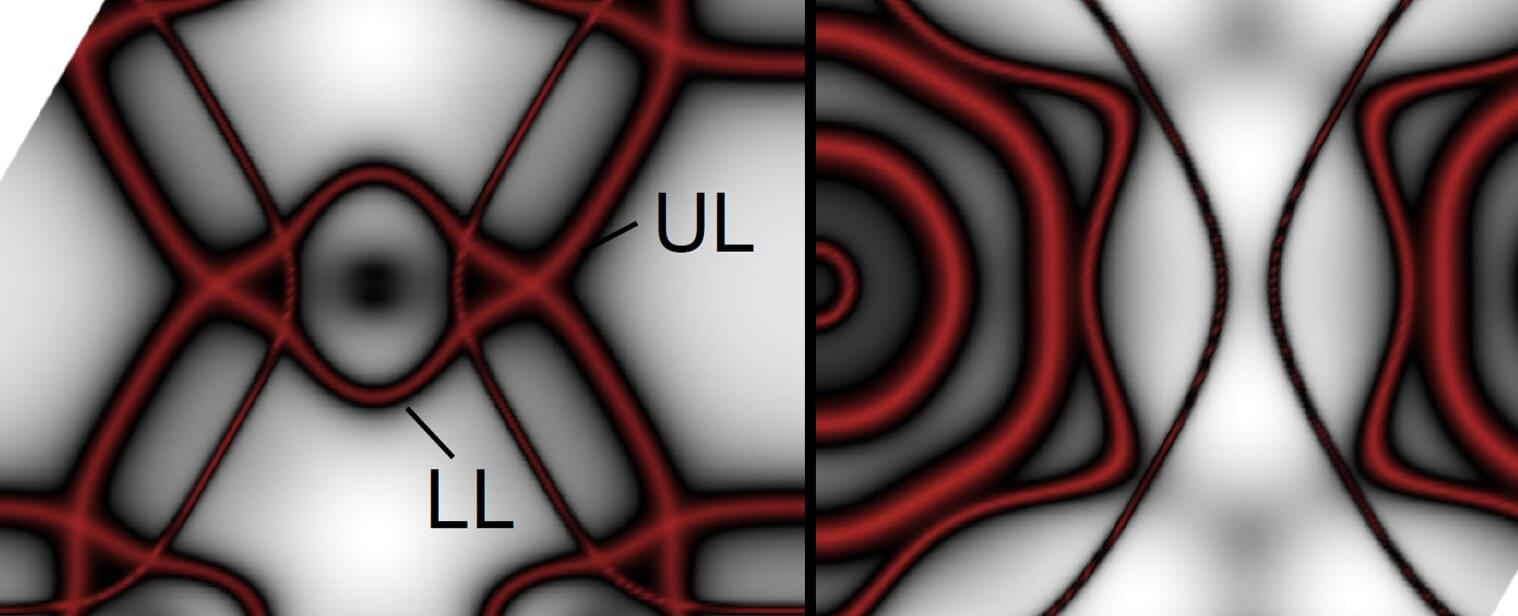
The element cobalt is considered a typical ferromagnet with no further secrets. However, an international team led by HZB researcher Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now uncovered complex topological features in its electronic structure. Spin-resolved measurements of the band structure (spin-ARPES) at BESSY II revealed entangled energy bands that cross each other along extended paths in specific crystallographic directions, even at room temperature. As a result, cobalt can be considered as a highly tunable and unexpectedly rich topological platform, opening new perspectives for exploiting magnetic topological states in future information technologies.
The findings are published in the journal Communications Materials.
Cobalt is an elementary ferromagnet, and its properties and crystal structure have long been known. However, an international team has now discovered that cobalt hosts an unexpectedly rich topological electronic structure that remains robust at room temperature, revealing a surprising new level of quantum complexity in this material.